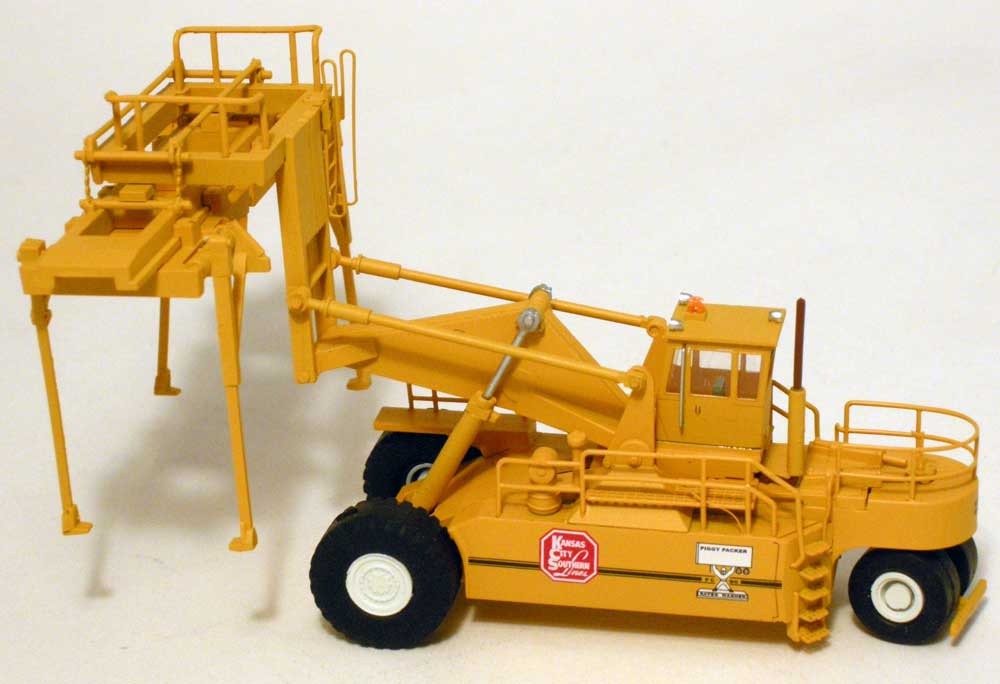
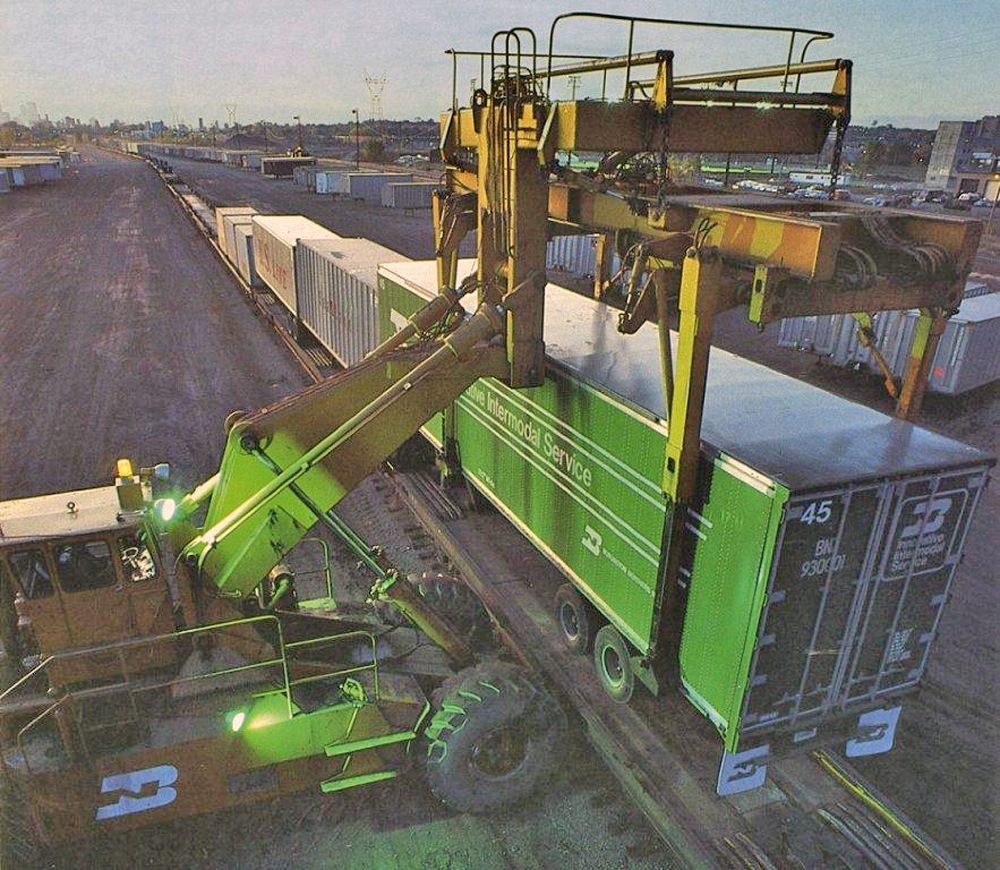
Prototype History: By the early 1960s, railroads in North America were routinely transporting truck trailers on specialized railroad cars called “piggyback” flat cars (known as Trailer On Flat Car, or TOFC). The loading and unloading of truck trailers from these flat cars was accomplished by way of a ramp at one end of the train, with a truck-tractor used to pull the trailer on and off the train. This was commonly referred to as “circus loading”, and was a time consuming process: by this method, trailers on piggyback flat cars could only be loaded or unloaded sequentially. Furthermore circus loading required a very skilled driver, one able to navigate the narrow confines of a flatcar, especially when backing up to pick up a trailer.
In 1968, the FWD Wagner Corp. developed the P-80 and the PC-90. The boom on the PC-90 (and P-80) was redesigned to eliminate the tilting of the trailers during lifting by including a pair of horizontal stabilizing bars that served as a parallelogram. Folding grapple arms replaced the clamshell lift mechanism, eliminating the 10-feet clearance required with the '70. Further, by 1968, ISO standards had been established for the emerging maritime container business, replacing the proprietary lift mechanisms for SeaLand, Matson and others. Nelson saw the growth potential in adapting the Piggy-Packer for container handling, and chose the lift mechanism that had been developed by Ropco Corp. The first dual-purpose machine equipped with a container spreader entered service in UP’s Seattle facility in 1968. Furthermore, lift capacity was beefed up to 90,000 lb (45 tons). The PC-90 quickly became the de facto standard for mechanization of TOFC operations.
In 1968, the FWD Wagner Corp. developed the P-80 and the PC-90. The boom on the PC-90 (and P-80) was redesigned to eliminate the tilting of the trailers during lifting by including a pair of horizontal stabilizing bars that served as a parallelogram. Folding grapple arms replaced the clamshell lift mechanism, eliminating the 10-feet clearance required with the '70. Further, by 1968, ISO standards had been established for the emerging maritime container business, replacing the proprietary lift mechanisms for SeaLand, Matson and others. Nelson saw the growth potential in adapting the Piggy-Packer for container handling, and chose the lift mechanism that had been developed by Ropco Corp. The first dual-purpose machine equipped with a container spreader entered service in UP’s Seattle facility in 1968. Furthermore, lift capacity was beefed up to 90,000 lb (45 tons). The PC-90 quickly became the de facto standard for mechanization of TOFC operations.
Road Name History: KCS began (with a different name) in 1890 under the direction of Arthur Stilwell for the purpose of building a railroad from Kansas City directly south along the Missouri – Kansas, Arkansas – Oklahoma, and Louisiana – Texas borders to the Gulf of Mexico. At the point where the railroad met the Gulf, Stillwell built a port complex and named it after himself, Port Arthur, Texas. Two years later, the company defaulted on a loan, Stilwell was kicked out and they changed the name of the railroad to Kansas City Southern. Stilwell went on to build the Kansas City Mexico & Orient.
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
The KCS steam fleet was, well, peculiar. They were the only railroad to use 0-6-6-0’s, not as heavy switchers, not as pushers, but as mainline road engines. 2-8-8-0’s were also used for heavy road service with Santa Fe types and Consolidations filling out the freight roster. 11 Pacifics handled the passenger trains. They were odd first in that they had 2 sand domes (rare on passenger power.) Second, they had a high mounted headlight but without a number plate in the middle of the smokebox door, giving the front a strange “faceless” appearance. A few of these Pacifics assigned to the Kansas City – Port Arthur “Flying Crow” were equipped with air horns that sounded like a cawing crow… Really! KCS also had 2 Shays used to muscle cars up and down the 10% grades of many Kansas City industrial spurs. (If you’ve been to Kansas City, you will understand why.) The pinnacle of the fleet was the J class 2-10-4’s, purchased to replace the 0-6-6-0’s in 1937. These were the last Texas types built by Lima and had sleek, jacketed boilers and enclosed cabs.
In 1939, the KCS acquired the Louisiana & Arkansas which ran from Dallas east to Shreveport and then New Orleans. Actually, it was the owners of the L&A that bought the KCS but for charter reasons, the deal was arranged so that KCS took control of L&A. L&A remained semi-autonomous in an SP-Cotton Belt sort of way. This brought the KCS system to over 1,660 miles (between Grand Trunk Western and Delaware & Hudson in relative size.) The L&A image began to fade away in the 1960s but it wasn’t fully merged into KCS until 1992.
Dieselization came primarily from EMD with E’s pulling the Flying Crow and Southern Belle, and F’s in freight service. These were delivered in the classic red, black and yellow with red being dominant on the freight units and yellow on the passenger units. A-B-B-A sets of Erie Builts were also used in freight service but were notorious for breaking knuckles on the hog-back hills of the Ozarks.
Switchers and first generation hood units were delivered in black with white trim (much like Illinois Central) with the name spelled out on the long hood. Hood units and switchers came from EMD, Alco, Baldwin and FM.
In the 1960s, the paint scheme was simplified to a solid red. This became known as Deramus Red after the line’s CEO William Deramus II. Deramus’s son (William III) was head of Chicago Great Western and later M-K-T, both of which used similar reds. While William II was a reasonably adept CEO, his son William III was less successful, at least as far as the railroad was concerned. Under William III, track deteriorated and customers fled, which in turn permitted him to cut more service and staff. Fewer, longer trains were dispatched. Meanwhile William III was pouring available cash into diversifying into less regulated industries. By the 1970s, KCS faced a triple threat. Track condition was at an all time low, the first generation diesels were wearing out and tonnage was increasing. A new CEO began to turn the railroad around. The red paint scheme was dumped for white with red lettering. Grain moving down from Kansas City was joined by petro-chemicals moving up from the coast. Powder River Coal joined the mix during this period.
KCS’s diversified holdings, including the Janus Fund, made KCS ripe for takeover. In 1985, leftist fundraiser George Soros attempted a hostile takeover but was foiled first by a real estate developer and then by a Deramus successor who had since moved to Hallmark Cards and then bought a large block of KCS stock.
Now a rousing success, KCS spun off Janus and other holdings and kept the railroad because that is where the REAL money was! In 2006, the Southern Belle red, yellow, and black paint scheme was re-introduced. A version of it was even applied to some new KCS freight cars (KCS freight cars had been notorious dull for decades with few having anything more than reporting marks to trumpet their owner.)
Brand/Importer Information: Wheels of Time was founded by Matthew Young in the fall of 1995. From an early age, Matthew has had a passion for trains, both in full-size and in miniature. His family frequently went out of their way so he could ride the train, or simply watch the action on the tracks. "On one occasion mom took us to San Francisco along the waterfront. Spotting a State Belt ALCo S-2 locomotive switching the wharves, I persuading my mom to follow it. I watched in wonder as I saw and heard the hit-cup sputtering of the ALCo engine as it revved-up to move railroad cars on and off the car float at Pier 43." Other early family experiences included watching Southern Pacific freight and Amtrak's San Joaquin Amfleet trains roll by as his family waited to be seated at Spenger's in Berkeley, which sat happily right next to the tracks. "My brother and I would shoot pictures of the trains with our Instantmatic 110 cameras, sometimes only getting the wheels or worse yet ... getting a real good close up of my big thumb."
Matthew and his brother built models of all kinds, but their model train career began in elementary school when they started making 3-D cardboard miniature trains from pictures found in the pages of Trains Magazine and Model Railroader Magazine. On a visit, many years later, with the late Richard Buike of Trackside Trains in Burlingame, California, the conversation turned to the lack of N-Scale passenger trains and how the few that existed didn't look right. "I told him right then and there that I was going to produce high quality, historically accurate passenger railroad cars. Even I was a little surprised when I said this." The first product was a 1950 Pullman-Standard "10-6" sleeping car made of brass. Wheels of Time became one of the first makers of historically accurate and realisticly detailed passenger train cars. At Wheels of Time, we research original equipment and recreate it with CAD software for production. We're lovers of history and sticklers for detail. On our line of Transit Motor Coaches (a fancy way of saying "buses"), even the destination *roll* signs are historically accurate. Be sure to check out all our beautiful and accurate products. We hope you'll come to share our passion for trains, here recreated in miniature. At Wheels of Time, you get to take home a piece of a fascinating history.
Wheels of Time manufactures historically accurate model trains, vehicles, and model railroad accessories with a real *wow* factor. Our obsession with detail and historical accuracy is reflected in our exceptional design and production: hold a Wheels of Time model in your hand and you'll be tempted to say, 'It's the real thing!'
Matthew and his brother built models of all kinds, but their model train career began in elementary school when they started making 3-D cardboard miniature trains from pictures found in the pages of Trains Magazine and Model Railroader Magazine. On a visit, many years later, with the late Richard Buike of Trackside Trains in Burlingame, California, the conversation turned to the lack of N-Scale passenger trains and how the few that existed didn't look right. "I told him right then and there that I was going to produce high quality, historically accurate passenger railroad cars. Even I was a little surprised when I said this." The first product was a 1950 Pullman-Standard "10-6" sleeping car made of brass. Wheels of Time became one of the first makers of historically accurate and realisticly detailed passenger train cars. At Wheels of Time, we research original equipment and recreate it with CAD software for production. We're lovers of history and sticklers for detail. On our line of Transit Motor Coaches (a fancy way of saying "buses"), even the destination *roll* signs are historically accurate. Be sure to check out all our beautiful and accurate products. We hope you'll come to share our passion for trains, here recreated in miniature. At Wheels of Time, you get to take home a piece of a fascinating history.
Wheels of Time manufactures historically accurate model trains, vehicles, and model railroad accessories with a real *wow* factor. Our obsession with detail and historical accuracy is reflected in our exceptional design and production: hold a Wheels of Time model in your hand and you'll be tempted to say, 'It's the real thing!'
Item created by: Powderman on 2018-11-19 10:36:13. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-06-05 18:41:09
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.