Specific Item Information:
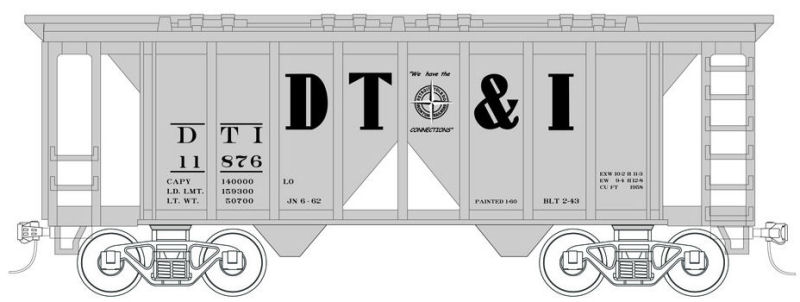
Detroit, Toledo & Ironton - Gray and Black
with 1 Yellow Car in Each Multi-Pack
Detroit, Toledo & Ironton - Gray and Black
with 1 Yellow Car in Each Multi-Pack
Model Information: This model was originally produced by V-Line. Deluxe Innovations later acquired the tooling. The deLuxe models of these common cars are weighted with the same copper slugs used in their box cars for superior tracking and immunity to magnetism.
Most releases feature more than one paint scheme variation within a road name. For instance, the Missouri Pacific set features cars delivered with MP reporting marks and painted "corrosion resistant gray" that is actually a tan color, and cars lettered for MoPac subsidiaries Missouri-Illinois and St. Louis Brownsville & Mexico (both carrying the traditional buzz saw logo) that are painted in a more traditional gray color. Some of the more modern paint schemes including Delaware & Hudson and National Bureau of Standards have the four-color ACI tags. ACI stands for Automated Car Identification and worked like a grocery store bar code reader using a color TV camera instead of a laser. Unfortunately, the tags couldn't be read if they were dirty and the system fell out of favor by the early 1980's. This aspect of 70's railroading is rarely modeled but we include it on appropriate cars.
Most releases feature more than one paint scheme variation within a road name. For instance, the Missouri Pacific set features cars delivered with MP reporting marks and painted "corrosion resistant gray" that is actually a tan color, and cars lettered for MoPac subsidiaries Missouri-Illinois and St. Louis Brownsville & Mexico (both carrying the traditional buzz saw logo) that are painted in a more traditional gray color. Some of the more modern paint schemes including Delaware & Hudson and National Bureau of Standards have the four-color ACI tags. ACI stands for Automated Car Identification and worked like a grocery store bar code reader using a color TV camera instead of a laser. Unfortunately, the tags couldn't be read if they were dirty and the system fell out of favor by the early 1980's. This aspect of 70's railroading is rarely modeled but we include it on appropriate cars.
Prototype History: This design had a life span that is truly enormous. The last cars of this design were built in the 1960's -- three decades after the first cars were built for Santa Fe. Quite a few of these cars are still in service. Because you have to stand on the roof in order to open the hatches, these cars were immune from the "No Roof Walk" rule of 1964, but a number would be scrapped when friction bearing trucks were outlawed. Amazingly, some cars are now being retired because they have hit the Federal Railroad Administration's 50 year rule!
Originally designed at the height of the Great Depression, the first ten cars of this design were delivered to Santa Fe in an austere black paint scheme. Covered hoppers have always been used for any bulk cargo that had to be protected from the elements. Some have the impression that covered hoppers are used mostly for grain. Nothing can be further from the truth. In fact, moving grain in covered hoppers has only been commonplace since the 1960's. Before that period, most grain moved in 40' box cars with grain doors temporarily nailed over the doorways. In the steam era, covered hoppers were used for cement, sand, clay, talc, and other powders. The cargo was loaded through eight square hatches in the roof. To empty the car, the hatches at the bottom are opened and the load spills out. At this point, some low man on the company ladder would have to climb into the car with a broom and sweep out the corners and the center sill. The American Car & Foundry covered hopper design was such a success that it became a defacto standard for years. Even Pullman Standard (ACF's arch enemy) built cars to the same design. The distinctive open triangles in the sides make these cars easily distinguishable even from a distance. ACF would also develop a version without the open triangles which was not as prolific as the version presented here. Amazingly, many of these cars are still in use today, in MOW and lineside service. Many have been rebuilt as ballast hoppers, including for SP, CSX, Amtrak, and Santa Fe.
Originally designed at the height of the Great Depression, the first ten cars of this design were delivered to Santa Fe in an austere black paint scheme. Covered hoppers have always been used for any bulk cargo that had to be protected from the elements. Some have the impression that covered hoppers are used mostly for grain. Nothing can be further from the truth. In fact, moving grain in covered hoppers has only been commonplace since the 1960's. Before that period, most grain moved in 40' box cars with grain doors temporarily nailed over the doorways. In the steam era, covered hoppers were used for cement, sand, clay, talc, and other powders. The cargo was loaded through eight square hatches in the roof. To empty the car, the hatches at the bottom are opened and the load spills out. At this point, some low man on the company ladder would have to climb into the car with a broom and sweep out the corners and the center sill. The American Car & Foundry covered hopper design was such a success that it became a defacto standard for years. Even Pullman Standard (ACF's arch enemy) built cars to the same design. The distinctive open triangles in the sides make these cars easily distinguishable even from a distance. ACF would also develop a version without the open triangles which was not as prolific as the version presented here. Amazingly, many of these cars are still in use today, in MOW and lineside service. Many have been rebuilt as ballast hoppers, including for SP, CSX, Amtrak, and Santa Fe.
Road Name History: The DT&I was born in 1905 with the sale and reorganization of the Detroit Southern Railroad. Beginning in Detroit, the DT&I carved a huge northwest to southeast arc around western Ohio, serving Lima (like the bean, not Peru), Springfield, Jackson, and finally the Ohio River port of Ironton on the Kentucky border. Toledo was reached via a short segment of trackage rights on the Ann Arbor.
In 1920, as part of a complicated solution to realigning a shipping channel that served Henry Ford’s River Rouge plant, Ford bought the DT&I. The Ford years brought a ban on facial hair, uniform white hats and an expectation that crews keep their overalls clean and tidy. He also strung catenary and bought heavy electric locomotives for a 17 mile line segment between his River Rouge plant and Carolton, Michigan. During this period, the DT&I closed for business on Sundays. In 1929, Ford sold the line to Pennroad Corporation, a holding company affiliated with the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The steam fleet of the DT&I was a pretty homely lot. 2-8-0s and Russian Decapods were the kings of the road for the first few decades. As the tide of traffic turned from coal and minerals from the south end of the line to automobiles from the north end of the line, DT&I went to Lima Locomotive Works for faster stronger 2-8-4 Berkshires. Although the DT&I Berks were light and stumpy by Berkshire standards, they were a bit too much for DT&I’s physical plant so their final steam orders were for very heavy Mikados ( 20 tons heavier than USRA Heavy Mikes.) By 1955, they had completely dieselized with 37 EMD GP7’s and GP9’s setup for short hood forward operation (interesting given their ties to the Pennsylvania Railroad who preferred long hood forward operation) and 24 various EMD switchers.
The DT&I diesel fleet has always been solid orange but the logo on the long hood was smaller and more reserved in the 1950s. Second generation diesels included 8 GP35’s, 21 GP38’s, 6 GP40’s, 5 SD38’s (used in hump service,) 8 GP38-2’s, and 20 GP40-2’s. Features included a general lack of dynamic brakes and nose mounted gong style bells (a feature familiar to fans of Chicago & North Western.)
The freight car fleet was very, very colorful. Often, special colors were used to identify groups of cars for large customers. Ocean blue boxcars were for General Mills, Army green went to a paper mill on the Soo Line, yellow went to Campbell Soup, and of course, the auto parts cars which came in sky blue, cypress green, and magenta.
In 1963, and with control having been passed from Pennroad to The Pennsylvania Company (another holding company at arms length from the PRR,) the DT&I gained control of the Ann Arbor from their parent Wabash, turning the AA orange. This was part of the complicated arrangements made in the run up to the Penn Central merger. PRR needed to end their control of Wabash but wanted to hold onto DT&I and Ann Arbor. DT&I control ended in 1973 when AA declared bankruptcy.
In 1976, the DT&I was profitable even though parent Penn Central was in bankruptcy. Therefore DT&I was not included in the Conrail consolidation. In fact Conrail gave DT&I trackage rights on their lines from Springfield to Cincinnati, which gave DT&I even more Ohio River access as well as friendly connections with Southern and Louisville & Nashville. Meanwhile, The Pennsylvania Company, stripped of its Penn Central parent, put the DT&I up for sale. Grand Trunk Western offered to buy it and Chessie and N&W offered to jointly buy it. The ICC went with Grand Trunk Western and the sale was completed in 1980. Some locomotives were painted in GTW blue and red but with DT&I logos. In 1983, the DT&I officially merged into GTW.
In 1920, as part of a complicated solution to realigning a shipping channel that served Henry Ford’s River Rouge plant, Ford bought the DT&I. The Ford years brought a ban on facial hair, uniform white hats and an expectation that crews keep their overalls clean and tidy. He also strung catenary and bought heavy electric locomotives for a 17 mile line segment between his River Rouge plant and Carolton, Michigan. During this period, the DT&I closed for business on Sundays. In 1929, Ford sold the line to Pennroad Corporation, a holding company affiliated with the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The steam fleet of the DT&I was a pretty homely lot. 2-8-0s and Russian Decapods were the kings of the road for the first few decades. As the tide of traffic turned from coal and minerals from the south end of the line to automobiles from the north end of the line, DT&I went to Lima Locomotive Works for faster stronger 2-8-4 Berkshires. Although the DT&I Berks were light and stumpy by Berkshire standards, they were a bit too much for DT&I’s physical plant so their final steam orders were for very heavy Mikados ( 20 tons heavier than USRA Heavy Mikes.) By 1955, they had completely dieselized with 37 EMD GP7’s and GP9’s setup for short hood forward operation (interesting given their ties to the Pennsylvania Railroad who preferred long hood forward operation) and 24 various EMD switchers.
The DT&I diesel fleet has always been solid orange but the logo on the long hood was smaller and more reserved in the 1950s. Second generation diesels included 8 GP35’s, 21 GP38’s, 6 GP40’s, 5 SD38’s (used in hump service,) 8 GP38-2’s, and 20 GP40-2’s. Features included a general lack of dynamic brakes and nose mounted gong style bells (a feature familiar to fans of Chicago & North Western.)
The freight car fleet was very, very colorful. Often, special colors were used to identify groups of cars for large customers. Ocean blue boxcars were for General Mills, Army green went to a paper mill on the Soo Line, yellow went to Campbell Soup, and of course, the auto parts cars which came in sky blue, cypress green, and magenta.
In 1963, and with control having been passed from Pennroad to The Pennsylvania Company (another holding company at arms length from the PRR,) the DT&I gained control of the Ann Arbor from their parent Wabash, turning the AA orange. This was part of the complicated arrangements made in the run up to the Penn Central merger. PRR needed to end their control of Wabash but wanted to hold onto DT&I and Ann Arbor. DT&I control ended in 1973 when AA declared bankruptcy.
In 1976, the DT&I was profitable even though parent Penn Central was in bankruptcy. Therefore DT&I was not included in the Conrail consolidation. In fact Conrail gave DT&I trackage rights on their lines from Springfield to Cincinnati, which gave DT&I even more Ohio River access as well as friendly connections with Southern and Louisville & Nashville. Meanwhile, The Pennsylvania Company, stripped of its Penn Central parent, put the DT&I up for sale. Grand Trunk Western offered to buy it and Chessie and N&W offered to jointly buy it. The ICC went with Grand Trunk Western and the sale was completed in 1980. Some locomotives were painted in GTW blue and red but with DT&I logos. In 1983, the DT&I officially merged into GTW.
Brand/Importer Information: DeLuxe Innovations is a "wholesale manufacturer" of model trains. We manufacture scale replica train models and sell them to hobby shops and distributors worldwide. 2013 marked the 20 year anniversary of DeLuxe Innovations brand trains. There are over 25 body styles in our product line and all of the cars in our single and multi-car packs have different road numbers. DeLuxe Innovations, Inc. is owned by Dave Ferrari, founder of Squeak N Products. We are located in Midland Park, New Jersey. When Dave purchased the business it was located in Burbank, California which would have been a bit of a long commute so the move to the East Coast was planned. Our first East Coast location was in Whippany, NJ along the Whippany River.
The business was started in 1993 by George Johnsen and Roberta Liebreich in Burbank, California. They had a philosophy that just wouldn't allow using a coal car as a "stand in" for a woodchip car, or printing any and all boxcar paint schemes on a PS-1. Starting with the release of the first ever etched metal parts for a ready to run car (1994's Twinstack's metal walkways) through the full dimension underframe and etched metal roofwalk (1996's 1944 AAR Boxcar) to the challenging RoadRailer system (2000), our products have been accurate to target the modeler or enthusiast.
You can also follow DeLuxe on Twitter
The business was started in 1993 by George Johnsen and Roberta Liebreich in Burbank, California. They had a philosophy that just wouldn't allow using a coal car as a "stand in" for a woodchip car, or printing any and all boxcar paint schemes on a PS-1. Starting with the release of the first ever etched metal parts for a ready to run car (1994's Twinstack's metal walkways) through the full dimension underframe and etched metal roofwalk (1996's 1944 AAR Boxcar) to the challenging RoadRailer system (2000), our products have been accurate to target the modeler or enthusiast.
You can also follow DeLuxe on Twitter
Item created by: Powderman on 2018-11-16 16:48:08. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-06-23 12:27:49
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.