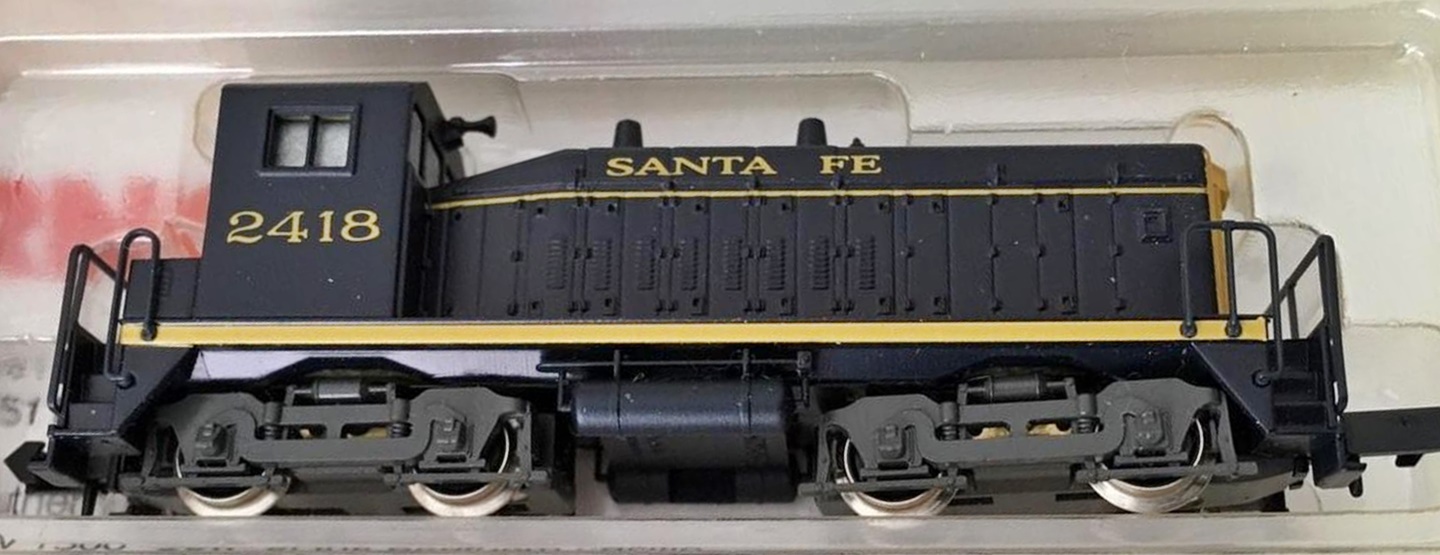
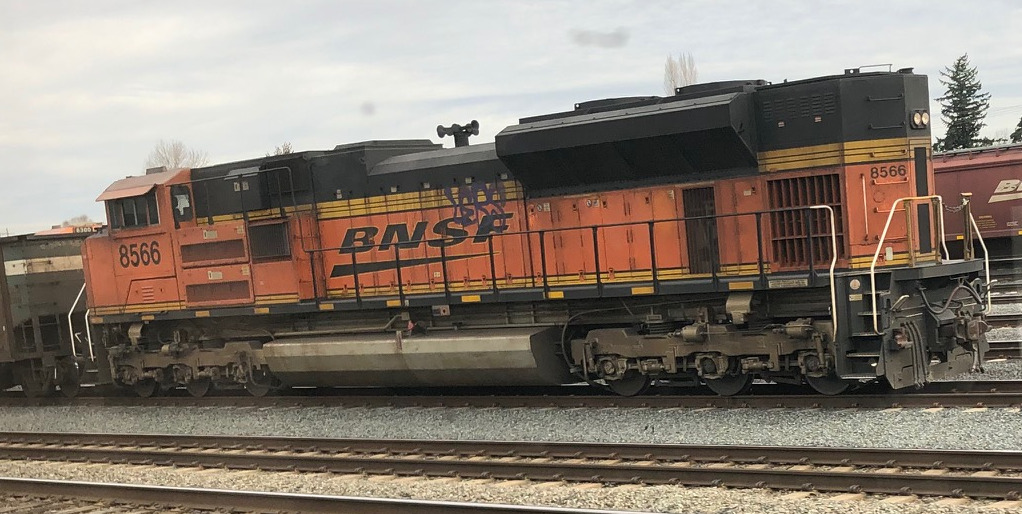
Model Information: Horizontal Brake Wheel is equivalent to Side-Mounted Brake Wheel. The wheel itself is vertical.
Prototype History: During the mid-19th century, attempts were made to ship agricultural products by rail. As early as 1842, the Western Railroad of Massachusetts was reported in the June 15 edition of the Boston Traveler to be experimenting with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage. The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the Northern Railroad (New York) (or NRNY, which later became part of the Rutland Railroad). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success since it was only functional in cold weather. That same year, the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice for cooling.
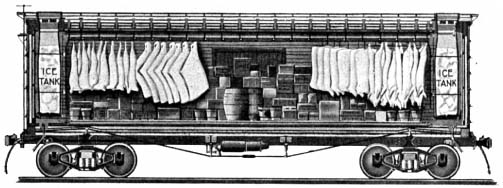
The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stock yards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, proving to be impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.
The use of ice to refrigerate and preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome stored ice and snow in caves, dugouts or ice houses lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 19th century, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required re-icing every 250 miles (400 km) to 400 miles (640 km).
From Wikipedia
The first consignment of dressed beef left the Chicago stock yards in 1857 in ordinary boxcars retrofitted with bins filled with ice. Placing meat directly against ice resulted in discoloration and affected the taste, proving to be impractical. During the same period Swift experimented by moving cut meat using a string of ten boxcars with their doors removed, and made a few test shipments to New York during the winter months over the Grand Trunk Railway (GTR). The method proved too limited to be practical.
The use of ice to refrigerate and preserve food dates back to prehistoric times. Through the ages, the seasonal harvesting of snow and ice was a regular practice of many cultures. China, Greece, and Rome stored ice and snow in caves, dugouts or ice houses lined with straw or other insulating materials. Rationing of the ice allowed the preservation of foods during hot periods, a practice that was successfully employed for centuries. For most of the 19th century, natural ice (harvested from ponds and lakes) was used to supply refrigerator cars. At high altitudes or northern latitudes, one foot tanks were often filled with water and allowed to freeze. Ice was typically cut into blocks during the winter and stored in insulated warehouses for later use, with sawdust and hay packed around the ice blocks to provide additional insulation. A late-19th century wood-bodied reefer required re-icing every 250 miles (400 km) to 400 miles (640 km).
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: Micro-Trains is the brand name used by both Kadee Quality Products and Micro-Trains Line. For a history of the relationship between the brand and the two companies, please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide.
Manufacturer Information:  Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
In October 1990 Kadee separated in two companies, with the newly created Micro-Trains® Line Co. continuing the Z, Nn3, and N Scale product ranges, with Kadee retaining the HO range.

In October 1990 Kadee separated in two companies, with the newly created Micro-Trains® Line Co. continuing the Z, Nn3, and N Scale product ranges, with Kadee retaining the HO range.
Commissioner Information: Brooklyn Locomotive Works was a hobby shop, specialized in N-scale, located in Manalapan, New Jersey, that also sells on-line. BLW regularly commissions special runs.
The company was founded by Pete Postel who announced that he would retired by end of 2018. His brother Paul should continue the business from his own shop Hogtrainz.com.
Brooklyn Locomotive Works (BLW) released special runs from various manufacturers under its own brand until approx. the mid-1980s. Thereafter the special runs where sold under the manufacturer's name and denoted as special runs for BLW. Hence in this database, we assign the BLW brand in the former case, and the original manufacturer's brand in the latter.
The company was founded by Pete Postel who announced that he would retired by end of 2018. His brother Paul should continue the business from his own shop Hogtrainz.com.
Brooklyn Locomotive Works (BLW) released special runs from various manufacturers under its own brand until approx. the mid-1980s. Thereafter the special runs where sold under the manufacturer's name and denoted as special runs for BLW. Hence in this database, we assign the BLW brand in the former case, and the original manufacturer's brand in the latter.
Item created by: gdm on 2020-03-27 09:43:10. Last edited by Alain LM on 2022-05-10 12:08:34
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.