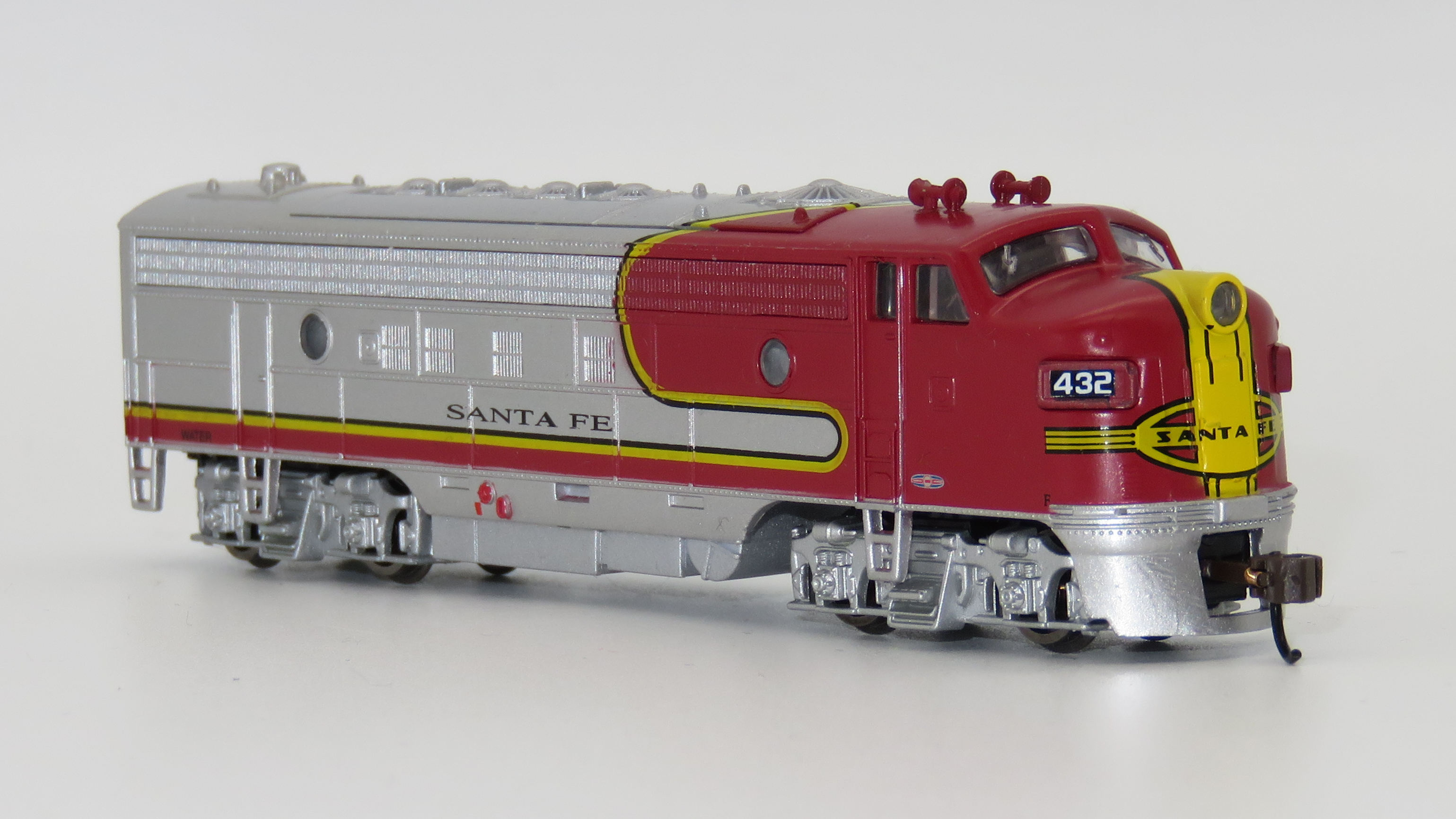
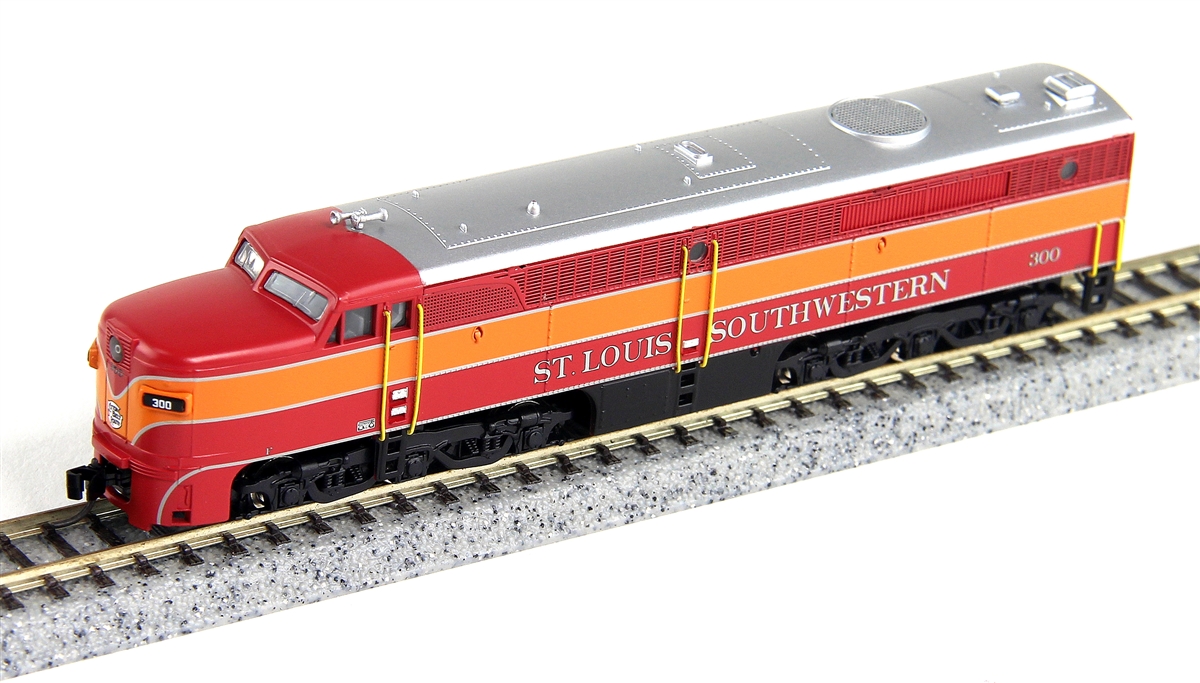
Specific Item Information: The Korean made Modeler Version of the Santa Fe FP7A can easily identified by the grey trucks and the grey tank. The Mechanismus is also different compared to the Chinese Trainset Version which comes with black trucks and tank.
Heavy diecast metal shell.
Heavy diecast metal shell.
Model Information: First run initially announced for Summer 2003 with MRSP $59.98; delivered in 2006.
Re-run in 2017 by MRC that acquired assets of Model-Power.
Re-run in 2017 by MRC that acquired assets of Model-Power.
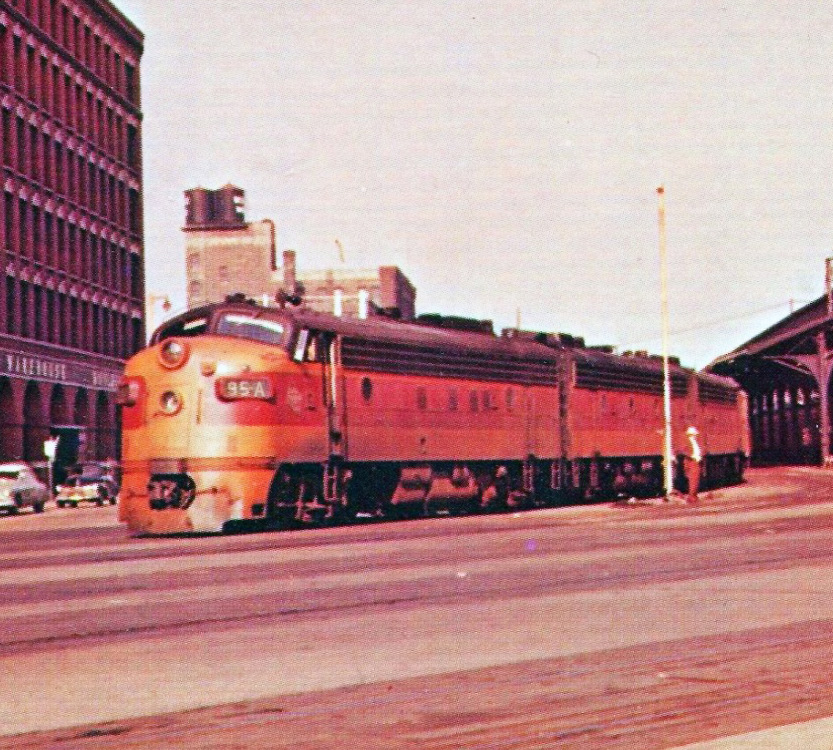
Prototype History: The EMD FP7 was a 1,500 horsepower (1,100 kW), B-B dual-service passenger and freight-hauling diesel locomotive produced between June 1949 and December 1953 by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division and General Motors Diesel. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant, excepting locomotives destined for Canada, in which case final assembly was at GMD's plant in London, Ontario. The FP7 was essentially EMD's F7A locomotive extended by four feet to give greater water capacity for the steam generator for heating passenger trains.
While EMD's E-units were successful passenger engines, their A1A-A1A wheel arrangement made them less useful in mountainous terrain. Several railroads had tried EMD's F3 in passenger service, but there was insufficient water capacity in an A-unit fitted with dynamic brakes. The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway's solution was to replace the steam generators in A-units with a water tank, and so only fitted steam generators into the B-units. The Northern Pacific Railway's solution was to fit extra water tanks into the first baggage car, and to pipe the water to the engines. The real breakthrough came when EMD recognized the problem and added the stretched FP7 to its catalog.
A total of 381 cab-equipped lead A units were built; unlike the freight series, no cables booster B units were sold. Regular F7B units were sometimes used with FP7 A units, since they, lacking cabs, had more room for water and steam generators. The FP7 and its successor, the FP9, were offshoots of GM-EMD's highly successful F-unit series of cab unit freight diesels.
F3s, F7s, and F9s equipped for passenger service are not FP-series locomotives, which although similar in appearance have distinctive differences, including but not limited to the greater body length. The extra 4 ft (1.2 m) of length was added behind the first body-side porthole, and can be recognised by the greater distance between that porthole and the first small carbody filter grille. The corresponding space beneath the body, behind the front truck, was also opened up; this either remained an empty space or was filled with a distinctive water tank shaped like a barrel mounted transversely.
Railroads found that Fs, with their better tractive effort performed much better than Es in passenger service on routes with stiff grades. However, as a freight model lacking steam generators it was not a possible unless a separate heating car was used or Es were in the consist. EMD corrected the issue with its FP7, released in the late 1940s, built at the same time as the F7. Surprisingly, for a variant model the locomotive sold quite well with nearly 400 examples manufactured (including those constructed by General Motors Diesel of London, Ontario). Today, numerous FP7s remain preserved and in operation around the country.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
While EMD's E-units were successful passenger engines, their A1A-A1A wheel arrangement made them less useful in mountainous terrain. Several railroads had tried EMD's F3 in passenger service, but there was insufficient water capacity in an A-unit fitted with dynamic brakes. The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway's solution was to replace the steam generators in A-units with a water tank, and so only fitted steam generators into the B-units. The Northern Pacific Railway's solution was to fit extra water tanks into the first baggage car, and to pipe the water to the engines. The real breakthrough came when EMD recognized the problem and added the stretched FP7 to its catalog.
A total of 381 cab-equipped lead A units were built; unlike the freight series, no cables booster B units were sold. Regular F7B units were sometimes used with FP7 A units, since they, lacking cabs, had more room for water and steam generators. The FP7 and its successor, the FP9, were offshoots of GM-EMD's highly successful F-unit series of cab unit freight diesels.
F3s, F7s, and F9s equipped for passenger service are not FP-series locomotives, which although similar in appearance have distinctive differences, including but not limited to the greater body length. The extra 4 ft (1.2 m) of length was added behind the first body-side porthole, and can be recognised by the greater distance between that porthole and the first small carbody filter grille. The corresponding space beneath the body, behind the front truck, was also opened up; this either remained an empty space or was filled with a distinctive water tank shaped like a barrel mounted transversely.
Railroads found that Fs, with their better tractive effort performed much better than Es in passenger service on routes with stiff grades. However, as a freight model lacking steam generators it was not a possible unless a separate heating car was used or Es were in the consist. EMD corrected the issue with its FP7, released in the late 1940s, built at the same time as the F7. Surprisingly, for a variant model the locomotive sold quite well with nearly 400 examples manufactured (including those constructed by General Motors Diesel of London, Ontario). Today, numerous FP7s remain preserved and in operation around the country.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
Road Name History: The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (reporting mark ATSF), often abbreviated as Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. Chartered in February 1859, the railroad reached the Kansas-Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farm land from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress. Despite the name, its main line never served Santa Fe, New Mexico, as the terrain was too difficult; the town ultimately was reached by a branch line from Lamy.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport, an enterprise that (at one time or another) included a tugboat fleet and an airline (the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway). Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not accessible by rail, and ferryboats on the San Francisco Bay allowed travelers to complete their westward journeys to the Pacific Ocean. The ATSF was the subject of a popular song, Harry Warren & Johnny Mercer's "On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe", written for the film, The Harvey Girls (1946).
The railroad officially ceased operations on December 31, 1996, when it merged with the Burlington Northern Railroad to form the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway.
Read more on Wikipedia.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport, an enterprise that (at one time or another) included a tugboat fleet and an airline (the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway). Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not accessible by rail, and ferryboats on the San Francisco Bay allowed travelers to complete their westward journeys to the Pacific Ocean. The ATSF was the subject of a popular song, Harry Warren & Johnny Mercer's "On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe", written for the film, The Harvey Girls (1946).
The railroad officially ceased operations on December 31, 1996, when it merged with the Burlington Northern Railroad to form the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Founded in the late 1960's by Michael Tager, the 3rd generation business specializes in quality hobby products serving the toy and hobby markets worldwide. During its 50 years of operation, Model Power has developed a full line of model railroading products, die-cast metal aircraft, and die-cast metal cars and trucks.
In early 2014, Model Power ceased its business operations. Its extensive portfolio of intellectual property and physical assets are now exclusively produced, marketed, sold, and distributed by MRC (Model Power, MetalTrain and Mantua) and by Daron (Postage Stamp Airplanes and Airliner Collection).
In early 2014, Model Power ceased its business operations. Its extensive portfolio of intellectual property and physical assets are now exclusively produced, marketed, sold, and distributed by MRC (Model Power, MetalTrain and Mantua) and by Daron (Postage Stamp Airplanes and Airliner Collection).
Item created by: klausnahr on 2020-08-08 10:48:16. Last edited by klausnahr on 2021-05-04 08:40:49
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.