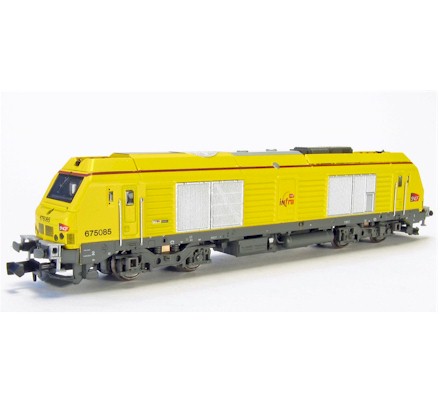
Model Information: Atlas introduced the SD60 in 1998. The SD50 and SD60M followed in 1999. In 2002 they revised the SD60M and SD50. In 2005, Atlas revised the SD60. All three models (SD60, SD60M and SD50) share the same mechanism and differ only in shell detailing. These models also come with uninstalled detail parts such as snow-plow and winterization hatches. These details must be installed by the owner.
The revised versions all carry typical post-2000 mechanisms. Therefore, we see features such as dial flywheels, all-wheel pickup and drive, blackened metal wheels, bi-directional lighting, a split-frame DCC-Ready chassis and easily-swappable body-mount couplers. The revised version feature Atlas' slow-speed motor, golden white LEDs and nicely painted two-tone handrails. Yes, they run very nicely.
The revised versions all carry typical post-2000 mechanisms. Therefore, we see features such as dial flywheels, all-wheel pickup and drive, blackened metal wheels, bi-directional lighting, a split-frame DCC-Ready chassis and easily-swappable body-mount couplers. The revised version feature Atlas' slow-speed motor, golden white LEDs and nicely painted two-tone handrails. Yes, they run very nicely.
DCC Information: The revised version of this model is DCC ready. It is available either in DC or DCC-equipped, with Lenz LE062XF for earlier runs, and with NCE N12A1 for more recent ones.
Models accept the following after market plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A1: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale SD60, SD60M, SD50 and others.
- TCS ALD4: Four Function decoder, for Atlas Long length Drop-in.
- NCE N12A1: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas SD50, SD60M, SD60.
Models accept the following after market plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A1: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale SD60, SD60M, SD50 and others.
- TCS ALD4: Four Function decoder, for Atlas Long length Drop-in.
- NCE N12A1: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas SD50, SD60M, SD60.
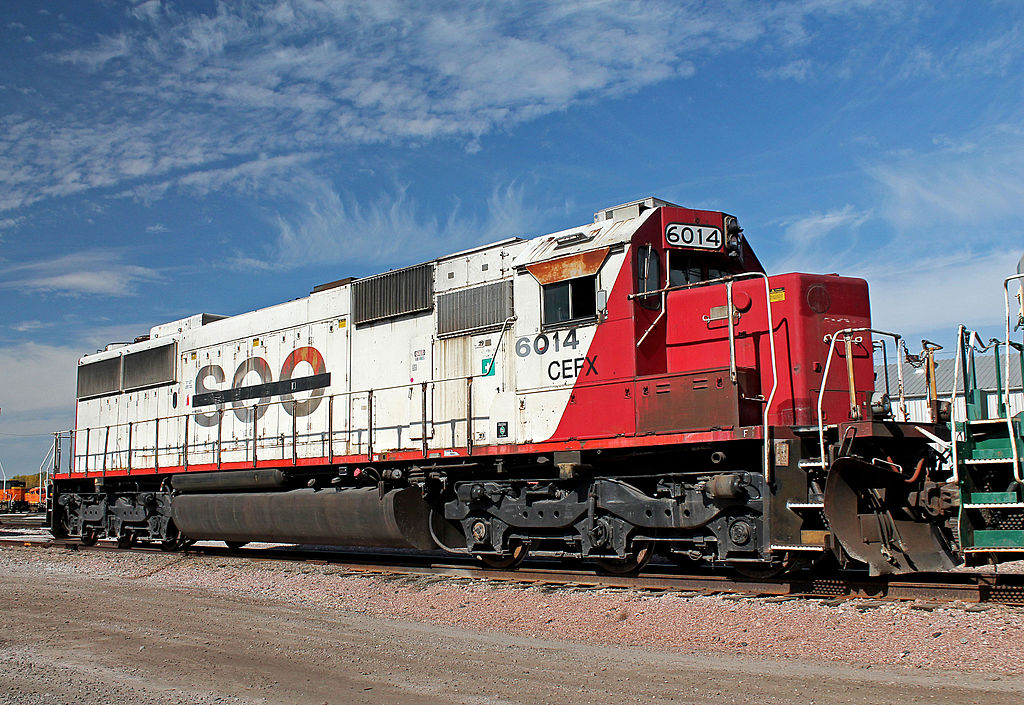
Prototype History: The EMD SD60 is a 3,800 horsepower (2,800 kW), 6-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division. Intended for heavy-duty drag freight or medium-speed freight service. It was introduced in 1984, and production ran until 1995.
The development of the 16-cylinder EMD 50 and 60 series locomotives in the late 1970s and early 1980s was spurred by the introduction of 3,600 horsepower (2,700 kW) 16-cylinder GE B36-7 (B-B) and GE C36-7 (C-C) locomotives by EMD's main competitor General Electric. EMD previously manufactured the 3,600 hp (2,700 kW) 20-cylinder SD45 and SD45-2 locomotives, but they had a reputation for high fuel consumption. In 1980, the SD50 model was added to the EMD Catalog. However, the SD50's electrical reliability was poor and, similarly, the 3,500 horsepower (2,600 kW) 16-645F engine had poor mechanical reliability, both believed to be largely due to excessive vibration from the 950 maximum rpm of the 645F prime mover. It was time to develop a replacement for the venerable 645 engine which, in its earlier 16-645E form, had proved to be exceptionally reliable. EMD therefore quickly commenced development of the SD60 series, which would eliminate the weaknesses of the SD50. The lessons learned in developing the 645F crankcase and crankshaft (for the earlier 20-645E, and the then-current 16-645F) were incorporated in the replacement, the 710G, first employed in the SD60. Although the carbody and frame are nearly indistinguishable from the earlier SD50, the SD60 featured the new 16-cylinder EMD 710G3A prime mover, AR-11 traction alternator, D-87 traction motors and a microprocessor-based control system that governed various electrical systems within the locomotive (e.g., wheel slip and transition).
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
The development of the 16-cylinder EMD 50 and 60 series locomotives in the late 1970s and early 1980s was spurred by the introduction of 3,600 horsepower (2,700 kW) 16-cylinder GE B36-7 (B-B) and GE C36-7 (C-C) locomotives by EMD's main competitor General Electric. EMD previously manufactured the 3,600 hp (2,700 kW) 20-cylinder SD45 and SD45-2 locomotives, but they had a reputation for high fuel consumption. In 1980, the SD50 model was added to the EMD Catalog. However, the SD50's electrical reliability was poor and, similarly, the 3,500 horsepower (2,600 kW) 16-645F engine had poor mechanical reliability, both believed to be largely due to excessive vibration from the 950 maximum rpm of the 645F prime mover. It was time to develop a replacement for the venerable 645 engine which, in its earlier 16-645E form, had proved to be exceptionally reliable. EMD therefore quickly commenced development of the SD60 series, which would eliminate the weaknesses of the SD50. The lessons learned in developing the 645F crankcase and crankshaft (for the earlier 20-645E, and the then-current 16-645F) were incorporated in the replacement, the 710G, first employed in the SD60. Although the carbody and frame are nearly indistinguishable from the earlier SD50, the SD60 featured the new 16-cylinder EMD 710G3A prime mover, AR-11 traction alternator, D-87 traction motors and a microprocessor-based control system that governed various electrical systems within the locomotive (e.g., wheel slip and transition).
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
Road Name History: KCS began (with a different name) in 1890 under the direction of Arthur Stilwell for the purpose of building a railroad from Kansas City directly south along the Missouri – Kansas, Arkansas – Oklahoma, and Louisiana – Texas borders to the Gulf of Mexico. At the point where the railroad met the Gulf, Stillwell built a port complex and named it after himself, Port Arthur, Texas. Two years later, the company defaulted on a loan, Stilwell was kicked out and they changed the name of the railroad to Kansas City Southern. Stilwell went on to build the Kansas City Mexico & Orient.
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: Steve German on 2016-04-11 15:10:26. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-07-29 11:54:09
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.