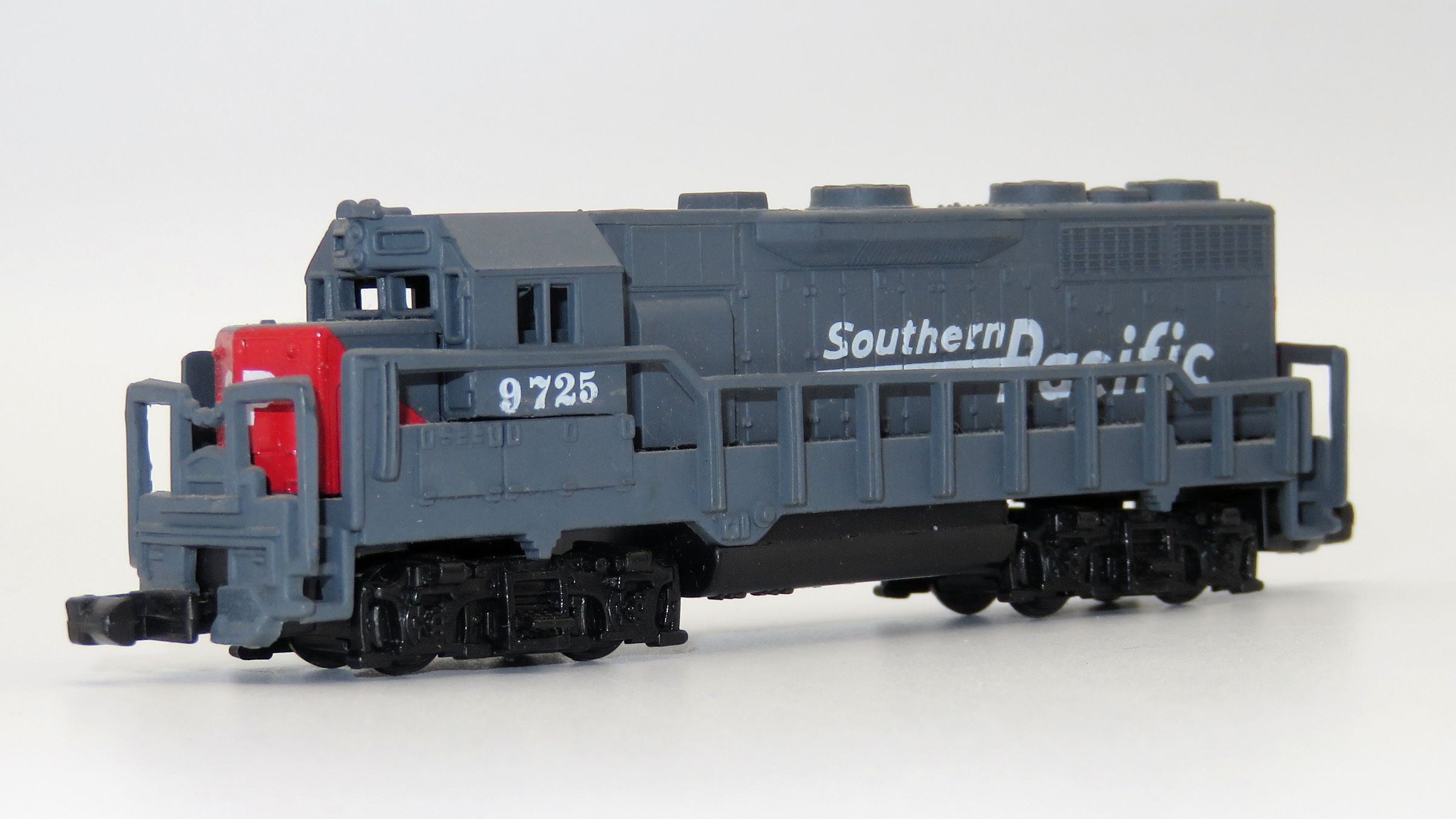
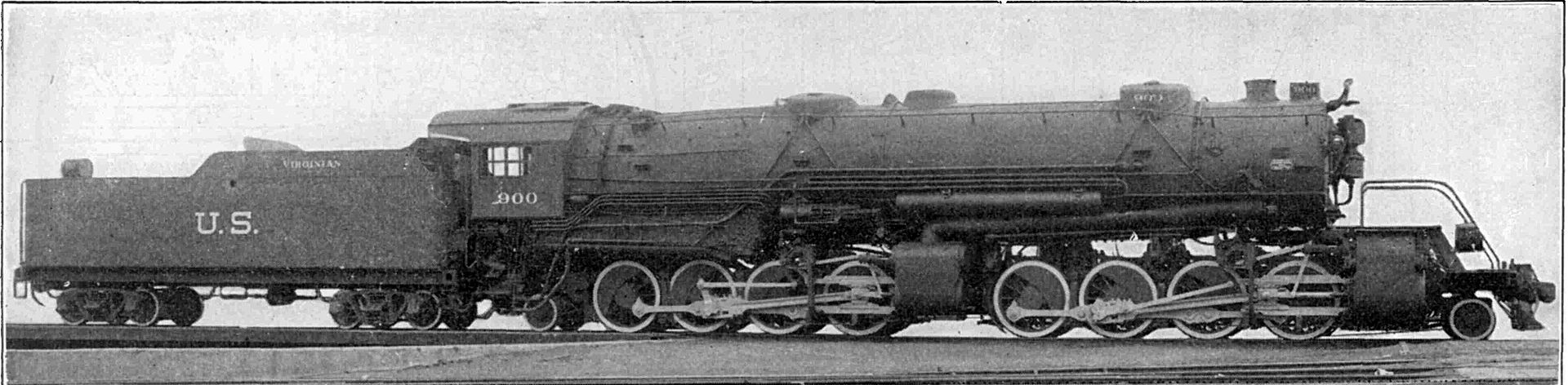
Model Information: This model as sold by Arnold Rapido includes a smoke generator. This model was also by MRC, Con-Cor and Rowa directly, but perhaps not with the smoke generator. Tender pickup. A smooth running model, but the motor was overtaxed and pulling power was modest.
DCC Information: This engine is not DCC-Compatible.
Prototype History: The USRA 2-8-8-2 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-8-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or (1'D)'D1' in UIC classification. A total of 106 locomotives were built to this plan for the USRA; postwar, it became a de facto standard design.
While the 2-8-8-2 had been built in the United States since 1909, most development work had gone into making subsequent locomotives larger and heavier. The Norfolk and Western Railway however, had taken development in a different direction. By using smaller cylinders and higher boiler pressure, the result was a locomotive capable of powerful performance, and a turn of speed higher than the 20 mph (32 km/h) maximum of the ‘traditional’ designs. The USRA 2-8-8-2 drew heavily on the Norfolk and Western Railway’s Y-2 class locomotive design, as their delegate to the 2-8-8-2 design committee had brought a full set of blueprints.
From Wikipedia
While the 2-8-8-2 had been built in the United States since 1909, most development work had gone into making subsequent locomotives larger and heavier. The Norfolk and Western Railway however, had taken development in a different direction. By using smaller cylinders and higher boiler pressure, the result was a locomotive capable of powerful performance, and a turn of speed higher than the 20 mph (32 km/h) maximum of the ‘traditional’ designs. The USRA 2-8-8-2 drew heavily on the Norfolk and Western Railway’s Y-2 class locomotive design, as their delegate to the 2-8-8-2 design committee had brought a full set of blueprints.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR) was an American Class I railroad, founded in 1846. Commonly referred to as the "Pennsy," the PRR was headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
The PRR was the largest railroad by traffic and revenue in the U.S. for the first half of the twentieth century. Over the years, it acquired, merged with or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1925, it operated 10,515 miles of rail line; in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific or Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Central (NYC), which carried around three-quarters of PRR's ton-miles.
At one time, the PRR was the largest publicly traded corporation in the world, with a budget larger than that of the U.S. government and a workforce of about 250,000 people. The corporation still holds the record for the longest continuous dividend history: it paid out annual dividends to shareholders for more than 100 years in a row.
In 1968, PRR merged with rival NYC to form the Penn Central Transportation Company, which filed for bankruptcy within two years. The viable parts were transferred in 1976 to Conrail, which was itself broken up in 1999, with 58 percent of the system going to the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), including nearly all of the former PRR. Amtrak received the electrified segment east of Harrisburg.
The PRR was the largest railroad by traffic and revenue in the U.S. for the first half of the twentieth century. Over the years, it acquired, merged with or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1925, it operated 10,515 miles of rail line; in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific or Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Central (NYC), which carried around three-quarters of PRR's ton-miles.
At one time, the PRR was the largest publicly traded corporation in the world, with a budget larger than that of the U.S. government and a workforce of about 250,000 people. The corporation still holds the record for the longest continuous dividend history: it paid out annual dividends to shareholders for more than 100 years in a row.
In 1968, PRR merged with rival NYC to form the Penn Central Transportation Company, which filed for bankruptcy within two years. The viable parts were transferred in 1976 to Conrail, which was itself broken up in 1999, with 58 percent of the system going to the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), including nearly all of the former PRR. Amtrak received the electrified segment east of Harrisburg.
Brand/Importer Information: In the hobby industry, few companies have built as bold and dynamic a reputation for quality products and technical achievement as Model Rectifier Corporation (MRC). More than a half century ago, MRC began its march toward hobby product leadership by designing model railroad train controls with a level of realism and power previously unavailable. Today, MRC's technology-rich Tech 6 and Prodigy DCC lead a long list of MRC engineered train controls and sound systems respected and enjoyed by millions of model railroad hobbyist around the world.
Success with model railroads led us to carry our passion for hobby quality and technology into the development of other outstanding brands and categories. Today, MRC is the exclusive distributor for some of the world's most respected hobby products as well as the creators and manufacturers of prominent proprietary lines. While our brands and products are diverse, they all share a common bond. Each product we sell meets stringent quality standards and exceeds the highest customer expectation levels. Extraordinary in its depth and breadth, MRC product lines include some of the world's most recognized hobby brands and category leaders.
Success with model railroads led us to carry our passion for hobby quality and technology into the development of other outstanding brands and categories. Today, MRC is the exclusive distributor for some of the world's most respected hobby products as well as the creators and manufacturers of prominent proprietary lines. While our brands and products are diverse, they all share a common bond. Each product we sell meets stringent quality standards and exceeds the highest customer expectation levels. Extraordinary in its depth and breadth, MRC product lines include some of the world's most recognized hobby brands and category leaders.
Manufacturer Information: Röwa was founded in 1961 by Willy Ade and Horst Röchling, the company name being an acronym of their combined names. For several years, much of Röwa’s energies were directed toward developing products for other model train manufacturers, notably Trix of Germany and, on occasion, Roco of Austria.
Production of model trains under the Röwa name began in the late 1960’s, ca. 1968. Much of the company’s products were in H0-Scale, but there was some interesting production in N-Scale.
The Röwa American-prototype N-Scale items were marketed in the United States by Model Rectifier Corporation (MRC) for a period of a few years. Both the locomotives and passenger cars were subsequently marketed by other companies in successive years. For example, Brawa and Con-Cor marketed the N&W Y-6b Mallet-type, and the Berkshire may have also been marketed in the same way. Con-Cor owned the passenger car tooling for a period of time, producing until the die-molds went out of production tolerances.
Röwa ended production around 1974 and the manufacturing tools and dies used to produce the trains were sold to other companies.
From this website.
Production of model trains under the Röwa name began in the late 1960’s, ca. 1968. Much of the company’s products were in H0-Scale, but there was some interesting production in N-Scale.
The Röwa American-prototype N-Scale items were marketed in the United States by Model Rectifier Corporation (MRC) for a period of a few years. Both the locomotives and passenger cars were subsequently marketed by other companies in successive years. For example, Brawa and Con-Cor marketed the N&W Y-6b Mallet-type, and the Berkshire may have also been marketed in the same way. Con-Cor owned the passenger car tooling for a period of time, producing until the die-molds went out of production tolerances.
Röwa ended production around 1974 and the manufacturing tools and dies used to produce the trains were sold to other companies.
From this website.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2020-12-08 14:26:50. Last edited by klausnahr on 2022-01-11 14:05:44
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.