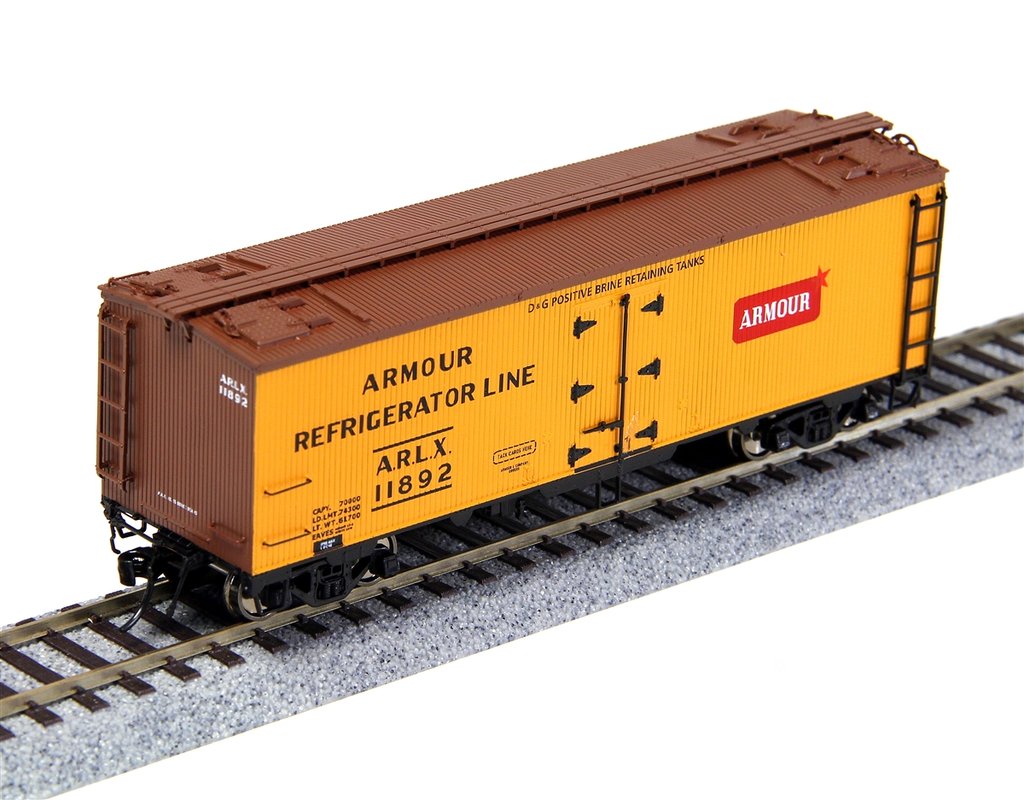
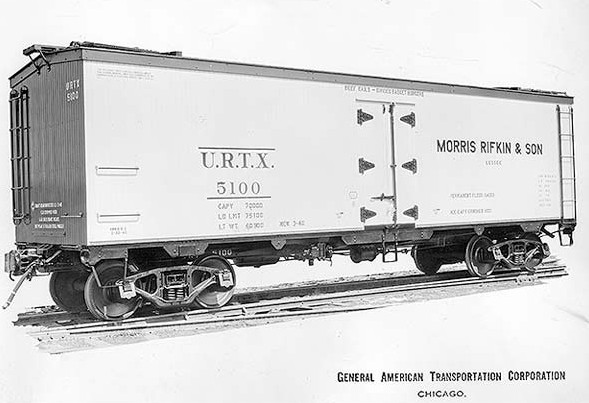
Model Information: This model was released in 2015 by Rapido Trains. This wood reefer is based on a design built between 1937 and 1941 by General American Transportation (GARX). Although built with a wooden sheathed body and roof that made them look like a car from an earlier era, these GARX cars were modern for their time.
Notable features of the General American meat reefer are wood body with three hinge doors (utilizing the GARX triangular hinge design), a wood roof with steel hatches and unique latches, side and end ladders, power handbrakes, and a steel underframe with a tabbed side sill. All of these features are included on the new Rapido model. Also found on the model is a FULL underframe with complete brake equipment, all new trucks with brake shoes in line with the wheel tread and new metal wheelsets. Micro-Trains couplers are fitted at the factory.
Notable features of the General American meat reefer are wood body with three hinge doors (utilizing the GARX triangular hinge design), a wood roof with steel hatches and unique latches, side and end ladders, power handbrakes, and a steel underframe with a tabbed side sill. All of these features are included on the new Rapido model. Also found on the model is a FULL underframe with complete brake equipment, all new trucks with brake shoes in line with the wheel tread and new metal wheelsets. Micro-Trains couplers are fitted at the factory.
Prototype History: During the mid-19th century, attempts were made to ship agricultural products by rail. As early as 1842, the Western Railroad of Massachusetts was reported in the June 15 edition of the Boston Traveler to be experimenting with innovative freight car designs capable of carrying all types of perishable goods without spoilage. The first refrigerated boxcar entered service in June 1851, on the Northern Railroad (New York) (or NRNY, which later became part of the Rutland Railroad). This "icebox on wheels" was a limited success since it was only functional in cold weather. That same year, the Ogdensburg and Lake Champlain Railroad (O&LC) began shipping butter to Boston in purpose-built freight cars, utilizing ice for cooling.
Between 1937 and 1941 by General American Transportation (GARX) built a specialized 37 foot meat reefer. Although built with a wooden sheathed body and roof that made them look like a car from an earlier era, these GARX cars were modern for their time. They were constructed on a steel under frame of similar construction to boxcar under frames then in common use and featured AB brakes, Equipco brake wheels and housings and Barber S-1 trucks. More than 940 cars were built to this configuration making it one of the most numerous meat reefer designs, and they lasted in service into the 1970s. They would normally be assigned to meat service only, running between meat packing houses and regional dealers throughout North America, Including Canada.
Notable features of the General American meat reefer are wood body with three hinge doors (utilizing the GARX triangular hinge design), a wood roof with steel hatches and unique latches, side and end ladders, power handbrakes, and a steel under frame with a tabbed side sill.
Between 1937 and 1941 by General American Transportation (GARX) built a specialized 37 foot meat reefer. Although built with a wooden sheathed body and roof that made them look like a car from an earlier era, these GARX cars were modern for their time. They were constructed on a steel under frame of similar construction to boxcar under frames then in common use and featured AB brakes, Equipco brake wheels and housings and Barber S-1 trucks. More than 940 cars were built to this configuration making it one of the most numerous meat reefer designs, and they lasted in service into the 1970s. They would normally be assigned to meat service only, running between meat packing houses and regional dealers throughout North America, Including Canada.
Notable features of the General American meat reefer are wood body with three hinge doors (utilizing the GARX triangular hinge design), a wood roof with steel hatches and unique latches, side and end ladders, power handbrakes, and a steel under frame with a tabbed side sill.
Road Name History:  The Armour Refrigerator Line (ARL, one of the Armour Car Lines) was a private refrigerator car line established in 1883 by Chicago meat packer Philip Armour, the founder of Armour and Company.
The Armour Refrigerator Line (ARL, one of the Armour Car Lines) was a private refrigerator car line established in 1883 by Chicago meat packer Philip Armour, the founder of Armour and Company.
To get his products to market, Armour followed the lead of rivals George Hammond and Gustavus Swift when he established the Armour Refrigerator Line in 1883. Armour's endeavor soon became the largest private refrigerator car fleet in America. By 1900, the company listed over 12,000 units on its roster (one-third of all the privately owned cars in the country), all built in Armour's own car plant.
One of the Armour Car Lines' subsidiaries was dedicated to produce hauling. In 1919 the Federal Trade Commission ordered the company's sale for anti-trust reasons. On March 18 of the following year the new entity, to be known as Fruit Growers Express (FGE), would take with it 4,280 pieces of rolling stock, repairs shops at Alexandria, Virginia and Jacksonville, Florida, and numerous ice plants and other facilities scattered throughout the East Coast.
The General American Transportation Corporation assumed ownership of the line in 1932.
From Wikipedia

To get his products to market, Armour followed the lead of rivals George Hammond and Gustavus Swift when he established the Armour Refrigerator Line in 1883. Armour's endeavor soon became the largest private refrigerator car fleet in America. By 1900, the company listed over 12,000 units on its roster (one-third of all the privately owned cars in the country), all built in Armour's own car plant.
One of the Armour Car Lines' subsidiaries was dedicated to produce hauling. In 1919 the Federal Trade Commission ordered the company's sale for anti-trust reasons. On March 18 of the following year the new entity, to be known as Fruit Growers Express (FGE), would take with it 4,280 pieces of rolling stock, repairs shops at Alexandria, Virginia and Jacksonville, Florida, and numerous ice plants and other facilities scattered throughout the East Coast.
The General American Transportation Corporation assumed ownership of the line in 1932.
From Wikipedia
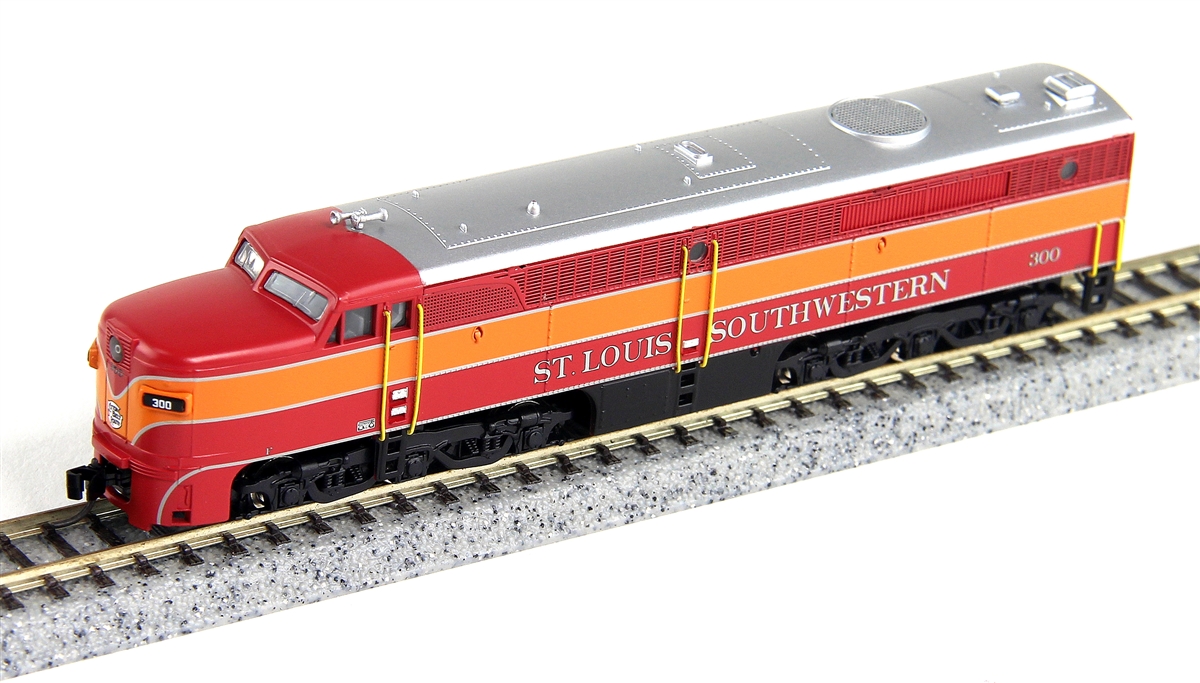
Brand/Importer Information: Rapido Trains Inc. is a high-end manufacturer of model trains and accessories in HO, OO and N (North American 1:160 and British 1:148) scales. The firm's mission is to recreate the entire rail travel experience, from fully-detailed interiors and under-frames on models to fully-wired telephone poles for model railroads.
The name RAPIDO was introduced by Canadian National in 1965 to headline the railway's high-speed intercity passenger services. Until the mid-1980s, RAPIDO stood for fast schedules, frequent trains, and superb service.
Today, Rapido Trains continues the RAPIDO concept with state-of-the-art models and attention to fine detail. This company is not related to the venerable (and now defunct) German manufacturer Arnold Rapido, nor the present-day Arnold (which is owned by the United Kingdom's Hornby), Canadian based Rapido Trains was founded in 2003.
The name RAPIDO was introduced by Canadian National in 1965 to headline the railway's high-speed intercity passenger services. Until the mid-1980s, RAPIDO stood for fast schedules, frequent trains, and superb service.
Today, Rapido Trains continues the RAPIDO concept with state-of-the-art models and attention to fine detail. This company is not related to the venerable (and now defunct) German manufacturer Arnold Rapido, nor the present-day Arnold (which is owned by the United Kingdom's Hornby), Canadian based Rapido Trains was founded in 2003.
Item created by: gdm on 2016-02-03 11:58:03. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-06-03 20:39:08
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.