Model Information: This is a very high quality model with all the features you would expect from a tooling made from 2010 on. It features: Die cast under frame for superior weight and tracking; Separate plastic under frame details; 100T trucks with Fox Valley metal wheels; Body mounted magnetic knuckle couplers; Detailed plastic body; Separate brake stand and brake wheel; and Etched metal grab irons, ladders, foot boards, stirrups, tow rings and retaining valve linkage.
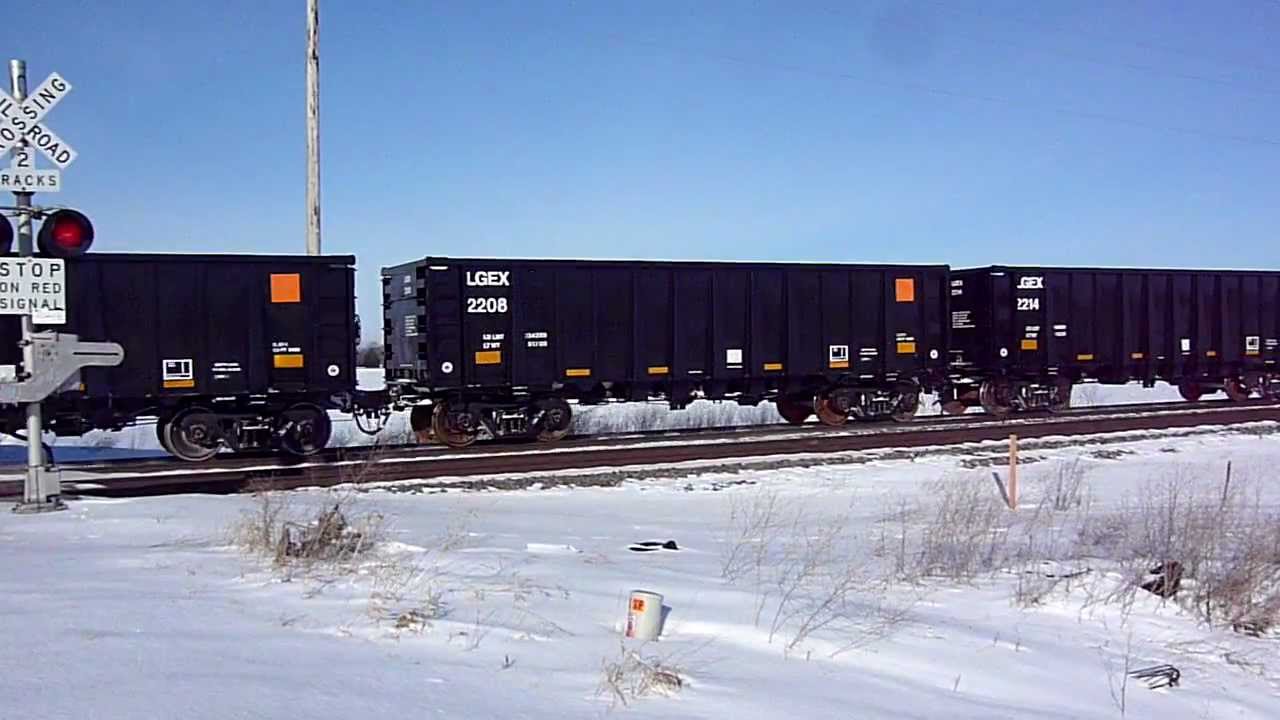
Prototype History: Thrall was a recognizable freight car manufacturing company in the 1960s to 1980s. Their designs still carry on today. The company focused on building specialized freight cars including high side gondolas, and rotary-dump gondolas for coal. In the 1980s, Thrall acquired five competing railcar manufacturers and became the largest such manufacturer of these cars in the United States.
In the 1960s, coal haulage shifted from open hopper cars to high-sided gondolas. Using a gondola, the railroads are able to haul a larger amount of coal per car since gondolas do not include the equipment needed for unloading. However, since these cars do not have hatches for unloading the products shipped in them, railroads must use rotary car dumpers (mechanisms that hold a car against a short section of track as the car and track are slowly rotated upside down to empty the car) or other means to empty them.
In the 1960s, coal haulage shifted from open hopper cars to high-sided gondolas. Using a gondola, the railroads are able to haul a larger amount of coal per car since gondolas do not include the equipment needed for unloading. However, since these cars do not have hatches for unloading the products shipped in them, railroads must use rotary car dumpers (mechanisms that hold a car against a short section of track as the car and track are slowly rotated upside down to empty the car) or other means to empty them.
Road Name History:  The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information:  Trainworx was founded in 1999 by Pat Sanders and is located in Delta Colorado. Their first freight car was the Quad hopper and it was released in 2000. They have been making N scale products ever since. Their website can be found at www.train-worx.com. As of 2016, they have produced 8 different rolling stock body styles as well as a range of different highway vehicles in N Scale. Their limited edition runs have proven a huge success with collectors and modelers enjoy the accuracy of all their products.
Trainworx was founded in 1999 by Pat Sanders and is located in Delta Colorado. Their first freight car was the Quad hopper and it was released in 2000. They have been making N scale products ever since. Their website can be found at www.train-worx.com. As of 2016, they have produced 8 different rolling stock body styles as well as a range of different highway vehicles in N Scale. Their limited edition runs have proven a huge success with collectors and modelers enjoy the accuracy of all their products.
Trainworx sells their products both through tradional retail channels as well as directly by phone order. When asked "What prompted you to found Trainworx?", Pat Sanders responded "There was a freight car that hadn't been done in N scale that I just had to have and it didn't look like anyone was ever going to make it."

Trainworx sells their products both through tradional retail channels as well as directly by phone order. When asked "What prompted you to found Trainworx?", Pat Sanders responded "There was a freight car that hadn't been done in N scale that I just had to have and it didn't look like anyone was ever going to make it."
Item created by: nscalestation on 2016-04-08 18:19:21. Last edited by gdm on 2021-02-16 07:38:07
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.