Specific Item Information: factory equipped with Digitrax DN136D
Model Information: This Rapido GMD-1 1000-series model features:
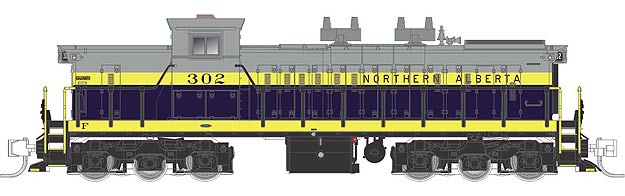
The 1000-series GMD-1 features A-1-A trucks to distribute its 120 tons over six axles and allow travel on light rail branches in the Prairies. The 1000-series GMD-1 was intended mainly for freight service, with its 65 MPH gearing and lack of a steam generator or pass-through steam lines. However, they could be used with Steam Generator Cars as their cabs were equipped with steam generator controls and blowdown buttons. All 78 1000-series GMD-1 locomotives were delivered between 1958 and 1960.
- N Scale DC/DCC dual mode (Digitrax factory decoder equipped) or equipped with an ESU DC/DCC/SOUND LokSound decoder
- Dummy plug included with silent models for optional straight DC operation
- 5-pole, skew-wound motor with excellent slow-speed performance
- Accurate dimensions from GMD blueprints and field measurements
- Heavy, die-cast chassis for great pulling power;
- Accurate 1000-series (6-axle) and 1600-series (rebuilt GMD-1A) variations
- A-1-A trucks with prototypically sized 40″ and 33″ wheels
- Full cab interior oriented the correct way (long hood forward for CN 1000-series, short hood forward for NAR and 1600-series)
- Body-mounted Micro-Trains couplers
- Up to six road numbers plus unnumbered for each paint scheme
- True GMD-1 sounds recorded from #1118 (formerly #1018) on the Alberta Prairie Railway
The 1000-series GMD-1 features A-1-A trucks to distribute its 120 tons over six axles and allow travel on light rail branches in the Prairies. The 1000-series GMD-1 was intended mainly for freight service, with its 65 MPH gearing and lack of a steam generator or pass-through steam lines. However, they could be used with Steam Generator Cars as their cabs were equipped with steam generator controls and blowdown buttons. All 78 1000-series GMD-1 locomotives were delivered between 1958 and 1960.
Prototype History: The GMD GMD-1 is a diesel locomotive originally produced by General Motors Diesel (GMD), the Canadian subsidiary of General Motors Electro-Motive Division, between August 1958 and April 1960. This switcher locomotive was powered by a 12-cylinder EMD 567C diesel engine, capable of producing 1,200 horsepower. The GMD-1 was built on either Flexicoil A1A-A1A (for light rail prairie branchlines) or Flexicoil B-B trucks. 101 examples of this locomotive were built for Canadian railways. 96 went to Canadian National Railway and the remaining 5 went to Northern Alberta Railways (that later became part of CN's fleet when they acquired majority interest in NAR).
The 1000-series GMD-1 features A-1-A trucks to distribute its 120 tons over six axles and allow travel on light rail branches in the Prairies. The 1000-series GMD-1 was intended mainly for freight service, with its 65 MPH gearing and lack of a steam generator or pass-through steam lines. However, they could be used with Steam Generator Cars as their cabs were equipped with steam generator controls and blowdown buttons. All 78 1000-series GMD-1 locomotives were delivered between 1958 and 1960.
The 1000-series GMD-1 features A-1-A trucks to distribute its 120 tons over six axles and allow travel on light rail branches in the Prairies. The 1000-series GMD-1 was intended mainly for freight service, with its 65 MPH gearing and lack of a steam generator or pass-through steam lines. However, they could be used with Steam Generator Cars as their cabs were equipped with steam generator controls and blowdown buttons. All 78 1000-series GMD-1 locomotives were delivered between 1958 and 1960.
Road Name History: NAR came together in 1929 when several railroads were combined under joint ownership of Canadian National and Canadian Pacific. One line ran from Edmonton, Alberta northeast to Lac La Biche and then Fort McMurray. The other line ran northwest from Edmonton to Smith where it turned west for Grande Prairie and ultimately to Dawson Creek just over the British Columbia border. A branch came off that main at McLennan north to Peace River then west to Hines Creek. Traffic on these lines was mostly grain.
In 1958, Pacific Great Eastern finished their line to Dawson Creek from the Pacific coast. This and new highways in the area syphoned traffic from NAR. In 1964, CN opened their isolated (from other CN lines) Great Slave Lake Railway from a junction on the NAR near Peace River to mines in the sub-Arctic region. This added considerable lead and zinc ore traffic to the NAR. Nevertheless, trains were infrequent on the NAR. With 923 route miles, NAR required just 21 diesels. The diesel fleet consisted of 10 GP9’s, 7 GMD1’s, and 4 SD38-2’s. To put that into perspective, the busy Clinchfield Railroad required nearly five times as many locomotives to run less than a third of the mileage.
In 1980, Canadian Pacific sold their half of NAR to Canadian National and on the first day of 1981, NAR operations were folded into CN.
In 1958, Pacific Great Eastern finished their line to Dawson Creek from the Pacific coast. This and new highways in the area syphoned traffic from NAR. In 1964, CN opened their isolated (from other CN lines) Great Slave Lake Railway from a junction on the NAR near Peace River to mines in the sub-Arctic region. This added considerable lead and zinc ore traffic to the NAR. Nevertheless, trains were infrequent on the NAR. With 923 route miles, NAR required just 21 diesels. The diesel fleet consisted of 10 GP9’s, 7 GMD1’s, and 4 SD38-2’s. To put that into perspective, the busy Clinchfield Railroad required nearly five times as many locomotives to run less than a third of the mileage.
In 1980, Canadian Pacific sold their half of NAR to Canadian National and on the first day of 1981, NAR operations were folded into CN.
Brand/Importer Information: Rapido Trains Inc. is a high-end manufacturer of model trains and accessories in HO, OO and N (North American 1:160 and British 1:148) scales. The firm's mission is to recreate the entire rail travel experience, from fully-detailed interiors and under-frames on models to fully-wired telephone poles for model railroads.
The name RAPIDO was introduced by Canadian National in 1965 to headline the railway's high-speed intercity passenger services. Until the mid-1980s, RAPIDO stood for fast schedules, frequent trains, and superb service.
Today, Rapido Trains continues the RAPIDO concept with state-of-the-art models and attention to fine detail. This company is not related to the venerable (and now defunct) German manufacturer Arnold Rapido, nor the present-day Arnold (which is owned by the United Kingdom's Hornby), Canadian based Rapido Trains was founded in 2003.
The name RAPIDO was introduced by Canadian National in 1965 to headline the railway's high-speed intercity passenger services. Until the mid-1980s, RAPIDO stood for fast schedules, frequent trains, and superb service.
Today, Rapido Trains continues the RAPIDO concept with state-of-the-art models and attention to fine detail. This company is not related to the venerable (and now defunct) German manufacturer Arnold Rapido, nor the present-day Arnold (which is owned by the United Kingdom's Hornby), Canadian based Rapido Trains was founded in 2003.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2016-07-16 09:09:13. Last edited by gdm on 2019-11-19 12:51:35
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.