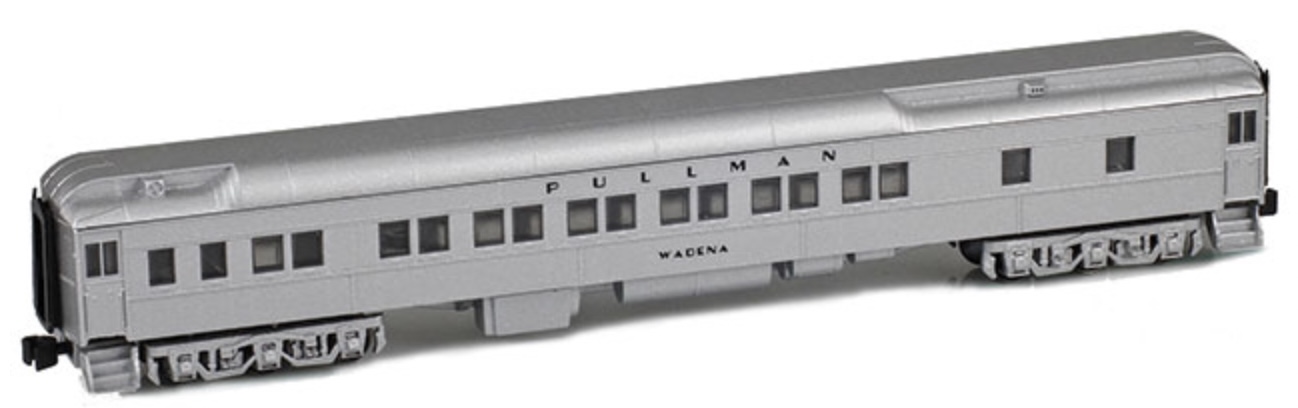
Model Information: These models are available in two different configurations - "Trough" hatches or "Round" hatches. Prior to their more recent "Ready-To-Run" state, they were available in kit form. Intermountain doesn't actually specify a prototype for this model, but it appears to be based on an NSC (National Steel Car) 4750 cf hopper.
Prototype History: ACF introduced their roundish cylindrical hoppers in the early 1960s. The cars differed greatly from the ribbed sided hoppers of the era. They have been made in 3-bay and 6-bay variations. These cylindrical hoppers were superseded on ACF’s production line by the Centerflow in 1964, a revolutionary design that influenced later covered hopper types. In the late 60s or early 70s Canada came out with 4-bay covered hoppers that appear to be derived from ACF’s pre-Centerflow cylindrical hoppers. These cars were used by CN, CP and various smaller Canadian shippers. There is some question as to why the Canadian builder based their design off the older cylindrical and not ACF’s newer Centerflow. It was likely a patent issue and copying it could have triggered legal action against the Canadian builders. There are also certain structural design differences between the cylindrical and centerflow cars and perhaps the decision to copy the cylindrical was based on the greater volume capacity of the cylindrical design.
Road Name History:  First of all, Milwaukee Road has only ever been a popular nickname. The real name from 1874 was Chicago Milwaukee & St. Paul. For the next 36 years, the CM&StP linked Chicago with Milwaukee, Green Bay, Madison, Wausau, the Twin Cities, Duluth, Kansas City and Omaha with a dense network of branches in Wisconsin, Iowa, southern Minnesota and eastern South Dakota. Essentially, the lines ended at the Missouri River.
First of all, Milwaukee Road has only ever been a popular nickname. The real name from 1874 was Chicago Milwaukee & St. Paul. For the next 36 years, the CM&StP linked Chicago with Milwaukee, Green Bay, Madison, Wausau, the Twin Cities, Duluth, Kansas City and Omaha with a dense network of branches in Wisconsin, Iowa, southern Minnesota and eastern South Dakota. Essentially, the lines ended at the Missouri River.
With a dearth of friendly western connections, CM&StP decided to build their own line to the Pacific. The original target was the bustling megalopolis of Eureka, California. However, they built toward Seattle instead. In 1909 the line opened. Along the way, they served Miles City, Lewiston, Great Falls, Harlowton and Butte, Montana; Avery, Idaho; and Spokane, Seattle and Tacoma, Washington. In 1912, they began to electrify two long segments, Harlowton, Montana to Avery, Idaho and Othello, Washington to Tacoma.
In 1921, they leased the Chicago Terre Haute & Southeastern and a bit later the Chicago Milwaukee & Gary to reach the coal fields of southern Indiana. Both roads were in trouble and dragged the CM&StP into receivership. In 1928, they emerged with a small name change. It was now the Chicago Milwaukee St. Paul & Pacific. Right after that, the nickname “Milwaukee Road” began to catch on.
The three Class One’s that already served the Pacific Northwest, Northern Pacific, Great Northern (along with their jointly owned minion Spokane Portland & Seattle) and Union Pacific were not pleased with their new neighbor and avoided building interchanges with them unless absolutely necessary. This left Milwaukee to haul whatever traffic they could originate or terminate on their own line or via a hand full of shortlines with which they interchanged. This is why when you see photos of Milwaukee Road trains west of the Dakotas, an exceptionally large majority of cars are lettered for Milwaukee Road.
Milwaukee’s steam fleet is generally quite handsome beginning with the period after WWI. Many locomotives were built in their own shops. The steam era came to an end on the Milwaukee in 1957.
The electrified lines were ruled by boxcabs and Bi-Polars for decades. In the 1950’s, Little Joe’s diverted from the Soviet Union arrived on the Milwaukee (and the South Shore.) By the late 60’s diesels began to regularly invade the electrified lines. Little Joes and diesels were MU’ed. The aging catenary could only handle so many electrics at a time so diesels filled the horsepower gap. By 1972, falling traffic, a declining fleet of serviceable electrics and the deteriorating catenary caused Milwaukee Road to de-energize the western lines lines with Avery to Harlowton lines following two years later.
Meanwhile on the east end, as a condition of the 1971 merger of Monon into L&N, Milwaukee Road received trackage rights from Chicago to Louisville. This gave Southern a friendly connection to Chicago it was losing with Monon.
In 1977, Milwaukee Road entered receivership again. This time, radical restructuring was needed. In 1980, everything west of Miles City, Montana was abandoned. Some lines were picked up by connections or spawned new shortlines but nearly 1,000 miles of track was pulled up. In 1982, Miles City to Ortonville, Minnesota was abandoned. Milwaukee was concentrating on their pre-1909 routes plus the new line to Louisville.
In an attempt to win back middle distance TOFC traffic, Milwaukee began running fast and short piggyback trains, usually behind a single SD40-2 and with a dozen or so 89’ flats. Unit coal trains added to the bottom line. By the mid-80s, the streamlined Milwaukee Road was up for sale and Grand Trunk Western, Chicago & North Western and Soo Line got into a bidding war. GTW had diverted 40,000 cars onto Milwaukee Road between Chicago and Duluth to help them turn a profit in 1983. Ironically, the ICC (which controlled mergers at the time) pushed GTW out of the contest leaving just C&NW and Soo. Furious, GTW diverted their 40,000 carloads off the Milwaukee. C&NW outbid Soo, but the ICC chose Soo Line anyway. Milwaukee Road merged into Soo Line in 1985. Almost immediately, Soo shops began painting big black rectangles over MILWAUKEE ROAD on the diesels, giving birth to the “bandit” paint scheme.

With a dearth of friendly western connections, CM&StP decided to build their own line to the Pacific. The original target was the bustling megalopolis of Eureka, California. However, they built toward Seattle instead. In 1909 the line opened. Along the way, they served Miles City, Lewiston, Great Falls, Harlowton and Butte, Montana; Avery, Idaho; and Spokane, Seattle and Tacoma, Washington. In 1912, they began to electrify two long segments, Harlowton, Montana to Avery, Idaho and Othello, Washington to Tacoma.
In 1921, they leased the Chicago Terre Haute & Southeastern and a bit later the Chicago Milwaukee & Gary to reach the coal fields of southern Indiana. Both roads were in trouble and dragged the CM&StP into receivership. In 1928, they emerged with a small name change. It was now the Chicago Milwaukee St. Paul & Pacific. Right after that, the nickname “Milwaukee Road” began to catch on.
The three Class One’s that already served the Pacific Northwest, Northern Pacific, Great Northern (along with their jointly owned minion Spokane Portland & Seattle) and Union Pacific were not pleased with their new neighbor and avoided building interchanges with them unless absolutely necessary. This left Milwaukee to haul whatever traffic they could originate or terminate on their own line or via a hand full of shortlines with which they interchanged. This is why when you see photos of Milwaukee Road trains west of the Dakotas, an exceptionally large majority of cars are lettered for Milwaukee Road.
Milwaukee’s steam fleet is generally quite handsome beginning with the period after WWI. Many locomotives were built in their own shops. The steam era came to an end on the Milwaukee in 1957.
The electrified lines were ruled by boxcabs and Bi-Polars for decades. In the 1950’s, Little Joe’s diverted from the Soviet Union arrived on the Milwaukee (and the South Shore.) By the late 60’s diesels began to regularly invade the electrified lines. Little Joes and diesels were MU’ed. The aging catenary could only handle so many electrics at a time so diesels filled the horsepower gap. By 1972, falling traffic, a declining fleet of serviceable electrics and the deteriorating catenary caused Milwaukee Road to de-energize the western lines lines with Avery to Harlowton lines following two years later.
Meanwhile on the east end, as a condition of the 1971 merger of Monon into L&N, Milwaukee Road received trackage rights from Chicago to Louisville. This gave Southern a friendly connection to Chicago it was losing with Monon.
In 1977, Milwaukee Road entered receivership again. This time, radical restructuring was needed. In 1980, everything west of Miles City, Montana was abandoned. Some lines were picked up by connections or spawned new shortlines but nearly 1,000 miles of track was pulled up. In 1982, Miles City to Ortonville, Minnesota was abandoned. Milwaukee was concentrating on their pre-1909 routes plus the new line to Louisville.
In an attempt to win back middle distance TOFC traffic, Milwaukee began running fast and short piggyback trains, usually behind a single SD40-2 and with a dozen or so 89’ flats. Unit coal trains added to the bottom line. By the mid-80s, the streamlined Milwaukee Road was up for sale and Grand Trunk Western, Chicago & North Western and Soo Line got into a bidding war. GTW had diverted 40,000 cars onto Milwaukee Road between Chicago and Duluth to help them turn a profit in 1983. Ironically, the ICC (which controlled mergers at the time) pushed GTW out of the contest leaving just C&NW and Soo. Furious, GTW diverted their 40,000 carloads off the Milwaukee. C&NW outbid Soo, but the ICC chose Soo Line anyway. Milwaukee Road merged into Soo Line in 1985. Almost immediately, Soo shops began painting big black rectangles over MILWAUKEE ROAD on the diesels, giving birth to the “bandit” paint scheme.
Brand/Importer Information: InterMountain was founded in 1985 by Fred Brummet. They got started in the model railroad business by producing O-Scale model kits. They got started in the N Scale business almost a decade later when in 1994 they introduced the 40-23 reefer car in kit form. Later, in 1998, they started producing RTR (Ready-to-Run) models. By the early 2000s, InterMountain phased out kit production in favor of the RTR models.
The InterMountain Railway company is located at 1224 Boston Ave in Longmont, CO. They are a manufacturer of HO, N and Z scale model trains. They have produced kits as well as RTR (Ready-To-Run) models. Their N Scale products include locomotives as well as rolling stock. Their rolling stock lineup includes Boxcars, Hoppers, Tank Cars, Reefers, Gondolas, Stock Cars and Flatcars.
Their locomotive releases have primarily been diesel units, with the one major exception being their series of AC-12 Cab Forward steam locos. Their diesel lineup includes F3's, F7's, F9's, SD40's, SD45's and FT units. They are known for quality and detail. They also release their rolling stock in larger varieties of road numbers than most of the other manufacturers.
The InterMountain Railway company is located at 1224 Boston Ave in Longmont, CO. They are a manufacturer of HO, N and Z scale model trains. They have produced kits as well as RTR (Ready-To-Run) models. Their N Scale products include locomotives as well as rolling stock. Their rolling stock lineup includes Boxcars, Hoppers, Tank Cars, Reefers, Gondolas, Stock Cars and Flatcars.
Their locomotive releases have primarily been diesel units, with the one major exception being their series of AC-12 Cab Forward steam locos. Their diesel lineup includes F3's, F7's, F9's, SD40's, SD45's and FT units. They are known for quality and detail. They also release their rolling stock in larger varieties of road numbers than most of the other manufacturers.
Item created by: dennis.kamper on 2022-01-10 06:36:54. Last edited by dennis.kamper on 2022-01-10 06:36:55
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.