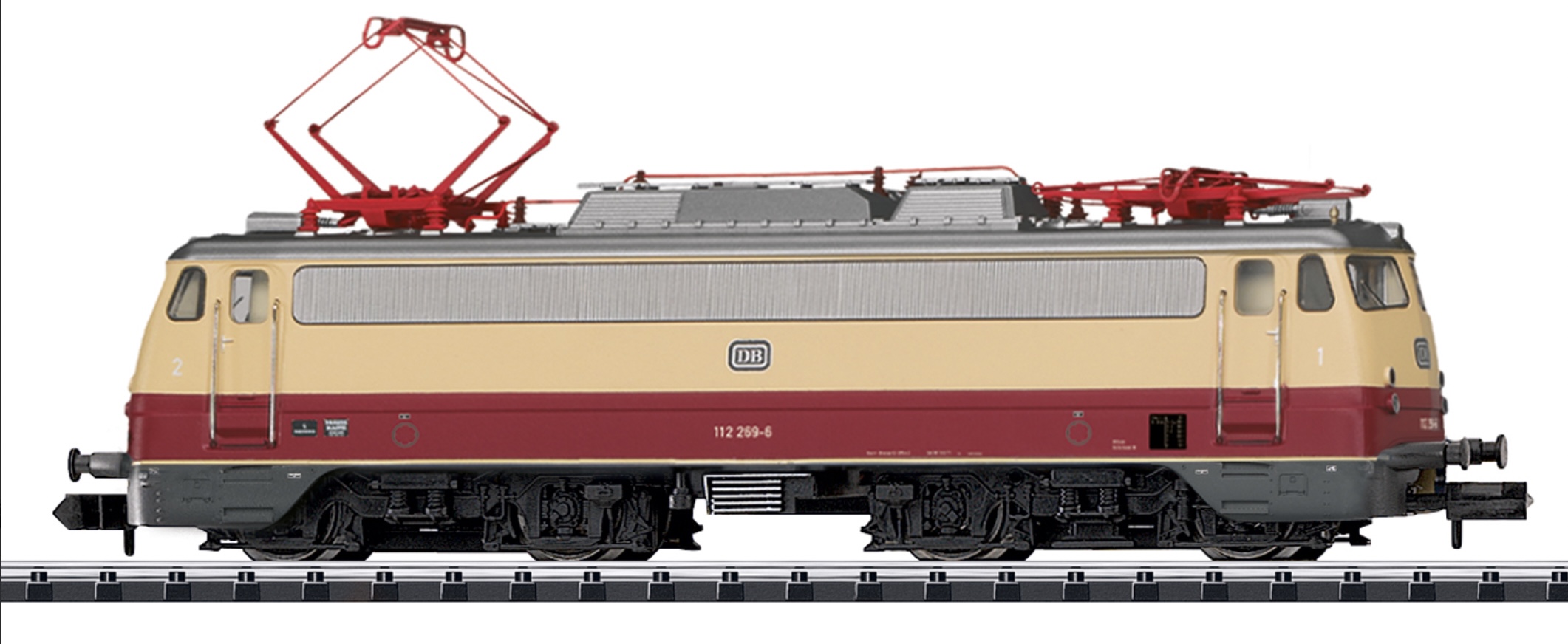
Specific Item Information: German Federal Railroad (DB) standard design electric locomotive, road number 112 269-6. Express locomotive with aerodynamic ends, including the so-called "Bügelfalte" / "Pants Crease". Basic paint scheme in crimson/ivory. Continuous rain gutter, skirting, and buffer cladding included. The locomotive looks as it did around 1974. Use: Passenger trains in long-distance service and occasionally in commuter and freight service.
Road Name History:  Deutsche Bundesbahn was the Western Germany DB before reunification. After World War II, Germany (and the DRG) was divided into 4 zones: US, British, French and Soviet. The first three eventually combined to form the Federal Republic of Germany (the West) and the Russian zone became the German Democratic Republic (the East). German territories beyond the Oder were ceded to Poland except for the northern part of East Prussia, which was ceded to the Soviet Union in 1945.
Deutsche Bundesbahn was the Western Germany DB before reunification. After World War II, Germany (and the DRG) was divided into 4 zones: US, British, French and Soviet. The first three eventually combined to form the Federal Republic of Germany (the West) and the Russian zone became the German Democratic Republic (the East). German territories beyond the Oder were ceded to Poland except for the northern part of East Prussia, which was ceded to the Soviet Union in 1945.
From 1949, the new governments assumed authority for railway operations. The DRG's (or DR's) successors were named Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB, German Federal Railways) in West Germany, and Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR, German State Railways) in East Germany kept the old name to hold tracking rights in western Berlin.
Unlike the DRG, which was a corporation, both the DB and the DR were federal state institutions, directly controlled by their respective transportation ministries. Railway service between East and West was restricted; there were around five well-controlled and secure checkpoints between West and East Germany, and about the same number between East Germany and West Berlin. Four transit routes existed between West Germany and West Berlin; citizens of West Berlin and West Germany were able to use these without too much harassment by the East German authorities.
The DB started in 1968 with changing the locomotive and passenger car serial numbers to the UIC norm. In 1970 the DR followed. The DB started experimenting with the Intercity trains in a new livery (bright orange).
In 1989, the Wall fell. Train frequency rapidly increased on the existing East/West corridors; closed links which had formerly crossed the border were re-opened. On 3 October 1990, Germany was reunified; however, this was not immediately the case with the railways. Administrative and organisational problems led to the decision to completely re-organize and reconnect Germany's railways. The so-called Bahnreform (Railway Reform) came into effect on 1 January 1994, when the State railways Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Reichsbahn were formally reunited to form the current German Railway Corporation (Deutsche Bahn).
From Wikipedia

From 1949, the new governments assumed authority for railway operations. The DRG's (or DR's) successors were named Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB, German Federal Railways) in West Germany, and Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR, German State Railways) in East Germany kept the old name to hold tracking rights in western Berlin.
Unlike the DRG, which was a corporation, both the DB and the DR were federal state institutions, directly controlled by their respective transportation ministries. Railway service between East and West was restricted; there were around five well-controlled and secure checkpoints between West and East Germany, and about the same number between East Germany and West Berlin. Four transit routes existed between West Germany and West Berlin; citizens of West Berlin and West Germany were able to use these without too much harassment by the East German authorities.
The DB started in 1968 with changing the locomotive and passenger car serial numbers to the UIC norm. In 1970 the DR followed. The DB started experimenting with the Intercity trains in a new livery (bright orange).
In 1989, the Wall fell. Train frequency rapidly increased on the existing East/West corridors; closed links which had formerly crossed the border were re-opened. On 3 October 1990, Germany was reunified; however, this was not immediately the case with the railways. Administrative and organisational problems led to the decision to completely re-organize and reconnect Germany's railways. The so-called Bahnreform (Railway Reform) came into effect on 1 January 1994, when the State railways Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Reichsbahn were formally reunited to form the current German Railway Corporation (Deutsche Bahn).
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Trix is a German company that originally made Trix metal construction sets. one of its co-founders was Stephan Bing, the son of the pioneer toy-maker industrialist Ignaz Bing. In 1935 the company began producing the electrically powered model trains that it became famous for, under the Trix Express label. Prior to the outbreak of World War II the Trix company produced a small range of fairly unrealistic AC powered three rail models running at 14 volts.
N gauge models under the Minitrix brand were made from the late 1960s mostly of European prototypes (German and British primarily). North American prototypes were also manufactured and marketed under the Aurora "Postage Stamp" brand; later these items were sold under the American Tortoise, Model Power and Con-Cor brands. Trix sometimes utilized North American consultants to aid in the design of this portion of the product line. The "Hornby Minitrix' brand was used in the 1980s for a short lived range of British outline models using the earlier product tooling.
Trix's owner in the 1980s and 1990s was Mangold, which went bankrupt in the late 1990s and Märklin purchased the assets in January 1997. In part, this purchase was a reflection of Märklin's need for added production capacity; Trix had been manufacturing certain items for Märklin in previous years. The purchase was also in response to the earlier purchase of the Karl Arnold company by the Italian company Rivarossi; Märklin were very keen to take over Trix market share in 2-rail H0 and especially Minitrix, until then Märklin had not marketed N gauge models. In 2003, Märklin introduced its first N gauge models under the well established Minitrix brand. A number Märklin H0 scale three-rail AC locomotives have also been introduced in two-rail DC versions under the Trix logo and many models are shared between the two brands.
From Wikipedia
N gauge models under the Minitrix brand were made from the late 1960s mostly of European prototypes (German and British primarily). North American prototypes were also manufactured and marketed under the Aurora "Postage Stamp" brand; later these items were sold under the American Tortoise, Model Power and Con-Cor brands. Trix sometimes utilized North American consultants to aid in the design of this portion of the product line. The "Hornby Minitrix' brand was used in the 1980s for a short lived range of British outline models using the earlier product tooling.
Trix's owner in the 1980s and 1990s was Mangold, which went bankrupt in the late 1990s and Märklin purchased the assets in January 1997. In part, this purchase was a reflection of Märklin's need for added production capacity; Trix had been manufacturing certain items for Märklin in previous years. The purchase was also in response to the earlier purchase of the Karl Arnold company by the Italian company Rivarossi; Märklin were very keen to take over Trix market share in 2-rail H0 and especially Minitrix, until then Märklin had not marketed N gauge models. In 2003, Märklin introduced its first N gauge models under the well established Minitrix brand. A number Märklin H0 scale three-rail AC locomotives have also been introduced in two-rail DC versions under the Trix logo and many models are shared between the two brands.
From Wikipedia
Item created by: CNW400 on 2022-05-26 12:21:06
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.