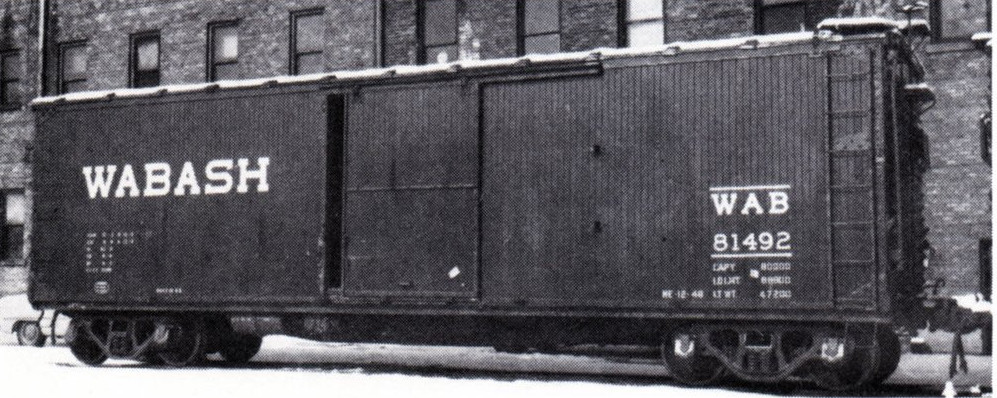
History: In US railroad terminology, a gondola is an open-topped rail vehicle used for transporting loose bulk materials. Because of their low side walls gondolas are also suitable for the carriage of such high-density cargos as steel plates or coils, or of bulky items such as prefabricated sections of rail track.
Composite gondolas date back to the early part of the 20th century. The USRA designed seven standard freight cars during World War I (only five of the designs were built during the years of USRA control). The USRA designers chose composite (wood and steel) construction to conserve as much sheet steel as possible for the war effort.
Next to the single-sheathed boxcar, the composite gondola was the most popular USRA-design car built with 20,000 cars delivered to 25 railroads. ... While all of these cars were built as composite cars with drop-bottom doors, many railroads later rebuilt these gons with steel sides
Composite gondolas date back to the early part of the 20th century. The USRA designed seven standard freight cars during World War I (only five of the designs were built during the years of USRA control). The USRA designers chose composite (wood and steel) construction to conserve as much sheet steel as possible for the war effort.
Next to the single-sheathed boxcar, the composite gondola was the most popular USRA-design car built with 20,000 cars delivered to 25 railroads. ... While all of these cars were built as composite cars with drop-bottom doors, many railroads later rebuilt these gons with steel sides
Railroad/Company: The United States Railroad Administration (USRA) was the name of the nationalized railroad system of the United States between December 28, 1917, and March 1st, 1920. It was possibly the largest American experiment with nationalization, and was undertaken against a background of war emergency.
On April 6th, 1917, the United States entered World War I, and very soon the nation's railroads proved inadequate to the task of serving the war effort. There were several sources of the problem. Although the carriers had made massive investments in the first years of the 20th century, there remained inadequacies in terminals, trackage, and rolling stock. Inflation struck the American economy, and when in 1906 Congress empowered the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) to set maximum shipping rates, the rail firms had difficulty securing revenue sufficient to keep pace with rising costs. The ICC did allow some increases in rates, however. Also, investors had overexpanded the nation's trackage, so by late 1915 fully one-sixth of the railroad trackage in the country belonged to roads in receivership (bankruptcy). The railroad unions (commonly called "brotherhoods"), desiring shorter working days and better pay, threatened strike action in the second half of 1916. To avert a strike, President Woodrow Wilson secured Congressional passage of the Adamson Act, which set the eight-hour work day as the industry standard. When the Supreme Court ruled the law constitutional, the carriers had no choice but to comply.
Over 100,000 railroad cars and 1,930 steam locomotives were ordered by the USRA at a cost of $380 million, all of new USRA standard designs, which were up-to-date and standardized types, designed to be the best that could be produced to replace outdated equipment.
From Wikipedia
On April 6th, 1917, the United States entered World War I, and very soon the nation's railroads proved inadequate to the task of serving the war effort. There were several sources of the problem. Although the carriers had made massive investments in the first years of the 20th century, there remained inadequacies in terminals, trackage, and rolling stock. Inflation struck the American economy, and when in 1906 Congress empowered the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) to set maximum shipping rates, the rail firms had difficulty securing revenue sufficient to keep pace with rising costs. The ICC did allow some increases in rates, however. Also, investors had overexpanded the nation's trackage, so by late 1915 fully one-sixth of the railroad trackage in the country belonged to roads in receivership (bankruptcy). The railroad unions (commonly called "brotherhoods"), desiring shorter working days and better pay, threatened strike action in the second half of 1916. To avert a strike, President Woodrow Wilson secured Congressional passage of the Adamson Act, which set the eight-hour work day as the industry standard. When the Supreme Court ruled the law constitutional, the carriers had no choice but to comply.
Over 100,000 railroad cars and 1,930 steam locomotives were ordered by the USRA at a cost of $380 million, all of new USRA standard designs, which were up-to-date and standardized types, designed to be the best that could be produced to replace outdated equipment.
From Wikipedia
Item Links: We found: 1 different collections associated with Rail - Rolling Stock (Freight) - Composite
- Collection N Scale Model Trains: 25 different items.
Item created by: gdm on 2019-03-01 11:07:27. Last edited by gdm on 2019-11-02 17:11:08
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.