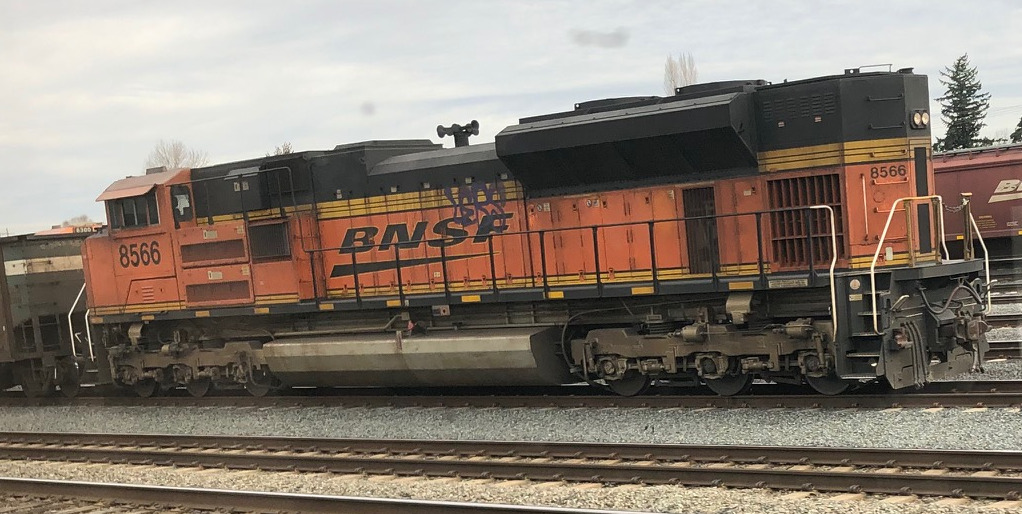
Specific Item Information:
- Era: 2012 to present
- Series 4130 to 4199; built 2012-2014
- Fully-assembled
- Multiple road numbers
- Operating LED-illuminated front deck-mounted ditch lights
- Printed and LED-illuminated number boards
- Factory-applied detail parts: wire grab irons, 3-hose MU clusters, uncoupling levers, windshield wipers, sunshades, brake wheel, and more
- Tall snowplow with open doors
- Operating knuckle couplers – Micro-Trains® compatible
- Body mounted coupler box – accepts Micro-Trains® 1015/1016 type couplers without modification
- Walkway with front and rear anticlimber
- Diamond plate anti-slip walkway tread
- Nose door without window
- Front LED-illuminated headlight with lenses on low short hood
- EMD ISO cab
- Detailed cab interior with floor, rear wall, seats, and desktop
- Tinted cab side windows
- Early EMD inverter box
- Cab roof octagonal antenna dome
- Lost wax brass cast Nathan AirChime K5LLA horn mounted on engine cab roof
- LED-illuminated high mounted vertical rear headlight
- Fuel tank with single fills per side
- Motor with 5-pole skew wound armature
- Dual flywheels
- All-wheel drive and electrical pick-up
- Printing and lettering legible under magnification
- Operates on Code 55 and 80 rail
- Packaging safely stores model
- Minimum Radius: 9 ¾”
- Recommended Radius: 11”
- ESU-LokSound 5 Micro DCC & sound decoder with "Full Throttle"
- Cube-type speaker
- Accurate EMD prime mover and auxiliary sounds, hor, bell, and more
- Operaters on both DC and DCC layouts
Model Information: Fox Valley introduced this model in 2014 with a second run in 2015. It is a modern split-frame locomotive with flywheels and other standard 3rd generation features. Specifically you will find:
Multiple Variations;
Front and Rear ditch lights;
High or Low Headlights;
Etched Metal Details;
Standard Cab;
Isolated Cab;
FVM's Sharp Paint and Lettering;
Wire Grab Irons;
Painted Handrails and Step Edges;
Correct Brass Horn .
The user-applied detail parts are a bit intimidating even for an intermediate modeler, but if you have the skills, you can make this model look awesome.
The user-applied detail parts are a bit intimidating even for an intermediate modeler, but if you have the skills, you can make this model look awesome.
DCC Information: Accepts NEM-651 plug-in decoder.
Prototype History: The EMD SD70 is a series of high-powered, single engined 4,000hp to 4,300hp, diesel-electric locomotives produced by Electro-Motive Division (EMD). All locomotives of this series are hood units with C-C trucks. Production commenced in late 1992 and since then over 4,000 units have been produced. The most produced models of the series are the SD70M, SD70MAC and SD70ACe models. All SD70 models were delivered with the self-steering radial truck HTCR , then from SD70ACe and SD70M-2 models, with non-radial HTSC truck. The radial truck allows the axles to steer in curves which reduces wear on the wheels and railhead.
The SD70ACe AC-traction diesel locomotive (most in the industry simply call them SD70 "Ace" or "Aces") is the successor to the older SD70MAC. It was first introduced in 2004, and has been in production since 2005. It was originally designed to comply with EPA Tier 2 locomotive emissions regulations. Beginning in 2012, newly built SD70ACe's were EPA Tier 3 compliant. SD70ACes are equipped with EMD's 16-710-G3C-T2 prime mover, rated at 4,300 horsepower (3,200 kW); later Tier 3 models are rated at 4,500 horsepower (3,400 kW). The model is still in production as EMD's primary long-haul domestic locomotive.
Although mechanically similar to earlier SD70 units, the SD70ACe rides on a new underframe and uses mostly new sheet metal above the frame. Electrical cables and air lines have been routed beneath the walkways on opposite sides, allowing easier access for maintenance. Continuing the designs of the SD80 and SD90 series, the radiator on the locomotive is nearly as wide as the cab, the center hood section is a step down below the roofline, and the dynamic brakes have been moved to the rear of the hood. The SD70ACe uses the cab design of late-model SD90MAC-H units, which uses rectangular window glass and is externally different from the two cab variations used on earlier SD70M and SD70MAC units. In 2008, EMD standardized the isolated cab on subsequent SD70ACes after non-isolated cab units were restricted from leading on BNSF Railway due to excessive cab vibration. Purchasers included ArcelorMittal, BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway, CSX Transportation, Ferromex, Kansas City Southern Railway, Montana Rail Link, Norfolk Southern Railway, CVG Ferrominera Orinoco, Union Pacific Railroad, Quebec North Shore and Labrador Railway, BHP Billiton, and shortline Arkansas and Missouri Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia, on American-Rails.com and on Locomotive wiki.
Full EMD SD70ACe data sheet on The Diesel Workshop.
The SD70ACe AC-traction diesel locomotive (most in the industry simply call them SD70 "Ace" or "Aces") is the successor to the older SD70MAC. It was first introduced in 2004, and has been in production since 2005. It was originally designed to comply with EPA Tier 2 locomotive emissions regulations. Beginning in 2012, newly built SD70ACe's were EPA Tier 3 compliant. SD70ACes are equipped with EMD's 16-710-G3C-T2 prime mover, rated at 4,300 horsepower (3,200 kW); later Tier 3 models are rated at 4,500 horsepower (3,400 kW). The model is still in production as EMD's primary long-haul domestic locomotive.
Although mechanically similar to earlier SD70 units, the SD70ACe rides on a new underframe and uses mostly new sheet metal above the frame. Electrical cables and air lines have been routed beneath the walkways on opposite sides, allowing easier access for maintenance. Continuing the designs of the SD80 and SD90 series, the radiator on the locomotive is nearly as wide as the cab, the center hood section is a step down below the roofline, and the dynamic brakes have been moved to the rear of the hood. The SD70ACe uses the cab design of late-model SD90MAC-H units, which uses rectangular window glass and is externally different from the two cab variations used on earlier SD70M and SD70MAC units. In 2008, EMD standardized the isolated cab on subsequent SD70ACes after non-isolated cab units were restricted from leading on BNSF Railway due to excessive cab vibration. Purchasers included ArcelorMittal, BNSF Railway, Canadian National Railway, CSX Transportation, Ferromex, Kansas City Southern Railway, Montana Rail Link, Norfolk Southern Railway, CVG Ferrominera Orinoco, Union Pacific Railroad, Quebec North Shore and Labrador Railway, BHP Billiton, and shortline Arkansas and Missouri Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia, on American-Rails.com and on Locomotive wiki.
Full EMD SD70ACe data sheet on The Diesel Workshop.
Road Name History: KCS began (with a different name) in 1890 under the direction of Arthur Stilwell for the purpose of building a railroad from Kansas City directly south along the Missouri – Kansas, Arkansas – Oklahoma, and Louisiana – Texas borders to the Gulf of Mexico. At the point where the railroad met the Gulf, Stillwell built a port complex and named it after himself, Port Arthur, Texas. Two years later, the company defaulted on a loan, Stilwell was kicked out and they changed the name of the railroad to Kansas City Southern. Stilwell went on to build the Kansas City Mexico & Orient.
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
Brand/Importer Information: Fox Valley Models is a small supplier of
model railroad and related products. FVM
started by finding solutions to different
challenges that model railroaders were
faced with. Our first products resulted
from a need to equip custom built
passenger cars with tinted windows made
of an ideal material; thin, flexible, easy to
cut, simple to install, available in multiple
colors and be affordable. We met those
needs and even included a frosted
version for the car's lavatory windows.
Other challenges inspired additional products including wooden grade crossings, trestles and different lineside structures. As our product line expands, input and requests from friends and customers help shape the product selection further.
Future products, under development, include more parts, structures, details and rolling stock. We strive to offer a good quality product at an affordable price.
Other challenges inspired additional products including wooden grade crossings, trestles and different lineside structures. As our product line expands, input and requests from friends and customers help shape the product selection further.
Future products, under development, include more parts, structures, details and rolling stock. We strive to offer a good quality product at an affordable price.
Item created by: CMK on 2022-08-12 23:48:52. Last edited by CMK on 2022-08-13 01:35:14
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.