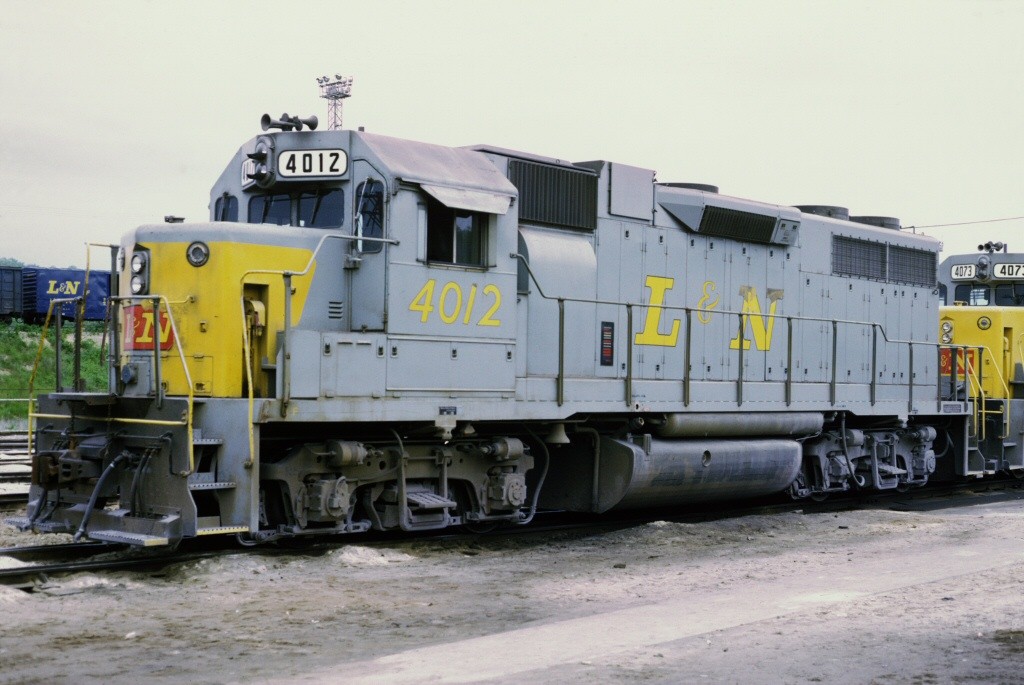
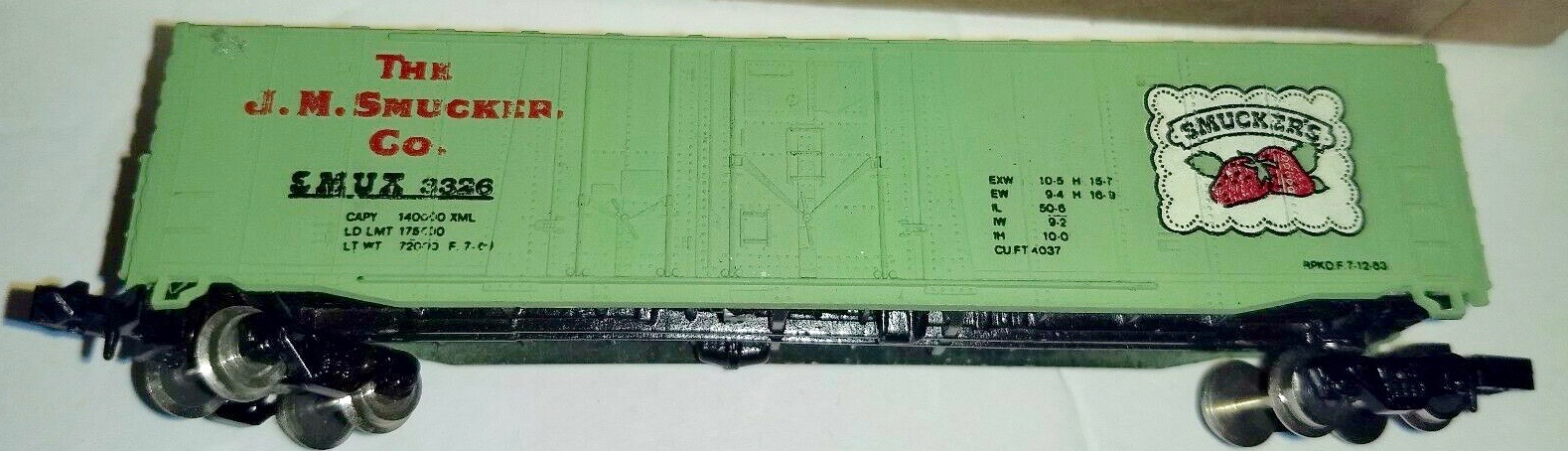
Model Information: The Atlas GP38 is made in China and has always been made in China. These mechanisms run fine but the first releases (1996) do not support drop in decoders. Both versions use a dual-flywheel, split frame chassis with a 5-Pole skew-wound motor.
DCC Information: Early Chinese versions are DCC-friendly requiring a complicated split-board DCC install. Later versions are DCC-Ready accepting a 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale GP40-2, U25B, SD35, Trainmaster, B23-7 and others (DN163A0) from digitrax.com. Unfortunately, the only way to tell which kind you have is to remove the shell and check the chassis. If it has two small lightboards, you have an old one in your hand. A single long lightboard indicates a DCC-Ready chassis.
As of the 2001 run, this model was also offered with factory-installed DCC decoder, first Lenz LE063XF and then (circa 2010s) a NCE decoder.
Since the 2018 run, it is only offered with ESU Loksound sound decoder without DCC no-sound option. So if you want a DCC no-sound, you'll need to install a decoder by yourself.
As of the 2001 run, this model was also offered with factory-installed DCC decoder, first Lenz LE063XF and then (circa 2010s) a NCE decoder.
Since the 2018 run, it is only offered with ESU Loksound sound decoder without DCC no-sound option. So if you want a DCC no-sound, you'll need to install a decoder by yourself.
Prototype History: The EMD GP38 is a 4-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between January 1966 and December 1971. The locomotive's power was provided by an EMD 645 16-cylinder engine which generated 2,000 horsepower (1.49 MW). The company built 706 GP38s for North American railroads. In 1972, it was replaced by an updated model, the GP38-2.
From Wikipedia
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: Ann Arbor was formed in 1895 to reorganize the bankrupt Toledo Ann Arbor & North Michigan. It ran from Toledo, Ohio through Ann Arbor, Michigan northwest to the coast of Lake Michigan at Frankfort. There, railroad car ferries forwarded the traffic to four ports across the lake. The rail portion was almost exactly 300 miles. Detroit Toledo & Ironton had control of the company between 1905 and 1910. In 1925, the Wabash took control of the Ann Arbor. As diesels began to arrive (mostly Alco FA's and RS1s) they came in Wabash blue, gray and white but with Ann Arbor lettering and a "marine" version of the flag on the nose. This is where it gets a bit complicated.
Wabash was controlled by the Pennsylvania Railroad who, in the early 60s, was planning their merger with the New York Central. They knew they would not be permitted to control Wabash through the merger and began arranging marriages to limit any negative impacts. They arranged for Wabash (whom they controlled) to be leased by Norfolk & Western (whom they didn't control but had considerable influence over) as part of N&W’s consolidation with Nickel Plate, Akron Canton & Youngstown, and Pittsburgh & West Virginia. For some reason, Ann Arbor was to stay in the PRR sphere and not go with the Wabash. So prior to that merger, Wabash sold the Ann Arbor to the Detroit Toledo & Ironton (whom PRR also controlled.) That was in 1963. At that point, AA traded in their blue, gray and white for DT&I orange with Ann Arbor lettering. As the 60s pressed on, demand for cross-lake ferry rail service dwindled until only the two Wisconsin routes remained. By 1972, AA was down to 15 locomotives. A year later, they declared bankruptcy. The line operated in receivership until April 1, 1976 which was Conrail's first day of operation. After a short time, Conrail announced that it wasn't interested in operating any AA route north of Ann Arbor, but the state of Michigan wanted to keep the road together. So Michigan Interstate took over as the designated operator of the Ann Arbor Railroad. “Michigan Interstate Railway Company Operator” lettering was applied to the short hoods of many AA locomotives. In 1982, all ferry operations ended and the following year AA was split between the Michigan Interstate, the Michigan Northern and the Tuscola & Saginaw Bay (later the Great Lakes Central.) Then in 1988, a new company bought the section from Toledo to Ann Arbor. That is the current "Ann Arbor Railroad." Ann Arbor joined the Watco shortline group in 2013.
The Ann Arbor Railroad owned a subsidiary, the Manistique and Lake Superior Railroad (M&LS), from somewhere shortly after that line's origin in 1909 until it was abandoned in 1968.
The Ann Arbor Railroad owned a subsidiary, the Manistique and Lake Superior Railroad (M&LS), from somewhere shortly after that line's origin in 1909 until it was abandoned in 1968.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: Steve German on 2016-04-11 19:32:56. Last edited by gdm on 2020-06-14 17:53:10
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.