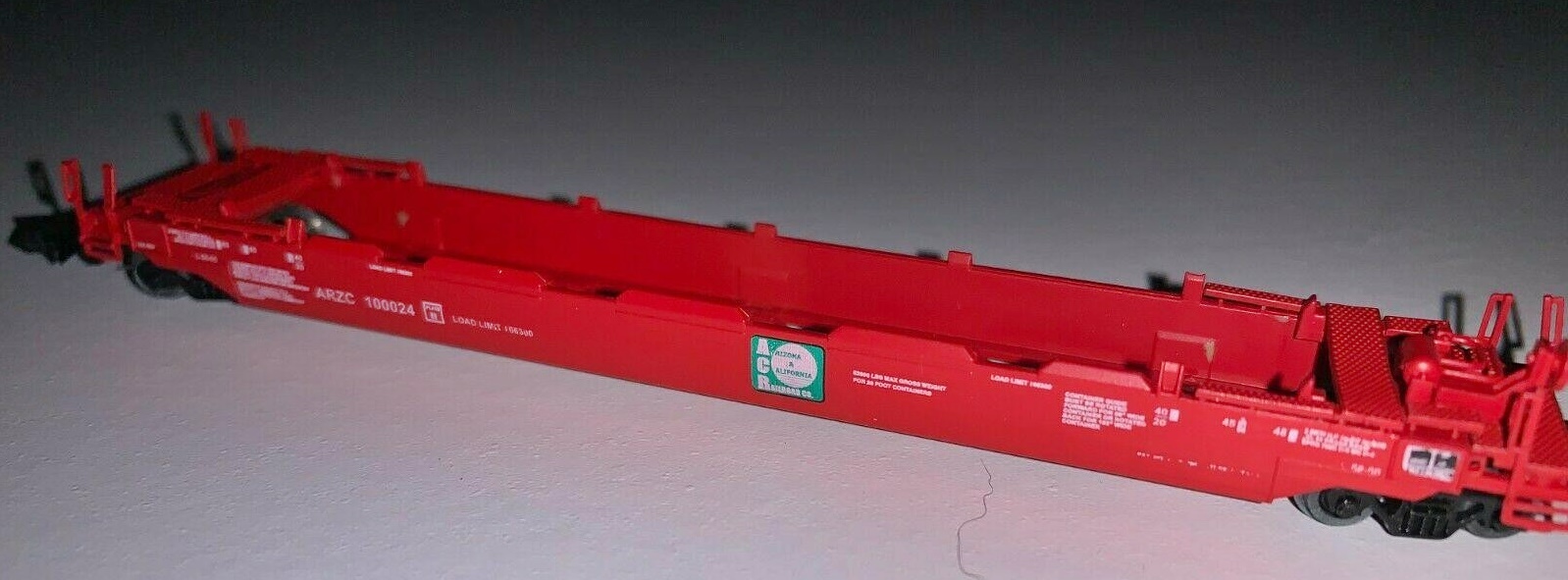
Specific Item Information: Twelve (12) different road numbers in this series 2630A-M
Prototype History: Double-stack container trains first hit the rails for regular service in 1981. The Southern Pacific Railroad had developed the idea to provide service for the Sea- Land maritime shipping company. SP's pioneering double-stack service let Sea- Land's containers take a shortcut from the west coast to the Gulf of Mexico bypassing the Panama Canal. From prototype car to production order, the SP spent a little over four years on the double-stack development project. The SP's double-stack cars featured unwieldy bulkheads on each end to prevent the loose top container from blowing off of the car. A new group at Greenbrier Intermodal designed a similar bulkhead car, even as other companies were starting to leave the bulkheads off of their stack cars. The support for the upper container came from inter-box connectors (IBCs) which had been used for years in oceangoing container shipping. Greenbrier and their car builder, Gunderson, wanted to get in on that market, and did so with their Maxi-Stack cars. But there was another new market out there: developing a single, two-truck stack car. Almost all of the existing cars in service were articulated, with the exception of one SP prototype car.
David DeBoer, a co-founder of Greenbrier, had been seeking to fill this single-well stack car niche, despite the "intermodal experts" at Trailer Train Corp. insisting that the only single-well car that could ride smoothly was a European-style 2-axle car. (In fact, it was DeBoer who wrote the reference book I used for much of this background. His Piggyback and Containers is a highly recommended read, and it was my first review item for MRN.) DeBoer sought advice from his retired former boss at the SP. This pitted the Doubting Thomases at TTX up against Bill Thomford, who had developed the SP's double-stack prototypes. Thomford laughed off Trailer Train's existence, pointing out that his own single-well, two-truck stack car had a million miles of reliable service under its belt. DeBoer went back to Greenbrier and the company got to work designing the car that TTX said was doomed to failure.
In 1990, Gunderson turned out the Husky Stack. Test engineers proved Thomford right, and the cars tracked perfectly. Trailer Train ended up reversing their initial claims and ordering 150 Husky Stack cars built with 48-foot wells in 1991. The Burlington Northern also ordered 75 cars and other buyers lined up later. The original 1991 model cars are still going strong for many different owners, including Trailer Train.
Husky Stack development has continued today, with the introduction of 53-foot wells and the "All-Purpose" Husky Stack, with trailer hitches on each end. In Greenbrier terms, the car is named the HS53 for the 53-foot well version.
David DeBoer, a co-founder of Greenbrier, had been seeking to fill this single-well stack car niche, despite the "intermodal experts" at Trailer Train Corp. insisting that the only single-well car that could ride smoothly was a European-style 2-axle car. (In fact, it was DeBoer who wrote the reference book I used for much of this background. His Piggyback and Containers is a highly recommended read, and it was my first review item for MRN.) DeBoer sought advice from his retired former boss at the SP. This pitted the Doubting Thomases at TTX up against Bill Thomford, who had developed the SP's double-stack prototypes. Thomford laughed off Trailer Train's existence, pointing out that his own single-well, two-truck stack car had a million miles of reliable service under its belt. DeBoer went back to Greenbrier and the company got to work designing the car that TTX said was doomed to failure.
In 1990, Gunderson turned out the Husky Stack. Test engineers proved Thomford right, and the cars tracked perfectly. Trailer Train ended up reversing their initial claims and ordering 150 Husky Stack cars built with 48-foot wells in 1991. The Burlington Northern also ordered 75 cars and other buyers lined up later. The original 1991 model cars are still going strong for many different owners, including Trailer Train.
Husky Stack development has continued today, with the introduction of 53-foot wells and the "All-Purpose" Husky Stack, with trailer hitches on each end. In Greenbrier terms, the car is named the HS53 for the 53-foot well version.
Road Name History: The ARZC was launched in 1991 by the ParkSierra Railgroup shortline family to purchase the Santa Fe line from Cadiz, California east to a connection with Santa Fe at Matthie, Arizona. They then ran on trackage rights on Santa Fe to Phoenix. The deal also included a branchline from Rice to Blythe and Ripley, California. In total, they operated nearly 300 miles of railroad. Traffic on the branch to Blythe faded away in 2007 and all but the first four miles of the branch was pulled up in 2011. In 2002, The ParkSierra shortline family was acquired by the RailAmerica shortline group who in turn was acquired by the Genesee & Wyoming shortline group in 2012. Traffic on the ARZC includes autos, lumber, LPG and steel. As of this writing, only one ARZC locomotive has been repainted into Genesee & Wyoming orange.
The Arizona and California Railroad (reporting mark ARZC) is a short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by RailAmerica, the former owner of the ARZC. The Genesee & Wyoming railroad holding company became the current owner in December 2012.
Read more on Wikipedia.
The Arizona and California Railroad (reporting mark ARZC) is a short line railroad that was a subdivision of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (ATSF). The ARZC began operations on May 9, 1991, when David Parkinson of the ParkSierra RailGroup purchased the line from the Santa Fe Railway. ParkSierra Railgroup was purchased in January 2002 by RailAmerica, the former owner of the ARZC. The Genesee & Wyoming railroad holding company became the current owner in December 2012.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: The Freight Yard was a hobby shop that did custom decoration and special runs of other manufacturers' N Scale products. It sold its custom products under several brands or collections: Premiere Editions, by The Freight Yard and Dreams Design.
It was located in Anaheim, California and then moved to 2006 in Phoenix, Arizona.
Established in the late 1980s, it stopped business under this name by the end of the 2000s.
The Freight Yard was owned and operated by Darren J. Cohen. Darren is now operating North Valley Trains.
The Freight Yard / Premiere Editions runs are usually available in series of two to twelve different numbers (suffixed A to M, with I not used).
The first two digits of the stock number correspond to the release year (9x being 199x, and 2x being 200x).
It was located in Anaheim, California and then moved to 2006 in Phoenix, Arizona.
Established in the late 1980s, it stopped business under this name by the end of the 2000s.
The Freight Yard was owned and operated by Darren J. Cohen. Darren is now operating North Valley Trains.
The Freight Yard / Premiere Editions runs are usually available in series of two to twelve different numbers (suffixed A to M, with I not used).
The first two digits of the stock number correspond to the release year (9x being 199x, and 2x being 200x).
Item created by: Alain LM on 2022-12-18 13:49:05
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.