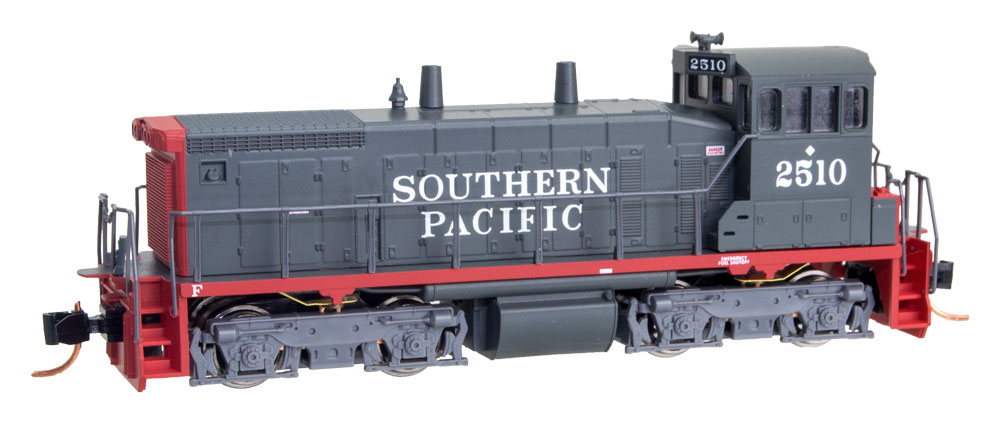
Specific Item Information: These powered SW1500 locomatives are gray with red front hood, steps, platforms and bottom sill. They were delivered to Southern Pacific between 1967 and 1973 by General Motors’ Electro- Motive Division. Many Class I’s purchased the model, very likely due to its extra horsepower, allowing it to be used in numerous applications.
Model Information: Micro-Trains introduced this model in 2014. It is MTL's first new locomotive model since their 2002 EMD FT release. The mechanism is very similar to the Life-Like mechanism they had previously used with several important upgrades including DCC-friendliness. The chassis is manufactured by Walthers/Life-Like in China. Apparently, Micro-Trains had finally run through the thousands of undecorated Life-Like SW9/1200's they had purchased for use in their train sets and needed a similar engine to serve the same purpose in their frequent new train-set releases. In response, Walthers (the current owner of Life-Like) was able to update the venerable mechanisms to modern standards. Micro-Trains makes and decorates the shells in their Oregon factory and combines them with the Walthers-supplied mechanisms. The new Micro-Trains/Walthers SW1500 is a solid upgrade from the original Life-Like switcher.
We asked Eric Smith from Micro-Trains why they elected to not use the same manufacturer for the Switchers as had made their FT units. He explained that the manufacturer of the FTs was no longer in business and that it was more efficient to use a revised version of the Life-Like switcher than to contract a complete new tooling from scratch.
The most important feature of the new mechanism is that it routes the power through a lightboard prior to sending it to the motor. This permits a drop-in DCC decoder upgrade. The motor performs similarly to the predecessor in that it can pull 15 or more cars on level track. The engine operation is similarly smooth and quiet.
The Walthers rep at the 2017 NSE convention stated that Walthers would also be releasing this locomotive with their own branding and shells "sometime in the future".
We asked Eric Smith from Micro-Trains why they elected to not use the same manufacturer for the Switchers as had made their FT units. He explained that the manufacturer of the FTs was no longer in business and that it was more efficient to use a revised version of the Life-Like switcher than to contract a complete new tooling from scratch.
The most important feature of the new mechanism is that it routes the power through a lightboard prior to sending it to the motor. This permits a drop-in DCC decoder upgrade. The motor performs similarly to the predecessor in that it can pull 15 or more cars on level track. The engine operation is similarly smooth and quiet.
The Walthers rep at the 2017 NSE convention stated that Walthers would also be releasing this locomotive with their own branding and shells "sometime in the future".
DCC Information: Newer (2017+?) releases accept TCS MT 1500 and Digitrax DN-126M2 decoders
Prototype History: The EMD SW1500 was a 1,500 hp (1,119 kW) Diesel-electric locomotive intended for switching service and built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division between June 1966 and January 1974. 808 examples were constructed. It was closely related to the less powerful EMD SW1000 model, forming a line of switchers powered by the new EMD 645 engine. The SW1500 replaced the SW1200 in the EMD product line, and was in turn replaced by the MP15DC.
The SW1500 was a substantially bulkier locomotive than the SW1200, with a much bulkier frame, larger cab and bigger hood. In many respects it was approaching a road switcher in abilities. While the SW1500 came as standard with AAR switcher trucks, the majority of them were delivered with the optional Flexicoil trucks which permitted speeds up to 60 mph (100 km/h). The SW1500 was, in fact, often operated as a road-switcher for branchline service, and continues in this role today.
From Wikipedia
The SW1500 was a substantially bulkier locomotive than the SW1200, with a much bulkier frame, larger cab and bigger hood. In many respects it was approaching a road switcher in abilities. While the SW1500 came as standard with AAR switcher trucks, the majority of them were delivered with the optional Flexicoil trucks which permitted speeds up to 60 mph (100 km/h). The SW1500 was, in fact, often operated as a road-switcher for branchline service, and continues in this role today.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The Southern Pacific Transportation Company (reporting mark SP), earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually called the Southern Pacific or (from the railroad's initials) Espee, was an American Class I railroad. It was absorbed in 1988 by the company that controlled the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad and eight years later became part of the Union Pacific Railroad.
The Southern Pacific Transportation Company (reporting mark SP), earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually called the Southern Pacific or (from the railroad's initials) Espee, was an American Class I railroad. It was absorbed in 1988 by the company that controlled the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad and eight years later became part of the Union Pacific Railroad.
The railroad was founded as a land holding company in 1865, later acquiring the Central Pacific Railroad by lease. By 1900 the Southern Pacific Company was a major railroad system incorporating many smaller companies, such as the Texas and New Orleans Railroad and Morgan's Louisiana and Texas Railroad. It extended from New Orleans through Texas to El Paso, across New Mexico and through Tucson, to Los Angeles, through most of California, including San Francisco and Sacramento. Central Pacific lines extended east across Nevada to Ogden, Utah, and reached north through Oregon to Portland. Other subsidiaries eventually included the St. Louis Southwestern Railway (Cotton Belt), the Northwestern Pacific Railroad at 328 miles (528 km), the 1,331 miles (2,142 km) Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico, and a variety of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge routes.
In 1929 SP/T&NO operated 13848 route-miles not including Cotton Belt, whose purchase of the Golden State Route circa 1980 nearly doubled its size to 3,085 miles (4,965 km), bringing total SP/SSW mileage to around 13,508 miles (21,739 km).
By the 1980s route mileage had dropped to 10,423 miles (16,774 km), mainly due to the pruning of branch lines. In 1988 the Southern Pacific was taken over by D&RGW parent Rio Grande Industries. The combined railroad kept the Southern Pacific name due to its brand recognition in the railroad industry and with customers of both constituent railroads. Along with the addition of the SPCSL Corporation route from Chicago to St. Louis, the total length of the D&RGW/SP/SSW system was 15,959 miles (25,684 km).
By 1996 years of financial problems had dropped SP's mileage to 13,715 miles (22,072 km), and it was taken over by the Union Pacific Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The railroad was founded as a land holding company in 1865, later acquiring the Central Pacific Railroad by lease. By 1900 the Southern Pacific Company was a major railroad system incorporating many smaller companies, such as the Texas and New Orleans Railroad and Morgan's Louisiana and Texas Railroad. It extended from New Orleans through Texas to El Paso, across New Mexico and through Tucson, to Los Angeles, through most of California, including San Francisco and Sacramento. Central Pacific lines extended east across Nevada to Ogden, Utah, and reached north through Oregon to Portland. Other subsidiaries eventually included the St. Louis Southwestern Railway (Cotton Belt), the Northwestern Pacific Railroad at 328 miles (528 km), the 1,331 miles (2,142 km) Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico, and a variety of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge routes.
In 1929 SP/T&NO operated 13848 route-miles not including Cotton Belt, whose purchase of the Golden State Route circa 1980 nearly doubled its size to 3,085 miles (4,965 km), bringing total SP/SSW mileage to around 13,508 miles (21,739 km).
By the 1980s route mileage had dropped to 10,423 miles (16,774 km), mainly due to the pruning of branch lines. In 1988 the Southern Pacific was taken over by D&RGW parent Rio Grande Industries. The combined railroad kept the Southern Pacific name due to its brand recognition in the railroad industry and with customers of both constituent railroads. Along with the addition of the SPCSL Corporation route from Chicago to St. Louis, the total length of the D&RGW/SP/SSW system was 15,959 miles (25,684 km).
By 1996 years of financial problems had dropped SP's mileage to 13,715 miles (22,072 km), and it was taken over by the Union Pacific Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Micro-Trains is the brand name used by both Kadee Quality Products and Micro-Trains Line. For a history of the relationship between the brand and the two companies, please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide.
Manufacturer Information:  Micro-Trains Line split off from Kadee Quality Products in 1990. Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
Micro-Trains Line split off from Kadee Quality Products in 1990. Kadee Quality Products originally got involved in N-Scale by producing a scaled-down version of their successful HO Magne-Matic knuckle coupler system. This coupler was superior to the ubiquitous 'Rapido' style coupler due to two primary factors: superior realistic appearance and the ability to automatically uncouple when stopped over a magnet embedded in a section of track. The success of these couplers in N-Scale quickly translated to the production of trucks, wheels and in 1972 a release of ready-to-run box cars.
Micro-Trains Line Co. split off from Kadee in 1990 to form a completely independent company. For this reason, products from this company can appear with labels from both enterprises. Due to the nature of production idiosyncrasies and various random factors, the rolling stock from Micro-Trains can have all sorts of interesting variations in both their packaging as well as the products themselves. When acquiring an MTL product it is very important to understand these important production variations that can greatly enhance (or decrease) the value of your purchase.
Please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide

Micro-Trains Line Co. split off from Kadee in 1990 to form a completely independent company. For this reason, products from this company can appear with labels from both enterprises. Due to the nature of production idiosyncrasies and various random factors, the rolling stock from Micro-Trains can have all sorts of interesting variations in both their packaging as well as the products themselves. When acquiring an MTL product it is very important to understand these important production variations that can greatly enhance (or decrease) the value of your purchase.
Please consult our Micro-Trains Collector's Guide
Item created by: gdm on 2015-07-19 19:36:23. Last edited by gdm on 2020-06-09 07:31:07
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.