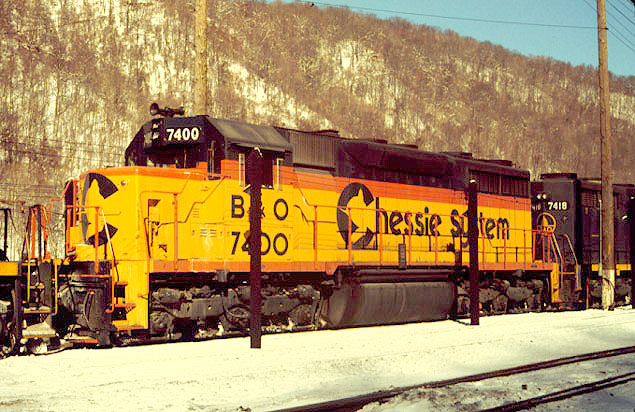
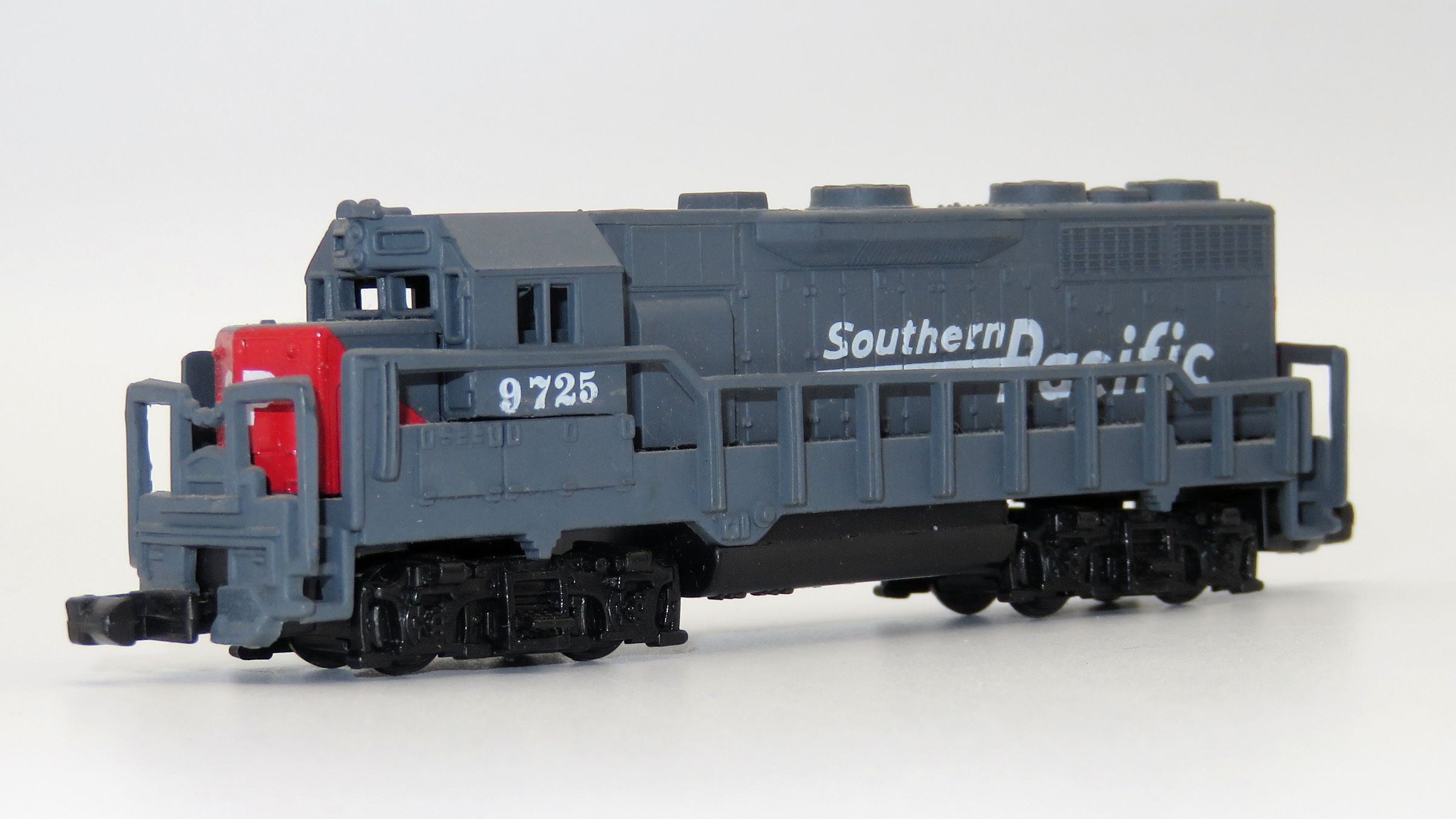
History: The EMD SD35 was one of the builder's first second-generation models, released during the mid-1960s. While the locomotive was not as successful as some of its other designs it did sell a few hundred examples during an era when railroads were only starting to realize the benefits of six-axle power. New features of the SD35, which dated back to the SD28 of 1965 was a redesigned frame and new Spartan Cab, commonly known as the standard cab. While EMD was experiencing growing competition from General Electric it was still in its prime and would make another run of phenomenal success during this time with models like the GP35, GP38 series, SD40 series, and others. About a dozen major railroads purchased the SD35 and a number of these remain in service. One example is known to be formally preserved, Baltimore & Ohio #7402 at the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad Museum, as well as the variant SDP35, Seaboard Air Line #1114 in Hamlet, North Carolina.
Between 1964 and 1966, EMD built a total of 360 six-axle 2,500hp SD35 locomotives. An additional 35 steam generator-equipped SDP35 locomotives were also built during this period. These were all part of EMD’s “35-Series” which also featured the four-axle, 2,250hp GP35 locomotive. All locomotives included the standard EMD 567-series prime mover. A stock model weighed 360,000 pounds, but many roads chose to add weight to increase the locomotive’s tractive effort. From the mid-1960s through the 1980s, the SD-35 could be found in road service on both large and mid-sized roads across the US. Today the number of active units has dwindled to a select few, including those operated by regional railroad Montana Rail Link. From American-Rails and Atlas.
Between 1964 and 1966, EMD built a total of 360 six-axle 2,500hp SD35 locomotives. An additional 35 steam generator-equipped SDP35 locomotives were also built during this period. These were all part of EMD’s “35-Series” which also featured the four-axle, 2,250hp GP35 locomotive. All locomotives included the standard EMD 567-series prime mover. A stock model weighed 360,000 pounds, but many roads chose to add weight to increase the locomotive’s tractive effort. From the mid-1960s through the 1980s, the SD-35 could be found in road service on both large and mid-sized roads across the US. Today the number of active units has dwindled to a select few, including those operated by regional railroad Montana Rail Link. From American-Rails and Atlas.
Railroad/Company: Electro-Motive Diesel (EMD) is an American manufacturer of diesel-electric locomotives, locomotive products and diesel engines for the rail industry. The company is owned by Caterpillar through its subsidiary Progress Rail Services Corporation.
Electro-Motive Diesel traces its roots to the Electro-Motive Engineering Corporation, a designer and marketer of gasoline-electric self-propelled rail cars founded in 1922 and later renamed Electro-Motive Company (EMC). In 1930, General Motors purchased Electro-Motive Company and the Winton Engine Co., combining the two to form its Electro-Motive Division (EMD) in 1941.
In 2005, GM sold EMD to Greenbriar Equity Group and Berkshire Partners, which formed Electro-Motive Diesel to facilitate the purchase. In 2010, Progress Rail Services completed the purchase of Electro-Motive Diesel from Greenbriar, Berkshire, and others.
EMD's headquarters, engineering facilities and parts manufacturing operations are based in McCook, Illinois, while its final locomotive assembly line is located in Muncie, Indiana. EMD also operates a traction motor maintenance, rebuild and overhaul facility in San Luis Potosí, Mexico.
As of 2008, EMD employed approximately 3,260 people, and in 2010 it held approximately 30 percent of the market for diesel-electric locomotives in North America.
From Wikipedia
Electro-Motive Diesel traces its roots to the Electro-Motive Engineering Corporation, a designer and marketer of gasoline-electric self-propelled rail cars founded in 1922 and later renamed Electro-Motive Company (EMC). In 1930, General Motors purchased Electro-Motive Company and the Winton Engine Co., combining the two to form its Electro-Motive Division (EMD) in 1941.
In 2005, GM sold EMD to Greenbriar Equity Group and Berkshire Partners, which formed Electro-Motive Diesel to facilitate the purchase. In 2010, Progress Rail Services completed the purchase of Electro-Motive Diesel from Greenbriar, Berkshire, and others.
EMD's headquarters, engineering facilities and parts manufacturing operations are based in McCook, Illinois, while its final locomotive assembly line is located in Muncie, Indiana. EMD also operates a traction motor maintenance, rebuild and overhaul facility in San Luis Potosí, Mexico.
As of 2008, EMD employed approximately 3,260 people, and in 2010 it held approximately 30 percent of the market for diesel-electric locomotives in North America.
From Wikipedia
Item Links: We found: 1 different collections associated with Rail - Locomotive - EMD SD35
- Collection N Scale Model Trains: 284 different items.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-01-31 09:49:35. Last edited by gdm on 2018-08-14 08:10:10
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.