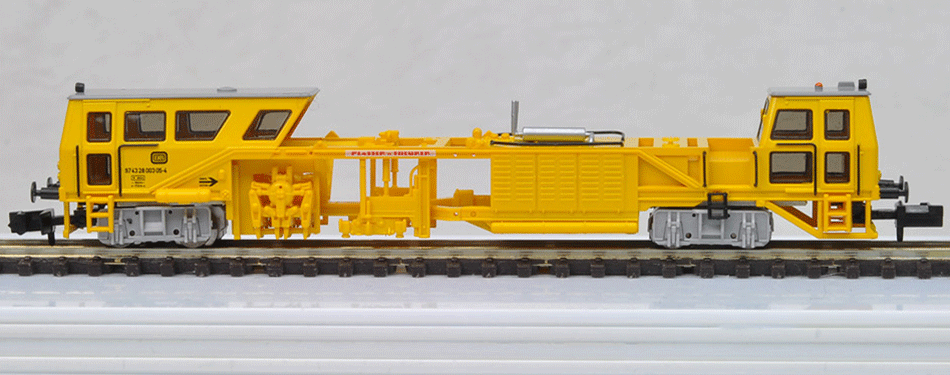
Model Information: Maintenance of Way Plasser & Theurer Duomatic 07-32 Multiple Tie Ballast Tamper. Factory assembled and decorated, with non-operating ballast tamper mechanisms, these models are motorized but have no lighting.
Although the German firm Lemke has partnered with Kato to produce European train models under the brand name Hobbytrain, the N-Scale Plasser & Theurer Duomatic 07-32 Ballast Tampers were not manufactured by Kato.
Although the German firm Lemke has partnered with Kato to produce European train models under the brand name Hobbytrain, the N-Scale Plasser & Theurer Duomatic 07-32 Ballast Tampers were not manufactured by Kato.
Prototype History: As they travel, trains generate enormous forces that will eventually change track geometry, which compromises both safety and ride comfort. To overcome this eventuality, the Austrian firm, Plasser & Theurer, developed its line of mechanized, hydraulic, measuring, track laying and railway maintenance of way leveling, lifting, lining and tamping machines.
Designed to produce stable road bed, using a squeezing movement, ballast tamping machines such as the Plasser & Theurer Duomatic, 07-32 utilize vibrating tamping tines to pack ballast underneath existing ties or sleepers.
Designed to produce stable road bed, using a squeezing movement, ballast tamping machines such as the Plasser & Theurer Duomatic, 07-32 utilize vibrating tamping tines to pack ballast underneath existing ties or sleepers.
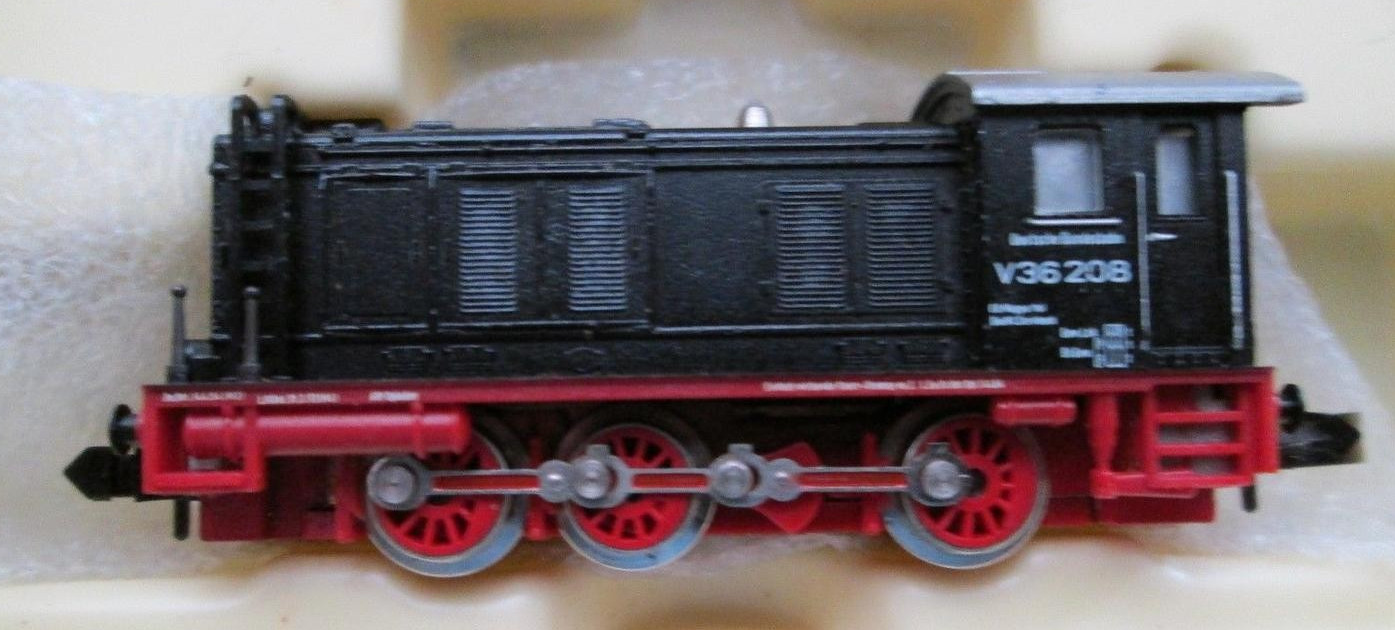
Road Name History:  Deutsche Bundesbahn was the Western Germany DB before reunification. After World War II, Germany (and the DRG) was divided into 4 zones: US, British, French and Soviet. The first three eventually combined to form the Federal Republic of Germany (the West) and the Russian zone became the German Democratic Republic (the East). German territories beyond the Oder were ceded to Poland except for the northern part of East Prussia, which was ceded to the Soviet Union in 1945.
Deutsche Bundesbahn was the Western Germany DB before reunification. After World War II, Germany (and the DRG) was divided into 4 zones: US, British, French and Soviet. The first three eventually combined to form the Federal Republic of Germany (the West) and the Russian zone became the German Democratic Republic (the East). German territories beyond the Oder were ceded to Poland except for the northern part of East Prussia, which was ceded to the Soviet Union in 1945.
From 1949, the new governments assumed authority for railway operations. The DRG's (or DR's) successors were named Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB, German Federal Railways) in West Germany, and Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR, German State Railways) in East Germany kept the old name to hold tracking rights in western Berlin.
Unlike the DRG, which was a corporation, both the DB and the DR were federal state institutions, directly controlled by their respective transportation ministries. Railway service between East and West was restricted; there were around five well-controlled and secure checkpoints between West and East Germany, and about the same number between East Germany and West Berlin. Four transit routes existed between West Germany and West Berlin; citizens of West Berlin and West Germany were able to use these without too much harassment by the East German authorities.
The DB started in 1968 with changing the locomotive and passenger car serial numbers to the UIC norm. In 1970 the DR followed. The DB started experimenting with the Intercity trains in a new livery (bright orange).
In 1989, the Wall fell. Train frequency rapidly increased on the existing East/West corridors; closed links which had formerly crossed the border were re-opened. On 3 October 1990, Germany was reunified; however, this was not immediately the case with the railways. Administrative and organisational problems led to the decision to completely re-organize and reconnect Germany's railways. The so-called Bahnreform (Railway Reform) came into effect on 1 January 1994, when the State railways Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Reichsbahn were formally reunited to form the current German Railway Corporation (Deutsche Bahn).
From Wikipedia

From 1949, the new governments assumed authority for railway operations. The DRG's (or DR's) successors were named Deutsche Bundesbahn (DB, German Federal Railways) in West Germany, and Deutsche Reichsbahn (DR, German State Railways) in East Germany kept the old name to hold tracking rights in western Berlin.
Unlike the DRG, which was a corporation, both the DB and the DR were federal state institutions, directly controlled by their respective transportation ministries. Railway service between East and West was restricted; there were around five well-controlled and secure checkpoints between West and East Germany, and about the same number between East Germany and West Berlin. Four transit routes existed between West Germany and West Berlin; citizens of West Berlin and West Germany were able to use these without too much harassment by the East German authorities.
The DB started in 1968 with changing the locomotive and passenger car serial numbers to the UIC norm. In 1970 the DR followed. The DB started experimenting with the Intercity trains in a new livery (bright orange).
In 1989, the Wall fell. Train frequency rapidly increased on the existing East/West corridors; closed links which had formerly crossed the border were re-opened. On 3 October 1990, Germany was reunified; however, this was not immediately the case with the railways. Administrative and organisational problems led to the decision to completely re-organize and reconnect Germany's railways. The so-called Bahnreform (Railway Reform) came into effect on 1 January 1994, when the State railways Deutsche Bundesbahn and Deutsche Reichsbahn were formally reunited to form the current German Railway Corporation (Deutsche Bahn).
From Wikipedia
Item created by: nscalemodeler160 on 2016-07-25 05:09:39. Last edited by Alain LM on 2019-04-22 16:41:17
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.