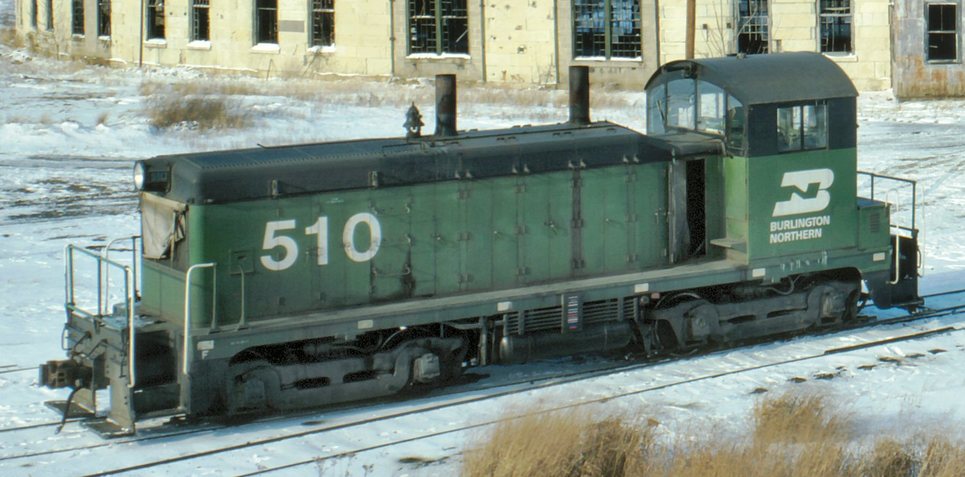Specific Item Information: Paragon4 Sound
Model Information: BLI released its NW2 and SW7 concurrently in 2019, using the same chassis, as the two engines are largely similar.
The main spotting differences are:
- Windows: Rounded on NW2, Rectangle on SW7.
- Forward radiator grid: Small on NW2, Large on SW7.
The main spotting differences are:
- Windows: Rounded on NW2, Rectangle on SW7.
- Forward radiator grid: Small on NW2, Large on SW7.
- Precision Drive Mechanism engineered for continuous heavy load towing and smooth slow speed operation
- Premium Caliber Painting with Authentic Paint Schemes
- Prototypical Light Operation with Golden White LED Headlight (and MARS Light Where Applicable)
- Die Cast Body with Die Cast chassis for Maximum Tractive Effort
- (2) Operating MicroTrains #1015 or Compatible Couplers
- Separately Applied Hand Rails, Grab Irons, Rear Diaphragm, and Horn(s)
- Will Operate on Code 55, 70, and 80 Rail
- Recommended Minimum Radius: 9.75 inches
DCC Information:
- NEW Paragon3 Sound & Operation System FEATURING ROLLING THUNDER (TM) with Authentic Sounds and Prototypical Operation in both DC and DCC environments
- Integral DCC Decoder with Back EMF for Industry Best Slow Speed Operation in DC and DCC
- Operates in DC & DCC (use DCMaster for DC Sound)
- Record & Play Operation - Records and plays back sounds and movements once or repeatedly for automatic operation
- 16-bit Sample Rate for exceptional high frequency sound clarity
- Alternate Whistle / Horn where applicable for locomotive with air horn and steam whistle - both the main whistle and alternate can be easily played
- Adjustable bell ringing interval for faster or slower bell
- Numerous user-mappable functions with available keys
- Passenger Station Ambient Sounds - Controlled with Function Key
- Freight Yard related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Lumber Yard Ambient Sounds - Controlled with Function Key
- Farm related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Crew Radio Communications - Controlled with Function Key
- Maintenance Yard related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Demo Mode for display and demonstrations
- Simple Programming with Integral DCC Decoder
- Individually adjustable sound volumes for most effects
Prototype History: The EMD NW2 is a 1,000 hp (750 kW), B-B switcher locomotive manufactured by General Motors Electro-Motive Division of La Grange, Illinois. The NW2 was manufactured from February 1939 to December 1949, and 1145 were produced – 1121 for the U.S., and 24 were exported to Canada. The 1,000 hp (750 kW) was achieved by using a 12-cylinder, model 567, and later, a model 567A engine.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the NW2 known as the TR, TR2, and TR3; 3 TR cow-calf paired sets, 36 TR2 cow-calf paired sets, and 2 TR3 cow-calf-calf sets were produced. The TR sets were built prior to World War II and the TR2 and TR3 sets were built postwar.
EMD’s NW2 switcher’s lifetime was nearly cut short just three years after its introduction, with the establishment of the War Production Board in 1942, which dictated that EMD was to halt all production of switching locomotives, manufacturing only road diesels during the years of 1942 to 1945. However, such was the popularity of this end cab switching locomotive that after the restriction was lifted, the NW2 sprung back as many railroads placed orders for this little 1000hp powerhouse; today these locomotives can still be found enjoying continued service in rail yards. They were to wear paint for 88 different railroads ... from class 1 giants such as UP (with 95 units, the largest user) all the way down to short-line and industrial roads with but 1 on the roster.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the NW2 known as the TR, TR2, and TR3; 3 TR cow-calf paired sets, 36 TR2 cow-calf paired sets, and 2 TR3 cow-calf-calf sets were produced. The TR sets were built prior to World War II and the TR2 and TR3 sets were built postwar.
EMD’s NW2 switcher’s lifetime was nearly cut short just three years after its introduction, with the establishment of the War Production Board in 1942, which dictated that EMD was to halt all production of switching locomotives, manufacturing only road diesels during the years of 1942 to 1945. However, such was the popularity of this end cab switching locomotive that after the restriction was lifted, the NW2 sprung back as many railroads placed orders for this little 1000hp powerhouse; today these locomotives can still be found enjoying continued service in rail yards. They were to wear paint for 88 different railroads ... from class 1 giants such as UP (with 95 units, the largest user) all the way down to short-line and industrial roads with but 1 on the roster.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
Road Name History: The New York Central Railroad (reporting mark NYC), known simply as the New York Central in its publicity, was a railroad operating in the Northeastern United States. Headquartered in New York City, the railroad served most of the Northeast, including extensive trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, and Massachusetts, plus additional trackage in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information:  Broadway Limited Imports, LLC defines itself as "the world's foremost producer of top-quality HO and N scale model trains".
Broadway Limited Imports, LLC defines itself as "the world's foremost producer of top-quality HO and N scale model trains".
The company was founded in 2002 and introduced its first N scale model in 2009.
Broadway Limited Imports is composed of a team of 15 fun loving individuals who are dedicated to creating the most realistic model railroading experience possible, with the best customer service possible.
The Broadway Limited Imports headquarters is located in Ormond Beach, Florida at 9 East Tower Circle. It's just under an hour's drive from Disney World.
About Broadway Limited Imports.

The company was founded in 2002 and introduced its first N scale model in 2009.
Broadway Limited Imports is composed of a team of 15 fun loving individuals who are dedicated to creating the most realistic model railroading experience possible, with the best customer service possible.
The Broadway Limited Imports headquarters is located in Ormond Beach, Florida at 9 East Tower Circle. It's just under an hour's drive from Disney World.
About Broadway Limited Imports.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2023-02-10 13:59:17. Last edited by CNW400 on 2023-02-10 13:59:18
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.