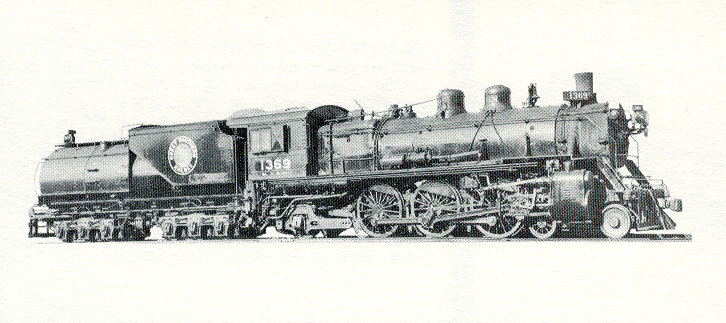
History: Among the first Pacifics to be delivered with superheaters, the Baldwin design betrays the industry's uncertainty about the best way to use the by-then clear benefits of hotter, drier steam. The H-4s were delivered with an unusually low boiler pressure setting, most likely to take advantage of the lesser strain on components that the more potent superheated steam appeared to allow.
Soon, however, the relatively weak thrust from these pistons led to a new tradeoff between boiler pressure and cylinder volume. Locobase 16276 shows the substantial makeover applied by the GN shops. The 1913 Lima batch (Locobase 3173) adopted much higher boiler pressure (210 psi/14.5 bar), but smaller 23 1/2" (597 mm) cylinders to retain a good factor of adhesion. These were served by 12" (305 mm) piston valves. If they hadn't been modified by then, Baldwin's locomotives followed suit within a year.
One document describes the road over which these engines ran, noting that one 129-mile section had a maximum grade of 1% and that the Pacifics averaged 30 mph (48 kph) with 11-12 cars over that section.
Soon, however, the relatively weak thrust from these pistons led to a new tradeoff between boiler pressure and cylinder volume. Locobase 16276 shows the substantial makeover applied by the GN shops. The 1913 Lima batch (Locobase 3173) adopted much higher boiler pressure (210 psi/14.5 bar), but smaller 23 1/2" (597 mm) cylinders to retain a good factor of adhesion. These were served by 12" (305 mm) piston valves. If they hadn't been modified by then, Baldwin's locomotives followed suit within a year.
One document describes the road over which these engines ran, noting that one 129-mile section had a maximum grade of 1% and that the Pacifics averaged 30 mph (48 kph) with 11-12 cars over that section.
Railroad/Company: The Baldwin Locomotive Works was an American builder of railroad locomotives. It was originally located in Philadelphia, and later moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania. Although the company was very successful as the largest producer of steam locomotives, its transition to the production of diesels was far less so. Later, when the early demand for diesel locomotives to replace steam tapered off, Baldwin could not compete in the marketplace. It stopped producing locomotives in 1956 and went out of business in 1972, having produced over 70,000 locomotives, the vast majority powered by steam.
In 1956, after 125 years of continuous locomotive production, Baldwin closed most of its Eddystone plant and ceased producing locomotives. The company instead concentrated on production of heavy construction equipment. More than 70,500 locomotives had been built when production ended. In 1965 Baldwin became a wholly owned subsidiary of Armour and Company. Greyhound Corporation purchased Armour and Company in 1970, and in 1972 Greyhound closed Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton for good.
From Wikipedia
In 1956, after 125 years of continuous locomotive production, Baldwin closed most of its Eddystone plant and ceased producing locomotives. The company instead concentrated on production of heavy construction equipment. More than 70,500 locomotives had been built when production ended. In 1965 Baldwin became a wholly owned subsidiary of Armour and Company. Greyhound Corporation purchased Armour and Company in 1970, and in 1972 Greyhound closed Baldwin-Lima-Hamilton for good.
From Wikipedia
Item Links: We found: 1 different collections associated with Rail - Locomotive - 4-6-2, Pacific H4
- Collection N Scale Model Trains: 2 different items.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-10-19 18:20:56
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.