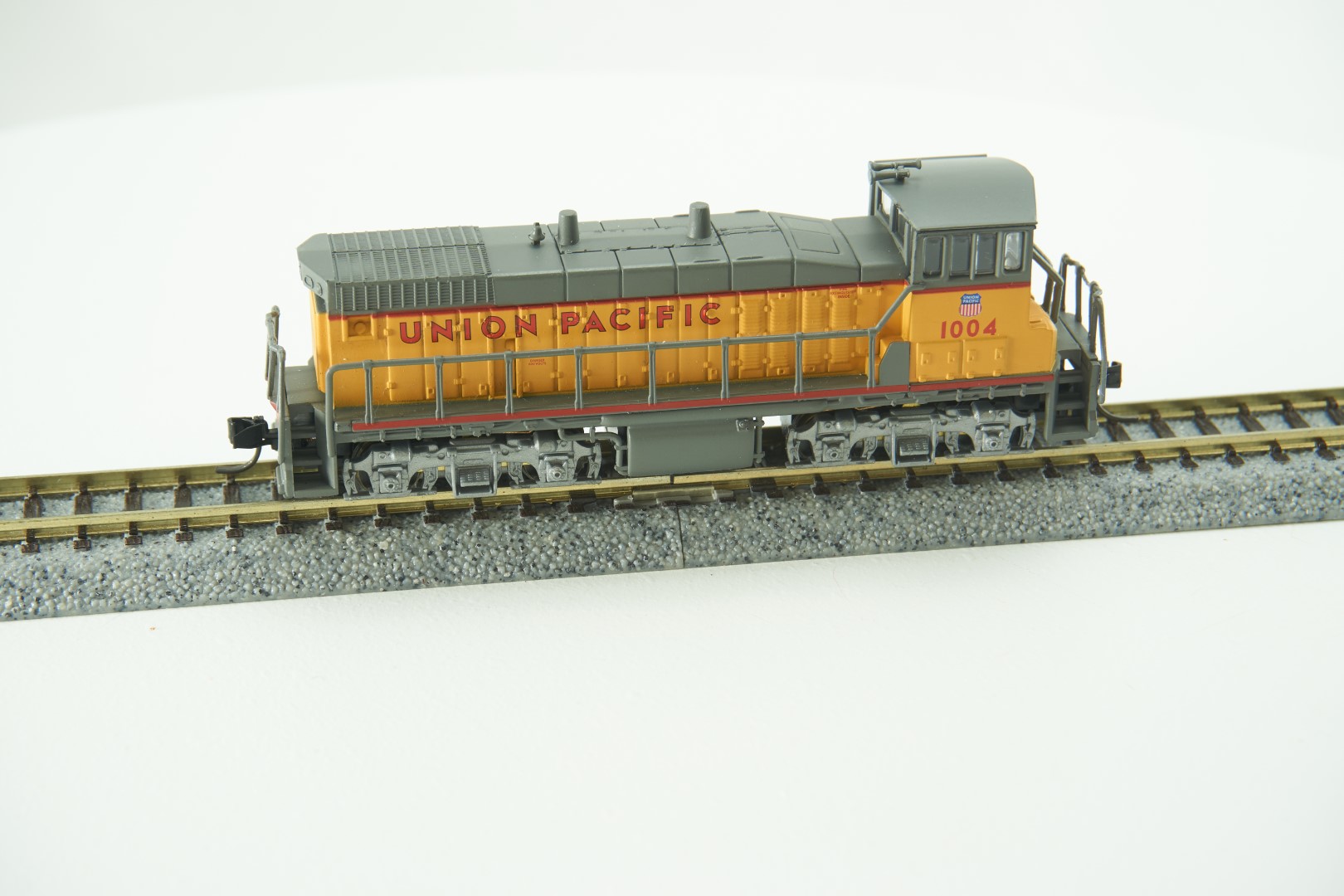
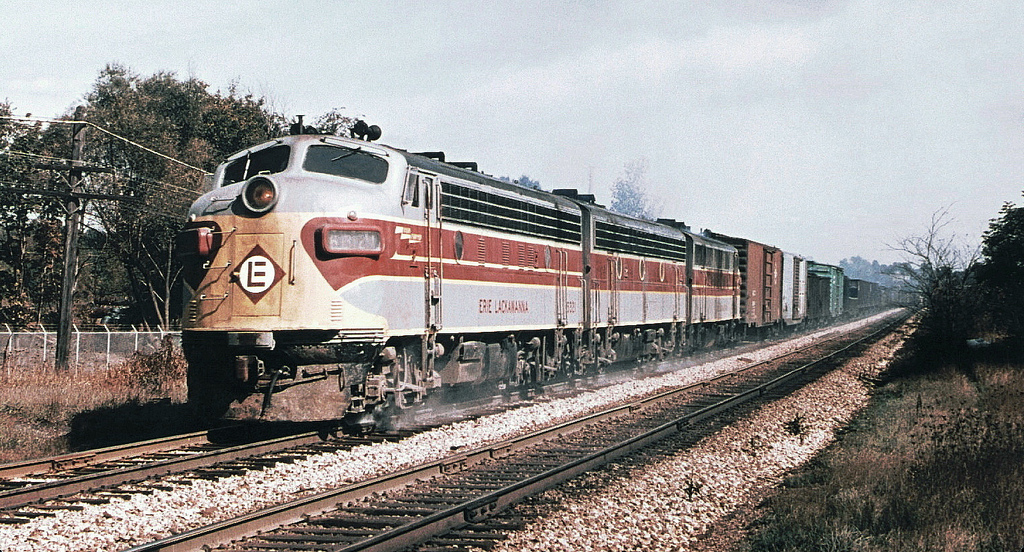
Prototype History: A freight train or goods train is a group of freight cars (US) or goods wagons (International Union of Railways) hauled by one or more locomotives on a railway, transporting cargo all or some of the way between the shipper and the intended destination as part of the logistics chain. Trains may haul bulk material, intermodal containers, general freight or specialized freight in purpose-designed cars. Rail freight practices and economics vary by country and region.
Diesel engines during the transition era were relatively primitive compared to their modern equivalents. Canada, Mexico and the United States are connected by an extensive, unified standard gauge rail network. Partially from Wikipedia
Diesel engines during the transition era were relatively primitive compared to their modern equivalents. Canada, Mexico and the United States are connected by an extensive, unified standard gauge rail network. Partially from Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: Lone Star was founded by Aubrey Robert Mills and Sidney James Ambridge in 1939 as the toy division of Die Casting Machine Tools Ltd. (DCMT) of London. DCMT was manufacturing diecasting machines and equipment. DCMT had made some toy cars for Crescent, and diecast toy cap-firing guns, which DCMT supplied under the "Lone Star" brand. "Lone Star" was a name that conjured up images of the Wild West, and while it was a reference to the Texas state flag (with its single star), the name also reminded children of the star-shaped Sheriff's badge that was often a key part of a cowboy costume.
Lone Star Locos appeared in the late 1950s as a range of fairly basic 000-scale diecast miniature trains and track, and were joined in the 1960s by the comparatively short-lived "Treble-O-Lectric" range of "proper" motorised 000-scale electric train sets. The motorised range was discontinued circa 1965. DCMT ceased its operation circa 1988.
The Lone Star Treble-O (triple O) rolling stock was scaled to 2mm to the foot (1:152) and track's gauge was 9mm.
Lone Star paved the way to the N scale model trains that would be soon after introduced by Arnold Rapido.
Read more on Irwin's Journal and on The Brighton Toy and Model Index.
Lone Star Locos appeared in the late 1950s as a range of fairly basic 000-scale diecast miniature trains and track, and were joined in the 1960s by the comparatively short-lived "Treble-O-Lectric" range of "proper" motorised 000-scale electric train sets. The motorised range was discontinued circa 1965. DCMT ceased its operation circa 1988.
The Lone Star Treble-O (triple O) rolling stock was scaled to 2mm to the foot (1:152) and track's gauge was 9mm.
Lone Star paved the way to the N scale model trains that would be soon after introduced by Arnold Rapido.
Read more on Irwin's Journal and on The Brighton Toy and Model Index.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-09-26 08:58:01. Last edited by gdm on 2020-06-20 05:43:13
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.