DCC Information: NEM-651 6-pin decoder socket present.
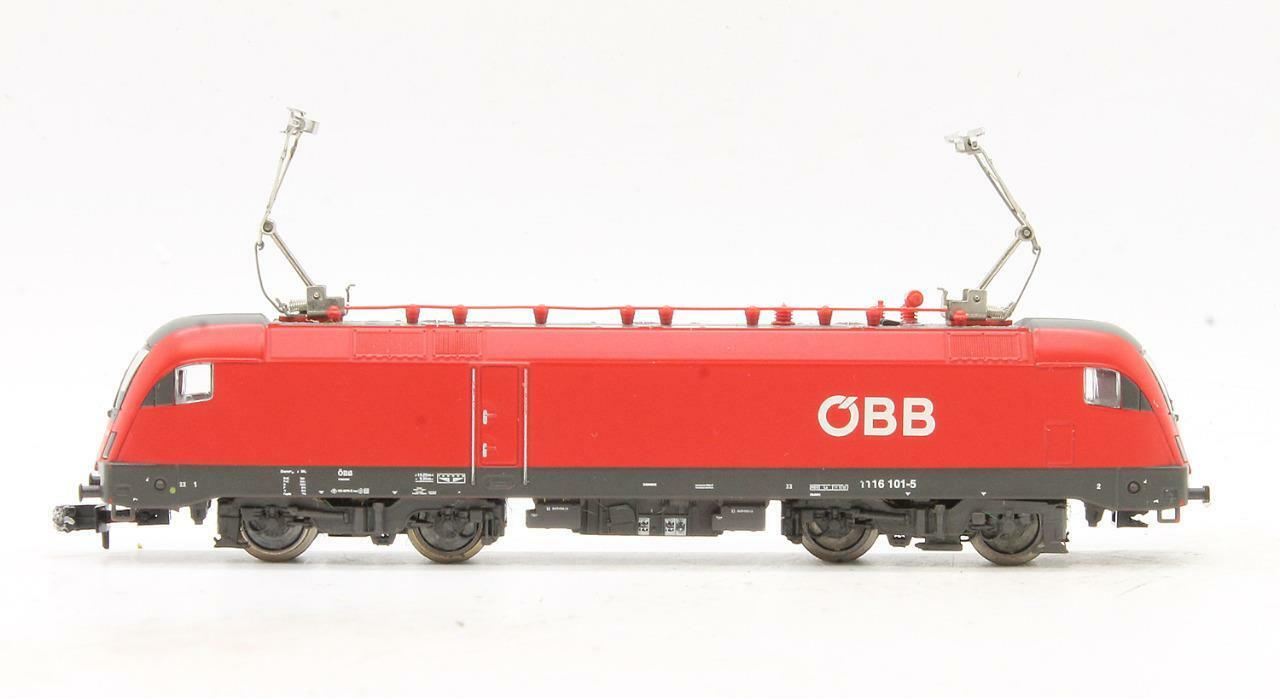
Prototype History: Based on the Siemens Eurosprinter concept, the ES 64 U was developed as a universal electric locomotive with a top speed of 230 km/h (140 mph). The ÖBB assigned the protected name Taurus to Class 1016 (and later to the Classes 1116 and 1216); since then all ES 64 U+ series are widely known as 'Taurus' locos.
The locomotives of this type are multi-system electric locomotives of the latest generation, which can be used for heavy freight traffic and the fast travel across borders. They currently operate in Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech republic, Germany, Italy, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland.
They have been produced in three different variants:
U64U - ÖBB BR 1016 - only operating on 15 kV 16 2/3 Hz AC supply in Austria.
Built: 1999–2006 - more than 300 produced for ÖBB (combined with BR 1116)
U64U2 - ÖBB BR 1116 - can also operate on 25 kV 50 Hz AC.
- also referred to as (Germany) Deutsche Bahn AG Class 182, (Hungary) MÁV Class 470, GySEV Class 1047
Built: 1999–2006 - more than 300 produced for ÖBB (combined with BR 1016)
U64U4 - ÖBB BR 1216 - can operate under 4 different 3-phase supplies.
- also referred to as (Slovenia) Slovenske železnice (SŽ) Class 541, (Poland) PKP Intercity (PKP IC) Class EU44 "Husarz", (Italy) FS E 190.
Built: 2005–2011 - initial order of 50 by ÖBB
On 2 September 2006 the locomotive 1216 025-7 (prior to delivery to ÖBB) set a new world record for conventional electric locomotives, when, during the trials near Nürnberg, it reached a top speed of 357 km/h (222 mph).
The locomotive was not modified for the record. Since then, this type has become the fastest locomotive in the world.
From Wikipedia
Read more (in German) about ES64U2 and ES64U4
The locomotives of this type are multi-system electric locomotives of the latest generation, which can be used for heavy freight traffic and the fast travel across borders. They currently operate in Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech republic, Germany, Italy, Hungary, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia and Switzerland.
They have been produced in three different variants:
U64U - ÖBB BR 1016 - only operating on 15 kV 16 2/3 Hz AC supply in Austria.
Built: 1999–2006 - more than 300 produced for ÖBB (combined with BR 1116)
U64U2 - ÖBB BR 1116 - can also operate on 25 kV 50 Hz AC.
- also referred to as (Germany) Deutsche Bahn AG Class 182, (Hungary) MÁV Class 470, GySEV Class 1047
Built: 1999–2006 - more than 300 produced for ÖBB (combined with BR 1016)
U64U4 - ÖBB BR 1216 - can operate under 4 different 3-phase supplies.
- also referred to as (Slovenia) Slovenske železnice (SŽ) Class 541, (Poland) PKP Intercity (PKP IC) Class EU44 "Husarz", (Italy) FS E 190.
Built: 2005–2011 - initial order of 50 by ÖBB
On 2 September 2006 the locomotive 1216 025-7 (prior to delivery to ÖBB) set a new world record for conventional electric locomotives, when, during the trials near Nürnberg, it reached a top speed of 357 km/h (222 mph).
The locomotive was not modified for the record. Since then, this type has become the fastest locomotive in the world.
From Wikipedia
Read more (in German) about ES64U2 and ES64U4
Road Name History:  The Austrian Federal Railways (German: Österreichische Bundesbahnen or ÖBB, formerly the Bundesbahn Österreich or BBÖ) is the national railway system of Austria, and the administrator of Liechtenstein's railways. The ÖBB group is owned entirely by the Republic of Austria and is divided into several separate businesses that manage the infrastructure and operate passenger and freight services.
The Austrian Federal Railways (German: Österreichische Bundesbahnen or ÖBB, formerly the Bundesbahn Österreich or BBÖ) is the national railway system of Austria, and the administrator of Liechtenstein's railways. The ÖBB group is owned entirely by the Republic of Austria and is divided into several separate businesses that manage the infrastructure and operate passenger and freight services.
The Austrian Federal Railways has had two discrete periods of existence. It was first formed in 1923, using the Bundesbahn Österreich name, as a successor to the Imperial Royal Austrian State Railways (kkStB), but was incorporated into the Deutsche Reichsbahn during the 1938-1945 Anschluss. It was reformed in 1947, using the slightly different Österreichische Bundesbahnen name, and remains in existence in this form.
Major changes currently being made to the Austrian railway network are the construction of the Wien Hauptbahnhof (Vienna main station), the Koralm Railway, the Semmering Base Tunnel and the Brenner Base Tunnel connection with Italy.
From Wikipedia

The Austrian Federal Railways has had two discrete periods of existence. It was first formed in 1923, using the Bundesbahn Österreich name, as a successor to the Imperial Royal Austrian State Railways (kkStB), but was incorporated into the Deutsche Reichsbahn during the 1938-1945 Anschluss. It was reformed in 1947, using the slightly different Österreichische Bundesbahnen name, and remains in existence in this form.
Major changes currently being made to the Austrian railway network are the construction of the Wien Hauptbahnhof (Vienna main station), the Koralm Railway, the Semmering Base Tunnel and the Brenner Base Tunnel connection with Italy.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: Trix is a German company that originally made Trix metal construction sets. one of its co-founders was Stephan Bing, the son of the pioneer toy-maker industrialist Ignaz Bing. In 1935 the company began producing the electrically powered model trains that it became famous for, under the Trix Express label. Prior to the outbreak of World War II the Trix company produced a small range of fairly unrealistic AC powered three rail models running at 14 volts.
N gauge models under the Minitrix brand were made from the late 1960s mostly of European prototypes (German and British primarily). North American prototypes were also manufactured and marketed under the Aurora "Postage Stamp" brand; later these items were sold under the American Tortoise, Model Power and Con-Cor brands. Trix sometimes utilized North American consultants to aid in the design of this portion of the product line. The "Hornby Minitrix' brand was used in the 1980s for a short lived range of British outline models using the earlier product tooling.
Trix's owner in the 1980s and 1990s was Mangold, which went bankrupt in the late 1990s and Märklin purchased the assets in January 1997. In part, this purchase was a reflection of Märklin's need for added production capacity; Trix had been manufacturing certain items for Märklin in previous years. The purchase was also in response to the earlier purchase of the Karl Arnold company by the Italian company Rivarossi; Märklin were very keen to take over Trix market share in 2-rail H0 and especially Minitrix, until then Märklin had not marketed N gauge models. In 2003, Märklin introduced its first N gauge models under the well established Minitrix brand. A number Märklin H0 scale three-rail AC locomotives have also been introduced in two-rail DC versions under the Trix logo and many models are shared between the two brands.
From Wikipedia
N gauge models under the Minitrix brand were made from the late 1960s mostly of European prototypes (German and British primarily). North American prototypes were also manufactured and marketed under the Aurora "Postage Stamp" brand; later these items were sold under the American Tortoise, Model Power and Con-Cor brands. Trix sometimes utilized North American consultants to aid in the design of this portion of the product line. The "Hornby Minitrix' brand was used in the 1980s for a short lived range of British outline models using the earlier product tooling.
Trix's owner in the 1980s and 1990s was Mangold, which went bankrupt in the late 1990s and Märklin purchased the assets in January 1997. In part, this purchase was a reflection of Märklin's need for added production capacity; Trix had been manufacturing certain items for Märklin in previous years. The purchase was also in response to the earlier purchase of the Karl Arnold company by the Italian company Rivarossi; Märklin were very keen to take over Trix market share in 2-rail H0 and especially Minitrix, until then Märklin had not marketed N gauge models. In 2003, Märklin introduced its first N gauge models under the well established Minitrix brand. A number Märklin H0 scale three-rail AC locomotives have also been introduced in two-rail DC versions under the Trix logo and many models are shared between the two brands.
From Wikipedia
Item created by: gdm on 2016-12-11 18:09:46. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-08-14 11:24:11
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.