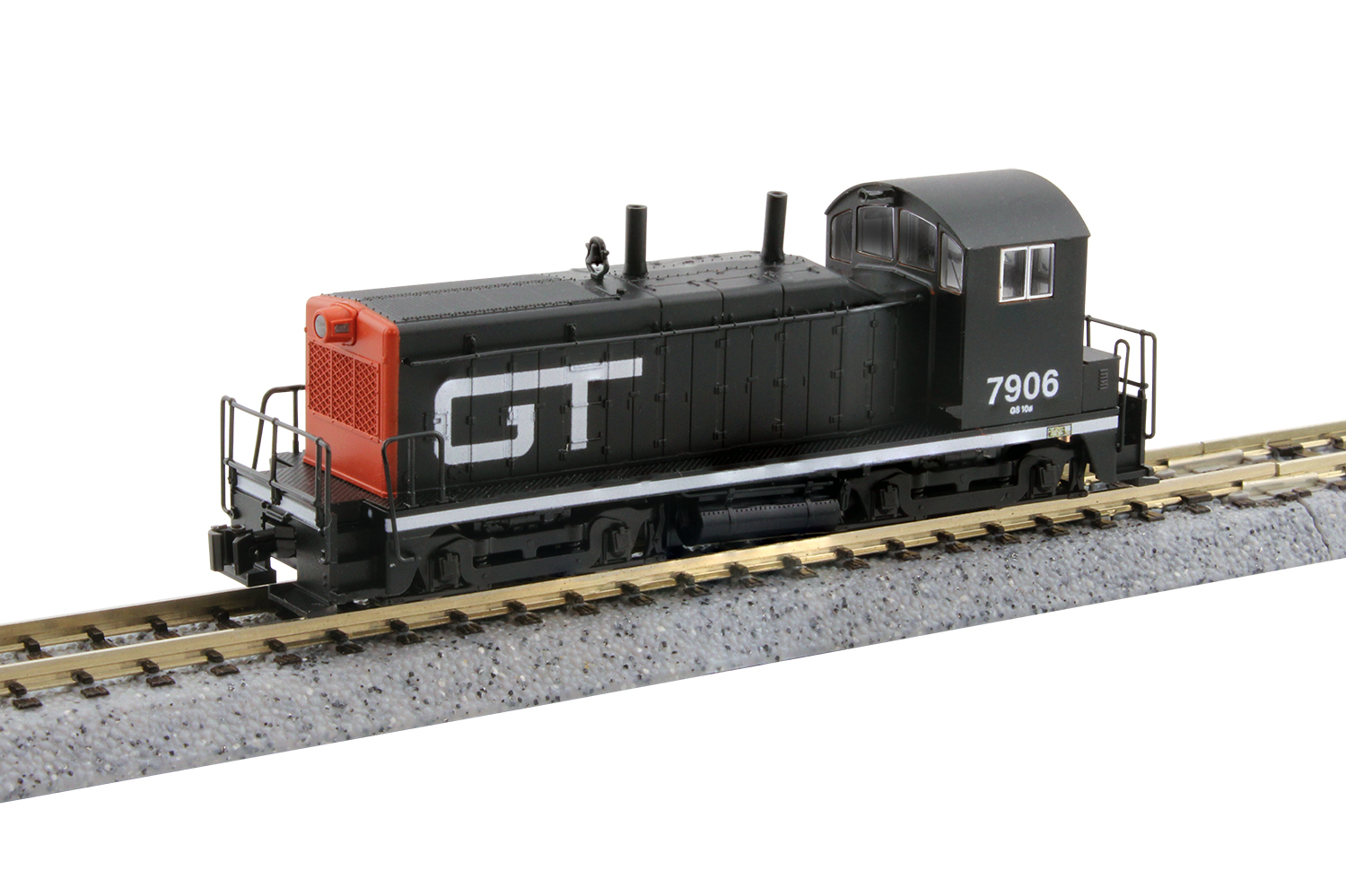
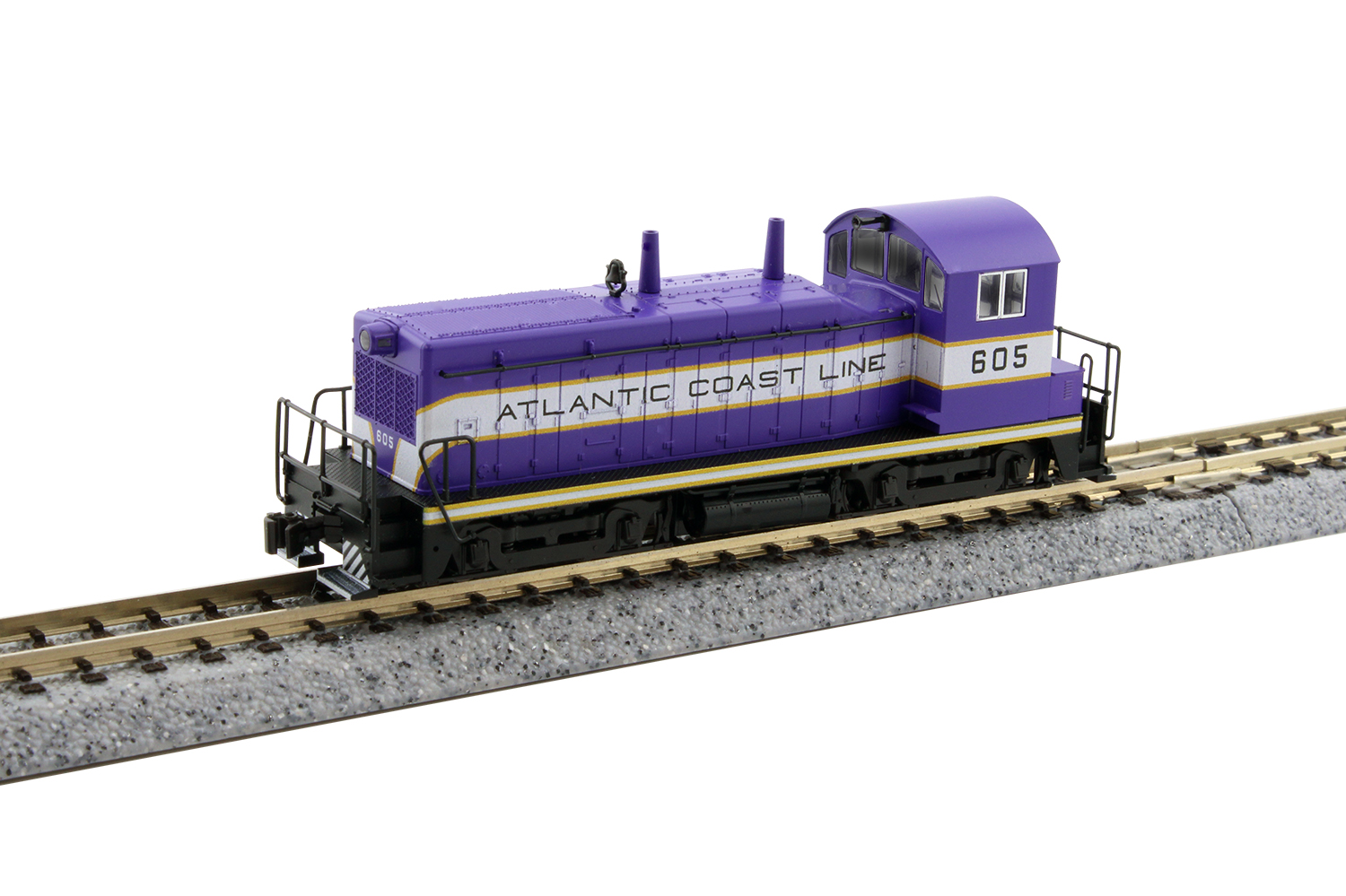
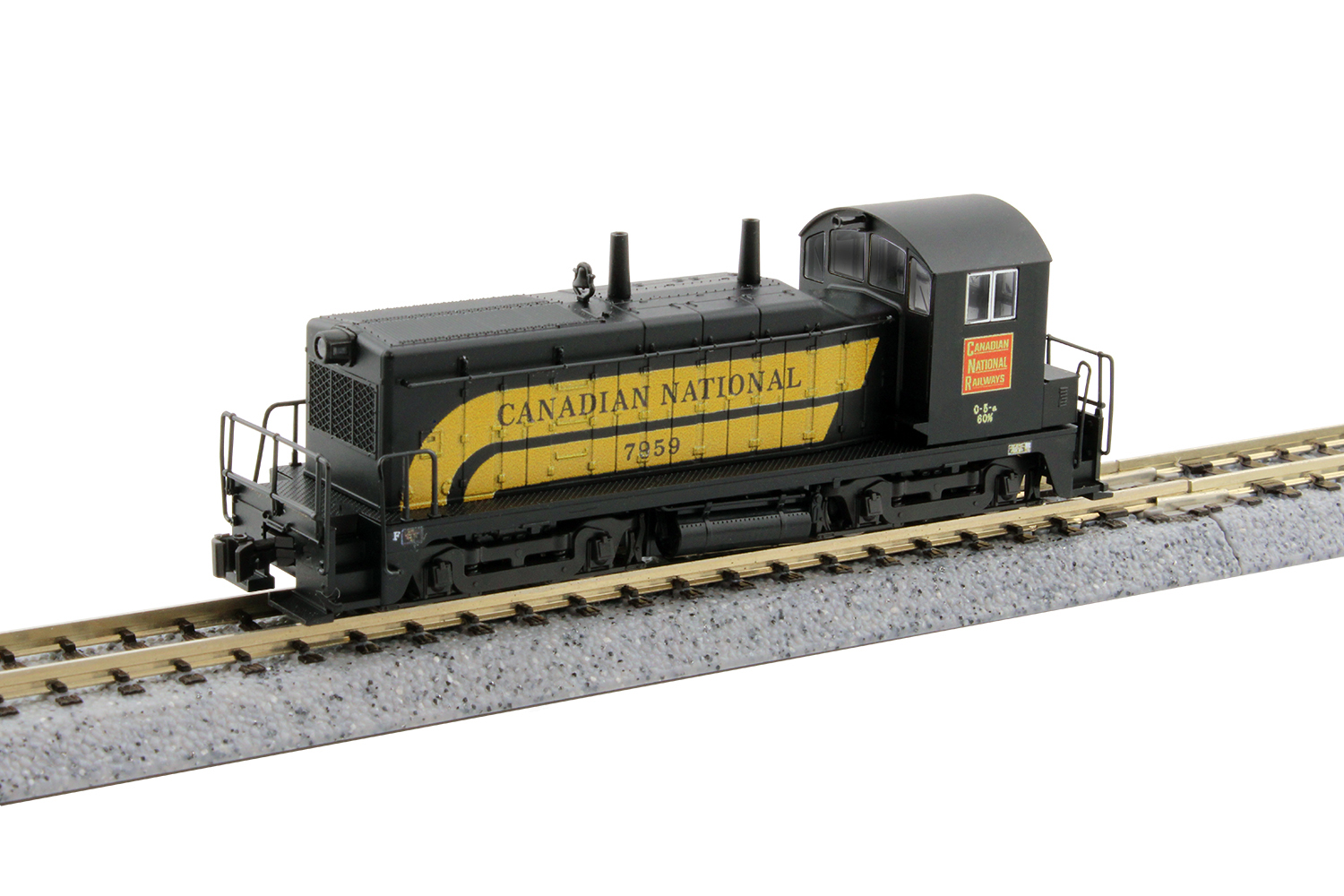
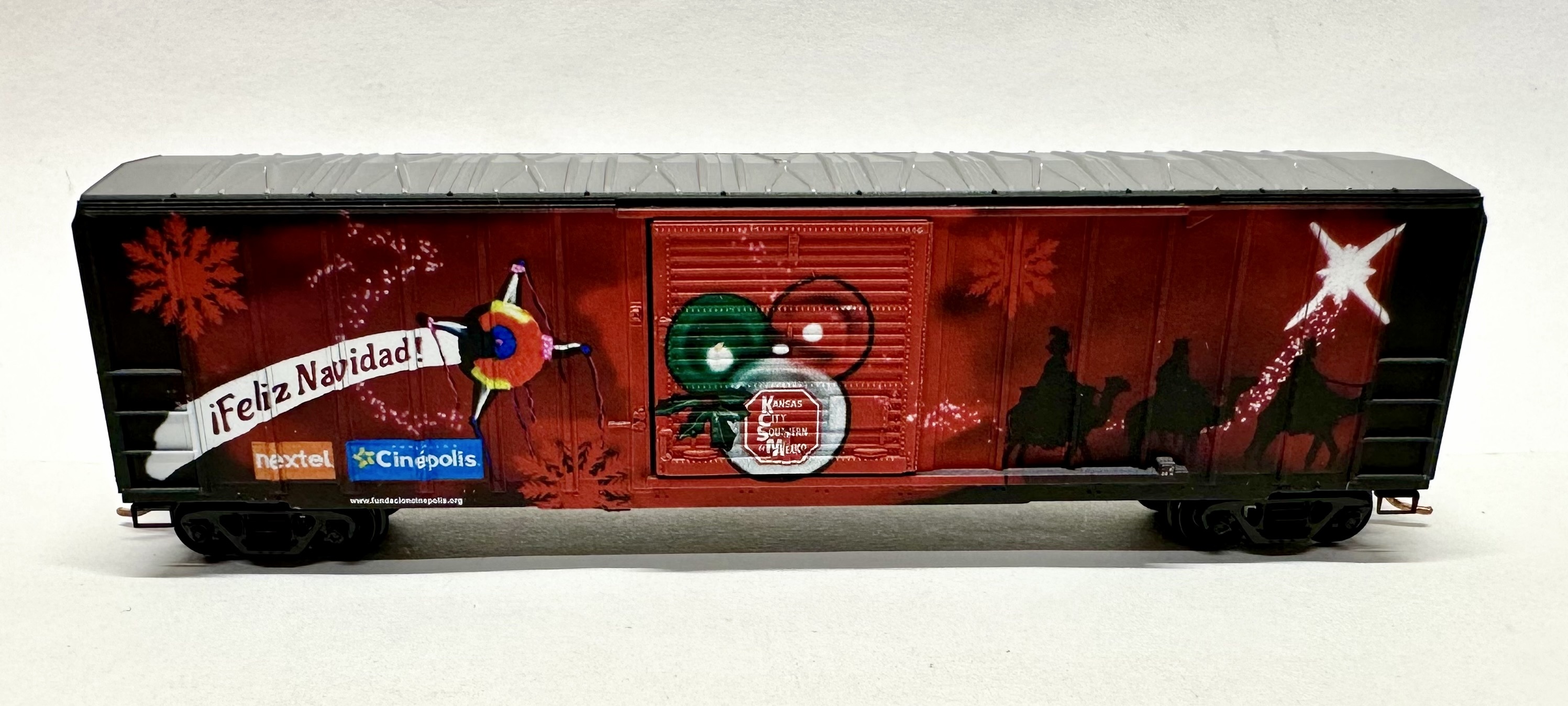
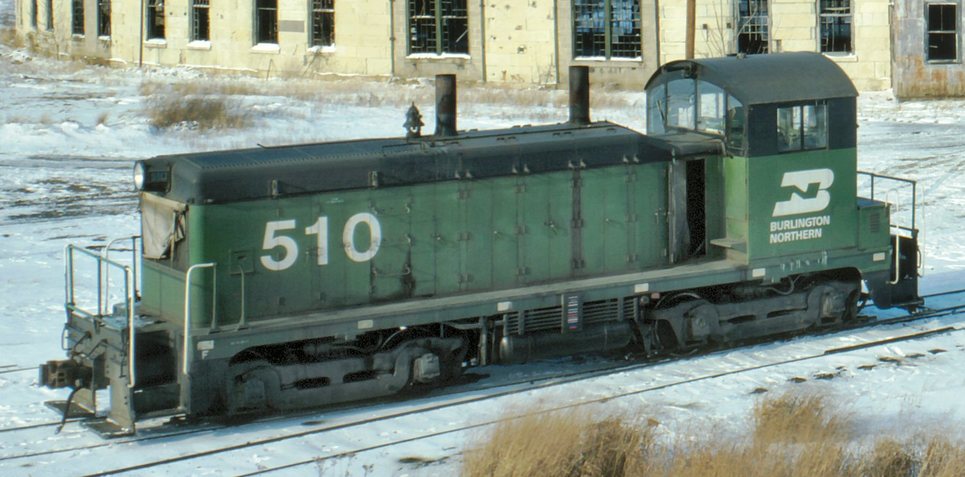Specific Item Information: Kobo NW-2 Switcher
Model Information: Kato introduced the NW2 switcher in 2007. This was Kato's first North American "Yard Switcher" and required Kato engineering a challenge to match the quality of their earlier releases using less physical space. The engine comes in DCC-Ready and DCC-Equipped (a rarity for Kato) versions.
This is a standard modern engine with flywheels, split-frame, blackened wheels and knuckle couplers. It runs smoothly and quietly and has been very popular with Kato fans (it being the first Kato switcher). The modern LED's light up the number-boards as well as the directional lights. It even sports interior cab details.
This is a standard modern engine with flywheels, split-frame, blackened wheels and knuckle couplers. It runs smoothly and quietly and has been very popular with Kato fans (it being the first Kato switcher). The modern LED's light up the number-boards as well as the directional lights. It even sports interior cab details.
DCC Information: For the DCC-ready versions, owners can install the DN123K3 decoder.
Prototype History: The EMD NW2 is a 1,000 hp (750 kW), B-B switcher locomotive manufactured by General Motors Electro-Motive Division of La Grange, Illinois. The NW2 was manufactured from February 1939 to December 1949, and 1145 were produced – 1121 for the U.S., and 24 were exported to Canada. The 1,000 hp (750 kW) was achieved by using a 12-cylinder, model 567, and later, a model 567A engine.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the NW2 known as the TR, TR2, and TR3; 3 TR cow-calf paired sets, 36 TR2 cow-calf paired sets, and 2 TR3 cow-calf-calf sets were produced. The TR sets were built prior to World War II and the TR2 and TR3 sets were built postwar.
EMD’s NW2 switcher’s lifetime was nearly cut short just three years after its introduction, with the establishment of the War Production Board in 1942, which dictated that EMD was to halt all production of switching locomotives, manufacturing only road diesels during the years of 1942 to 1945. However, such was the popularity of this end cab switching locomotive that after the restriction was lifted, the NW2 sprung back as many railroads placed orders for this little 1000hp powerhouse; today these locomotives can still be found enjoying continued service in rail yards. They were to wear paint for 88 different railroads ... from class 1 giants such as UP (with 95 units, the largest user) all the way down to short-line and industrial roads with but 1 on the roster.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the NW2 known as the TR, TR2, and TR3; 3 TR cow-calf paired sets, 36 TR2 cow-calf paired sets, and 2 TR3 cow-calf-calf sets were produced. The TR sets were built prior to World War II and the TR2 and TR3 sets were built postwar.
EMD’s NW2 switcher’s lifetime was nearly cut short just three years after its introduction, with the establishment of the War Production Board in 1942, which dictated that EMD was to halt all production of switching locomotives, manufacturing only road diesels during the years of 1942 to 1945. However, such was the popularity of this end cab switching locomotive that after the restriction was lifted, the NW2 sprung back as many railroads placed orders for this little 1000hp powerhouse; today these locomotives can still be found enjoying continued service in rail yards. They were to wear paint for 88 different railroads ... from class 1 giants such as UP (with 95 units, the largest user) all the way down to short-line and industrial roads with but 1 on the roster.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
Road Name History:  The Grand Trunk Western dates from 1928 as part of the Canadian government’s process of nationalizing some major Canadian railroads (under the name Canadian National) including the Grand Trunk Railway which had built the line. The GT lines in Michigan, Indiana and Illinois were combined under the Grand Trunk Western banner. The GTW linked the Canadian border at Port Huron (north of Detroit, Michigan) with Chicago via Durand, Lansing, and South Bend. There were also routes to Detroit, Pontiac, Bay City, Carson City, and the Lake Michigan car ferry port of Muskegon (with ferry service to Wisconsin where GTW maintained a small yard and stationed a switcher.) The GTW had about 1,000 route miles during this period. So, the GTW was an American railroad that was a wholly owned subsidiary of a Canadian corporation, wholly owned by the Canadian government. In 1970, GTW was made a subsidiary of Grand Trunk Corporation (still wholly owned by CN) which also held sister roads Central Vermont, Duluth Winnipeg & Pacific and Grand Trunk (which operated in New York and New England.) This was done to give CN’s american employees more opportunities to advance in the organization.
The Grand Trunk Western dates from 1928 as part of the Canadian government’s process of nationalizing some major Canadian railroads (under the name Canadian National) including the Grand Trunk Railway which had built the line. The GT lines in Michigan, Indiana and Illinois were combined under the Grand Trunk Western banner. The GTW linked the Canadian border at Port Huron (north of Detroit, Michigan) with Chicago via Durand, Lansing, and South Bend. There were also routes to Detroit, Pontiac, Bay City, Carson City, and the Lake Michigan car ferry port of Muskegon (with ferry service to Wisconsin where GTW maintained a small yard and stationed a switcher.) The GTW had about 1,000 route miles during this period. So, the GTW was an American railroad that was a wholly owned subsidiary of a Canadian corporation, wholly owned by the Canadian government. In 1970, GTW was made a subsidiary of Grand Trunk Corporation (still wholly owned by CN) which also held sister roads Central Vermont, Duluth Winnipeg & Pacific and Grand Trunk (which operated in New York and New England.) This was done to give CN’s american employees more opportunities to advance in the organization.
The GTW steam fleet looked very much like what you would see on the CN but GTW’s engines were built in the U.S. by Alco, Lima, and Baldwin. A fleet of 58 Alco built Mikes handled the prime road freight assignments until augmented by 43 4-8-4’s from Alco and Lima. Parent CN also relied heavily on 4-8-4’s so this was not a surprise. The last of these was delivered in 1944. Despite picking up F units and geeps for freight service early on, GTW was late to retire steam. The last run (in passenger service no less) was in 1960!
The first generation of diesels included F’s and GP9’s (set up long hood forward as on parent CN) followed by GP18’s for freight service. GTW went to EMD and Alco for switchers. Road units were painted in a green and gold scheme essentially the same as that of CN but with their own lettering and logos.
In 1962, GTW adopted a new “noodle” logo using the letters GT to conform to CN’s own noodle logo adopted two years before. Locomotives were painted black with Morency Orange ends (later replaced with red) with light gray frame stripes and lettering. Cab units received the familiar “sergeant stripe” scheme used on CN. GTW’s second generation of diesels (which also introduced the switch to low short hoods and running short-hood-forward) began in 1969 with the delivery of SD40’s followed by GP38AC and GP38-2 models. In December of 1971, GTW switched from black to blue with red ends and white frame stripe and lettering.
In addition to acting as a link from Chicago to eastern Canada, GTW was also an important carrier for the auto industry. Their freight car fleet included large numbers of auto parts boxcars and auto racks. In the early 70’s, GTW adopted the motto, “the Good Track road” on their freight cars to set them apart from their derailment prone neighbor Penn Central.
In 1980, GTW acquired another railroad critical to the auto industry, the Detroit Toledo & Ironton. This gave GTW routes from Detroit to the Ohio River. A year later, they acquired Norfolk & Western’s half of the Detroit & Toledo Shore Line, merging that small bridge line connecting Detroit with Toledo.
At this point, GTW was over 1,500 miles long with 262 diesels and nearly 12,000 cars. In 1995, GTW’s parent Canadian National was privatized, at which point there was less need for the US subsidiaries to have distinctly separate identities. Grand Trunk Western continues as a “paper railroad” but operations on these lines are now run as part of the greater Canadian National system.

The GTW steam fleet looked very much like what you would see on the CN but GTW’s engines were built in the U.S. by Alco, Lima, and Baldwin. A fleet of 58 Alco built Mikes handled the prime road freight assignments until augmented by 43 4-8-4’s from Alco and Lima. Parent CN also relied heavily on 4-8-4’s so this was not a surprise. The last of these was delivered in 1944. Despite picking up F units and geeps for freight service early on, GTW was late to retire steam. The last run (in passenger service no less) was in 1960!
The first generation of diesels included F’s and GP9’s (set up long hood forward as on parent CN) followed by GP18’s for freight service. GTW went to EMD and Alco for switchers. Road units were painted in a green and gold scheme essentially the same as that of CN but with their own lettering and logos.
In 1962, GTW adopted a new “noodle” logo using the letters GT to conform to CN’s own noodle logo adopted two years before. Locomotives were painted black with Morency Orange ends (later replaced with red) with light gray frame stripes and lettering. Cab units received the familiar “sergeant stripe” scheme used on CN. GTW’s second generation of diesels (which also introduced the switch to low short hoods and running short-hood-forward) began in 1969 with the delivery of SD40’s followed by GP38AC and GP38-2 models. In December of 1971, GTW switched from black to blue with red ends and white frame stripe and lettering.
In addition to acting as a link from Chicago to eastern Canada, GTW was also an important carrier for the auto industry. Their freight car fleet included large numbers of auto parts boxcars and auto racks. In the early 70’s, GTW adopted the motto, “the Good Track road” on their freight cars to set them apart from their derailment prone neighbor Penn Central.
In 1980, GTW acquired another railroad critical to the auto industry, the Detroit Toledo & Ironton. This gave GTW routes from Detroit to the Ohio River. A year later, they acquired Norfolk & Western’s half of the Detroit & Toledo Shore Line, merging that small bridge line connecting Detroit with Toledo.
At this point, GTW was over 1,500 miles long with 262 diesels and nearly 12,000 cars. In 1995, GTW’s parent Canadian National was privatized, at which point there was less need for the US subsidiaries to have distinctly separate identities. Grand Trunk Western continues as a “paper railroad” but operations on these lines are now run as part of the greater Canadian National system.
Brand/Importer Information: KATO U.S.A. was established in 1986, with the first U.S. locomotive model (the GP38-2, in N-Scale) released in 1987. Since that time, KATO has come to be known as one of the leading manufacturers of precision railroad products for the modeling community. KATO's parent company, Sekisui Kinzoku Co., Ltd., is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan.
In addition to producing ready-to-run HO and N scale models that are universally hailed for their high level of detail, craftsmanship and operation, KATO also manufactures UNITRACK. UNITRACK is the finest rail & roadbed modular track system available to modelers today. With the track and roadbed integrated into a single piece, UNITRACK features a nickel-silver rail and a realistic-looking roadbed. Patented UNIJOINERS allow sections to be snapped together quickly and securely, time after time if necessary.
The Kato U.S.A. office and warehouse facility is located in Schaumburg, Illinois, approximately 30 miles northwest of Chicago. All research & development of new North American products is performed here, in addition to the sales and distribution of merchandise to a vast network of wholesale representatives and retail dealers. Models requiring service sent in by hobbyists are usually attended to at this location as well. The manufacturing of all KATO products is performed in Japan.
Supporters of KATO should note that there is currently no showroom or operating exhibit of models at the Schaumburg facility. Furthermore, model parts are the only merchandise sold directly to consumers. (Please view the Parts Catalog of this website for more specific information.)
In addition to producing ready-to-run HO and N scale models that are universally hailed for their high level of detail, craftsmanship and operation, KATO also manufactures UNITRACK. UNITRACK is the finest rail & roadbed modular track system available to modelers today. With the track and roadbed integrated into a single piece, UNITRACK features a nickel-silver rail and a realistic-looking roadbed. Patented UNIJOINERS allow sections to be snapped together quickly and securely, time after time if necessary.
The Kato U.S.A. office and warehouse facility is located in Schaumburg, Illinois, approximately 30 miles northwest of Chicago. All research & development of new North American products is performed here, in addition to the sales and distribution of merchandise to a vast network of wholesale representatives and retail dealers. Models requiring service sent in by hobbyists are usually attended to at this location as well. The manufacturing of all KATO products is performed in Japan.
Supporters of KATO should note that there is currently no showroom or operating exhibit of models at the Schaumburg facility. Furthermore, model parts are the only merchandise sold directly to consumers. (Please view the Parts Catalog of this website for more specific information.)
Commissioner Information: Kobo Customs is Kato's department in charge of custom models
Item created by: grothe77 on 2025-01-16 00:00:48. Last edited by grothe77 on 2025-01-16 00:00:50
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.