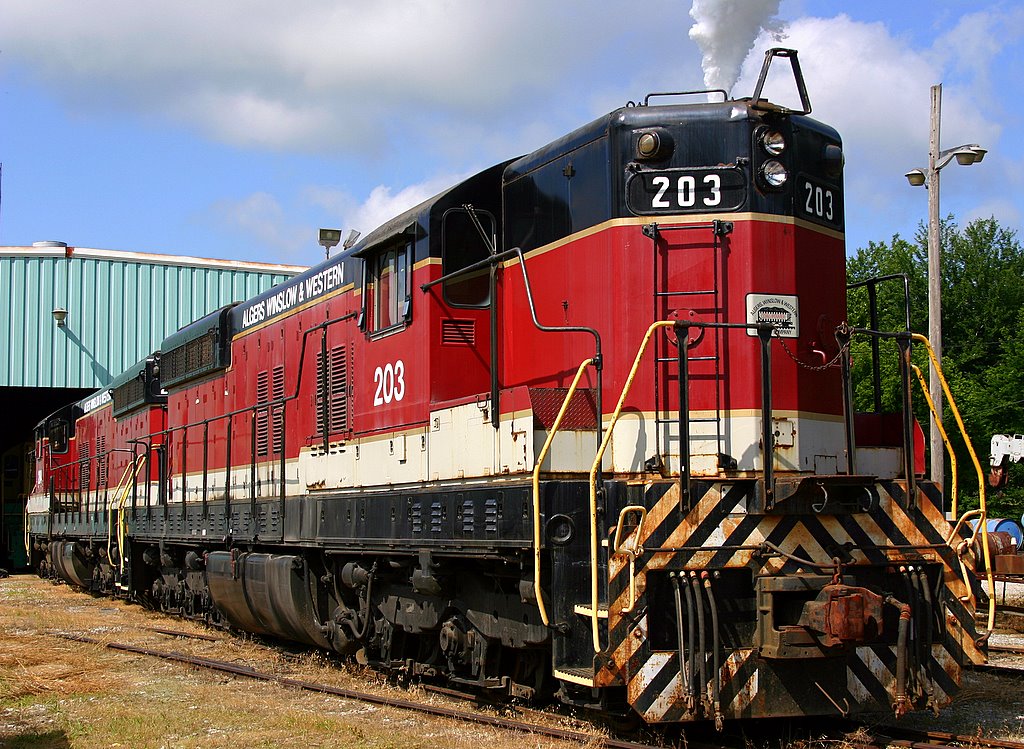
Model Information: The model was introduced in 1990 and the early releases were made by Kato Japan for Atlas. From 2004 on, the models were made in China and the internals were modified to a more modern mechanism. The Atlas SD7, SD9, SD24 and SD26 all share the same internal mechanism and differ only in their shell details. The modern releases fall under the "Classic" label for the SD7 and SD9 models and "Master" label for the SD24 and SD 26.
The early releases featured the Kato-designed "low friction drive" which had been successfully introduced in their Kato-branded U30C model). This design allowed clean transfer of current from wheels to long copper strips to the chassis and then to the lightboard. This may not sound innovative, as many modern mechanisms use this design today, but in 1990 it was a game-changer. The post-2004 releases are fairly standard "modern" mechanisms featuring a split-frame, dual-flywheels, and magnetic operating knuckle couplers. They run quiet and smooth and can pull 30 or more standard-weight cars.
The early releases featured the Kato-designed "low friction drive" which had been successfully introduced in their Kato-branded U30C model). This design allowed clean transfer of current from wheels to long copper strips to the chassis and then to the lightboard. This may not sound innovative, as many modern mechanisms use this design today, but in 1990 it was a game-changer. The post-2004 releases are fairly standard "modern" mechanisms featuring a split-frame, dual-flywheels, and magnetic operating knuckle couplers. They run quiet and smooth and can pull 30 or more standard-weight cars.
DCC Information: Models produced from 2006 are DCC Ready or Dual-Model Decoder Equipped. They accept the following drop-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A0: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale GP40-2, U25B, SD35, Trainmaster, B23-7 and others
- TCS AMD4 (Installation for Atlas SD-9)
- NCE N12A0: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas GP40-2, U25B, U23B, B23-7, 30-7, 36-7, GP38, SD25, TRAINMASTER, etc.
- MRC 1812: N-Scale Sound Decoder for most Atlas short/medium locos (selection of 4 prime movers - might not be prototypical for this model however)
Earlier DCC factory-equipped versions were fitted with Lenz LE063XF decoders, whereas most recent versions are fitted with NCE N12A0 decoders. The Atlas version of these decoders will respond to manufacturer's address "127" (CV8) i.e. "Atlas Model Railroad Products", though being identical to their original manufacturer's specification.
- Digitrax DN163A0: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale GP40-2, U25B, SD35, Trainmaster, B23-7 and others
- TCS AMD4 (Installation for Atlas SD-9)
- NCE N12A0: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas GP40-2, U25B, U23B, B23-7, 30-7, 36-7, GP38, SD25, TRAINMASTER, etc.
- MRC 1812: N-Scale Sound Decoder for most Atlas short/medium locos (selection of 4 prime movers - might not be prototypical for this model however)
Earlier DCC factory-equipped versions were fitted with Lenz LE063XF decoders, whereas most recent versions are fitted with NCE N12A0 decoders. The Atlas version of these decoders will respond to manufacturer's address "127" (CV8) i.e. "Atlas Model Railroad Products", though being identical to their original manufacturer's specification.
Prototype History: An SD9 is a 6-axle diesel locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between January 1954 and June 1959. An EMD 567C 16-cylinder engine generated 1,750 horsepower (1.30 MW). This model is, externally, similar to its predecessor, the SD7, but this model, internally, features the improved and much more maintainable 567C engine. The principal spotting feature are the classification lights on the ends of the locomotive, above the number board. The SD9's classification lights are on a small pod, canted outward. The last phase of construction had a carbody similar to the SD18 and SD24, and used two 48-inch (1,219 mm) cooling fans instead of four 36-inch (914 mm) cooling fans.
Four hundred and seventy-one SD9s were built for American railroads and 44 for export.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Full EMD SD9 data sheet on The Diesel Workshop.
Four hundred and seventy-one SD9s were built for American railroads and 44 for export.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Full EMD SD9 data sheet on The Diesel Workshop.
Road Name History: The Norfolk Southern Railway (reporting mark NS) is a Class I railroad in the United States; began in 1982 and 1990. With headquarters in Norfolk, Virginia, the company operates 36,200 route miles in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia, and has rights in Canada from Buffalo to Toronto and over the Albany to Montreal route. NS is responsible for maintaining 29,000 miles, with the remainder being operated under trackage rights from other parties responsible for maintenance. The common commodity hauled on the railroad is coal from mines in Indiana, Kentucky, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia. The railroad also offers the most intermodal network in eastern North America.
NS is a major transporter of domestic and export coal. The railroad's major sources of the mineral are located in: Pennsylvania's Cambria and Indiana counties, as well as the Monongahela Valley; West Virginia; and the Appalachia regions of Virginia, Kentucky, and Tennessee. In Pennsylvania, NS also receives coal through interchange with R.J. Corman Railroad/Pennsylvania Lines at Cresson, Pennsylvania, originating in the "Clearfield Cluster". NS's export of West Virginia bituminous coal, begins transport on portions of the well-engineered former Virginian Railway and the former N&W double-tracked line in Eastern Virginia to its Lambert's Point coal pier on Hampton Roads at Norfolk. Coal transported by NS is thus exported to steel mills and power plants around the world. The company is also a major transporter of auto parts and completed vehicles. It operates intermodal container and TOFC (trailer on flat car) trains, some in conjunction with other railroads. NS was the first railway to employ roadrailers, which are highway truck trailers with interchangeable wheel sets.
The Norfolk Southern Railway's parent Norfolk Southern Corporation is a Norfolk, Virginia-based parent company. Norfolk Southern Corporation was incorporated on July 23, 1980 in the Commonwealth of Virginia and is publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the symbols NSC. The primary business function of Norfolk Southern Corporation is the rail transportation of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished goods across the Southeast, East, and Midwest United States. The corporation further facilitates transport to the remainder of the United States through interchange with other rail carriers while also serving overseas transport needs by serving several Atlantic and Gulf Coast ports. As of October 1, 2014 Norfolk Southern Corporation's total public stock value was slightly over $34.5 billion.
Read more on Wikipedia.
NS is a major transporter of domestic and export coal. The railroad's major sources of the mineral are located in: Pennsylvania's Cambria and Indiana counties, as well as the Monongahela Valley; West Virginia; and the Appalachia regions of Virginia, Kentucky, and Tennessee. In Pennsylvania, NS also receives coal through interchange with R.J. Corman Railroad/Pennsylvania Lines at Cresson, Pennsylvania, originating in the "Clearfield Cluster". NS's export of West Virginia bituminous coal, begins transport on portions of the well-engineered former Virginian Railway and the former N&W double-tracked line in Eastern Virginia to its Lambert's Point coal pier on Hampton Roads at Norfolk. Coal transported by NS is thus exported to steel mills and power plants around the world. The company is also a major transporter of auto parts and completed vehicles. It operates intermodal container and TOFC (trailer on flat car) trains, some in conjunction with other railroads. NS was the first railway to employ roadrailers, which are highway truck trailers with interchangeable wheel sets.
The Norfolk Southern Railway's parent Norfolk Southern Corporation is a Norfolk, Virginia-based parent company. Norfolk Southern Corporation was incorporated on July 23, 1980 in the Commonwealth of Virginia and is publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the symbols NSC. The primary business function of Norfolk Southern Corporation is the rail transportation of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished goods across the Southeast, East, and Midwest United States. The corporation further facilitates transport to the remainder of the United States through interchange with other rail carriers while also serving overseas transport needs by serving several Atlantic and Gulf Coast ports. As of October 1, 2014 Norfolk Southern Corporation's total public stock value was slightly over $34.5 billion.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: Steve German on 2016-04-17 16:58:35
Last edited by: Alain LM on 2020-05-23 11:49:49
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
Last edited by: Alain LM on 2020-05-23 11:49:49
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.