Specific Item Information: Paragon4 Sound
Model Information: BLI released its NW2 and SW7 concurrently in 2019, using the same chassis, as the two engines are largely similar.
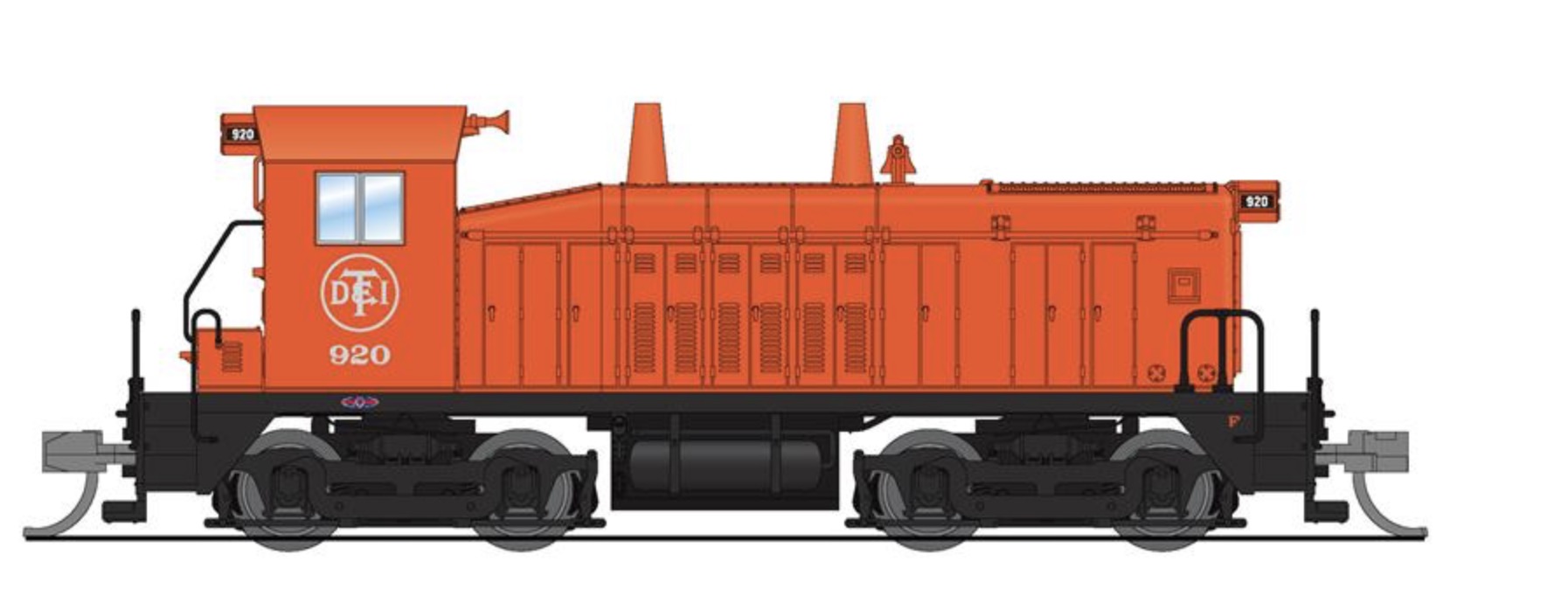
The main spotting differences are:
- Windows: Rounded on NW2, Rectangle on SW7.
- Forward radiator grid: Small on NW2, Large on SW7.
The main spotting differences are:
- Windows: Rounded on NW2, Rectangle on SW7.
- Forward radiator grid: Small on NW2, Large on SW7.
- Precision Drive Mechanism engineered for continuous heavy load towing and smooth slow speed operation
- Premium Caliber Painting with Authentic Paint Schemes
- Prototypical Light Operation with Golden White LED Headlight (and MARS Light Where Applicable)
- Die Cast Body with Die Cast chassis for Maximum Tractive Effort
- (2) Operating MicroTrains #1015 or Compatible Couplers
- Separately Applied Hand Rails, Grab Irons, Rear Diaphragm, and Horn(s)
- Will Operate on Code 55, 70, and 80 Rail
- Recommended Minimum Radius: 9.75 inches
DCC Information:
- NEW Paragon3 Sound & Operation System FEATURING ROLLING THUNDER (TM) with Authentic Sounds and Prototypical Operation in both DC and DCC environments
- Integral DCC Decoder with Back EMF for Industry Best Slow Speed Operation in DC and DCC
- Operates in DC & DCC (use DCMaster for DC Sound)
- Record & Play Operation - Records and plays back sounds and movements once or repeatedly for automatic operation
- 16-bit Sample Rate for exceptional high frequency sound clarity
- Alternate Whistle / Horn where applicable for locomotive with air horn and steam whistle - both the main whistle and alternate can be easily played
- Adjustable bell ringing interval for faster or slower bell
- Numerous user-mappable functions with available keys
- Passenger Station Ambient Sounds - Controlled with Function Key
- Freight Yard related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Lumber Yard Ambient Sounds - Controlled with Function Key
- Farm related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Crew Radio Communications - Controlled with Function Key
- Maintenance Yard related radio chatter - Controlled with Function Key
- Demo Mode for display and demonstrations
- Simple Programming with Integral DCC Decoder
- Individually adjustable sound volumes for most effects
Prototype History: The EMD SW7 is a 1,200 hp (895 kW), B-B switcher locomotive manufactured by General Motors Electro-Motive Division of La Grange, Illinois. The SW7 was manufactured from October 1949 to January 1951 and 489 were produced. The 1,200 hp (895 kW) was achieved by using a 12-cylinder, model 567A engine.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the SW7 known as the TR4; 15 TR4 cow-calf paired sets were produced.
The EMD SW7 debuted in October, 1949 and looked to follow the success of the previous SW1 and NW2 models, which combined, sold more than 1,800 units between 1939 and 1953. The SW7 used the traditional EMC/EMD carbody design, that was tapered near the cab and featured EMD's classic conical exhaust stacks above the hood. Length remained the same at just over 44-feet and it continued to use GM's model D37 traction motors. The biggest difference, to date, with the EMD SW7 over any previous model was simply horsepower. Also, by the time the SW7 was developed the "SW" designation EMC originally used, which stood for six-hundred horsepower, welded frame had long since been dropped with EMD simply having refer to "switcher."
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
EMD also offered a cow-calf version of the SW7 known as the TR4; 15 TR4 cow-calf paired sets were produced.
The EMD SW7 debuted in October, 1949 and looked to follow the success of the previous SW1 and NW2 models, which combined, sold more than 1,800 units between 1939 and 1953. The SW7 used the traditional EMC/EMD carbody design, that was tapered near the cab and featured EMD's classic conical exhaust stacks above the hood. Length remained the same at just over 44-feet and it continued to use GM's model D37 traction motors. The biggest difference, to date, with the EMD SW7 over any previous model was simply horsepower. Also, by the time the SW7 was developed the "SW" designation EMC originally used, which stood for six-hundred horsepower, welded frame had long since been dropped with EMD simply having refer to "switcher."
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com.
Road Name History: The DT&I was born in 1905 with the sale and reorganization of the Detroit Southern Railroad. Beginning in Detroit, the DT&I carved a huge northwest to southeast arc around western Ohio, serving Lima (like the bean, not Peru), Springfield, Jackson, and finally the Ohio River port of Ironton on the Kentucky border. Toledo was reached via a short segment of trackage rights on the Ann Arbor.
In 1920, as part of a complicated solution to realigning a shipping channel that served Henry Ford’s River Rouge plant, Ford bought the DT&I. The Ford years brought a ban on facial hair, uniform white hats and an expectation that crews keep their overalls clean and tidy. He also strung catenary and bought heavy electric locomotives for a 17 mile line segment between his River Rouge plant and Carolton, Michigan. During this period, the DT&I closed for business on Sundays. In 1929, Ford sold the line to Pennroad Corporation, a holding company affiliated with the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The steam fleet of the DT&I was a pretty homely lot. 2-8-0s and Russian Decapods were the kings of the road for the first few decades. As the tide of traffic turned from coal and minerals from the south end of the line to automobiles from the north end of the line, DT&I went to Lima Locomotive Works for faster stronger 2-8-4 Berkshires. Although the DT&I Berks were light and stumpy by Berkshire standards, they were a bit too much for DT&I’s physical plant so their final steam orders were for very heavy Mikados ( 20 tons heavier than USRA Heavy Mikes.) By 1955, they had completely dieselized with 37 EMD GP7’s and GP9’s setup for short hood forward operation (interesting given their ties to the Pennsylvania Railroad who preferred long hood forward operation) and 24 various EMD switchers.
The DT&I diesel fleet has always been solid orange but the logo on the long hood was smaller and more reserved in the 1950s. Second generation diesels included 8 GP35’s, 21 GP38’s, 6 GP40’s, 5 SD38’s (used in hump service,) 8 GP38-2’s, and 20 GP40-2’s. Features included a general lack of dynamic brakes and nose mounted gong style bells (a feature familiar to fans of Chicago & North Western.)
The freight car fleet was very, very colorful. Often, special colors were used to identify groups of cars for large customers. Ocean blue boxcars were for General Mills, Army green went to a paper mill on the Soo Line, yellow went to Campbell Soup, and of course, the auto parts cars which came in sky blue, cypress green, and magenta.
In 1963, and with control having been passed from Pennroad to The Pennsylvania Company (another holding company at arms length from the PRR,) the DT&I gained control of the Ann Arbor from their parent Wabash, turning the AA orange. This was part of the complicated arrangements made in the run up to the Penn Central merger. PRR needed to end their control of Wabash but wanted to hold onto DT&I and Ann Arbor. DT&I control ended in 1973 when AA declared bankruptcy.
In 1976, the DT&I was profitable even though parent Penn Central was in bankruptcy. Therefore DT&I was not included in the Conrail consolidation. In fact Conrail gave DT&I trackage rights on their lines from Springfield to Cincinnati, which gave DT&I even more Ohio River access as well as friendly connections with Southern and Louisville & Nashville. Meanwhile, The Pennsylvania Company, stripped of its Penn Central parent, put the DT&I up for sale. Grand Trunk Western offered to buy it and Chessie and N&W offered to jointly buy it. The ICC went with Grand Trunk Western and the sale was completed in 1980. Some locomotives were painted in GTW blue and red but with DT&I logos. In 1983, the DT&I officially merged into GTW.
In 1920, as part of a complicated solution to realigning a shipping channel that served Henry Ford’s River Rouge plant, Ford bought the DT&I. The Ford years brought a ban on facial hair, uniform white hats and an expectation that crews keep their overalls clean and tidy. He also strung catenary and bought heavy electric locomotives for a 17 mile line segment between his River Rouge plant and Carolton, Michigan. During this period, the DT&I closed for business on Sundays. In 1929, Ford sold the line to Pennroad Corporation, a holding company affiliated with the Pennsylvania Railroad.
The steam fleet of the DT&I was a pretty homely lot. 2-8-0s and Russian Decapods were the kings of the road for the first few decades. As the tide of traffic turned from coal and minerals from the south end of the line to automobiles from the north end of the line, DT&I went to Lima Locomotive Works for faster stronger 2-8-4 Berkshires. Although the DT&I Berks were light and stumpy by Berkshire standards, they were a bit too much for DT&I’s physical plant so their final steam orders were for very heavy Mikados ( 20 tons heavier than USRA Heavy Mikes.) By 1955, they had completely dieselized with 37 EMD GP7’s and GP9’s setup for short hood forward operation (interesting given their ties to the Pennsylvania Railroad who preferred long hood forward operation) and 24 various EMD switchers.
The DT&I diesel fleet has always been solid orange but the logo on the long hood was smaller and more reserved in the 1950s. Second generation diesels included 8 GP35’s, 21 GP38’s, 6 GP40’s, 5 SD38’s (used in hump service,) 8 GP38-2’s, and 20 GP40-2’s. Features included a general lack of dynamic brakes and nose mounted gong style bells (a feature familiar to fans of Chicago & North Western.)
The freight car fleet was very, very colorful. Often, special colors were used to identify groups of cars for large customers. Ocean blue boxcars were for General Mills, Army green went to a paper mill on the Soo Line, yellow went to Campbell Soup, and of course, the auto parts cars which came in sky blue, cypress green, and magenta.
In 1963, and with control having been passed from Pennroad to The Pennsylvania Company (another holding company at arms length from the PRR,) the DT&I gained control of the Ann Arbor from their parent Wabash, turning the AA orange. This was part of the complicated arrangements made in the run up to the Penn Central merger. PRR needed to end their control of Wabash but wanted to hold onto DT&I and Ann Arbor. DT&I control ended in 1973 when AA declared bankruptcy.
In 1976, the DT&I was profitable even though parent Penn Central was in bankruptcy. Therefore DT&I was not included in the Conrail consolidation. In fact Conrail gave DT&I trackage rights on their lines from Springfield to Cincinnati, which gave DT&I even more Ohio River access as well as friendly connections with Southern and Louisville & Nashville. Meanwhile, The Pennsylvania Company, stripped of its Penn Central parent, put the DT&I up for sale. Grand Trunk Western offered to buy it and Chessie and N&W offered to jointly buy it. The ICC went with Grand Trunk Western and the sale was completed in 1980. Some locomotives were painted in GTW blue and red but with DT&I logos. In 1983, the DT&I officially merged into GTW.
Brand/Importer Information:  Broadway Limited Imports, LLC defines itself as "the world's foremost producer of top-quality HO and N scale model trains".
Broadway Limited Imports, LLC defines itself as "the world's foremost producer of top-quality HO and N scale model trains".
The company was founded in 2002 and introduced its first N scale model in 2009.
Broadway Limited Imports is composed of a team of 15 fun loving individuals who are dedicated to creating the most realistic model railroading experience possible, with the best customer service possible.
The Broadway Limited Imports headquarters is located in Ormond Beach, Florida at 9 East Tower Circle. It's just under an hour's drive from Disney World.
About Broadway Limited Imports.

The company was founded in 2002 and introduced its first N scale model in 2009.
Broadway Limited Imports is composed of a team of 15 fun loving individuals who are dedicated to creating the most realistic model railroading experience possible, with the best customer service possible.
The Broadway Limited Imports headquarters is located in Ormond Beach, Florida at 9 East Tower Circle. It's just under an hour's drive from Disney World.
About Broadway Limited Imports.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2023-02-10 12:46:15
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.