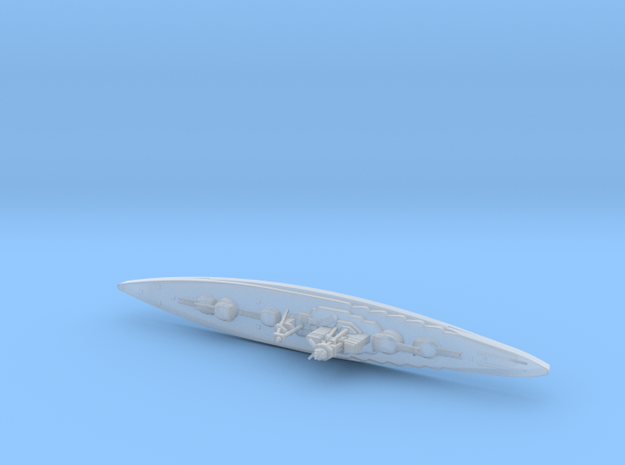
Model Information: Precision Master first released this body style in kit form. Later on, they released the same body as a RTR (Ready-to-Run) model. In 2005, Red Caboose acquired this tooling from PM. Red Caboose released this model in RTR form. The 4740 model can be distinguished from the 4750 model by counting the ribs. The 4740 has 16 ribs and the 4750 has 18 ribs. The ribs on the 4750 are a little chubbier as well.
In 2015, this tooling, along with all other Red Caboose N Scale molds, was acquired by Fox Valley, who has since produced at least one run of these cars. The recent Fox Valley releases (2017) have redone the underframe to carry body-mount couplers and blackened metal wheels - which is very nice to see and makes this model a 3rd generation piece of rolling stock.
In 2015, this tooling, along with all other Red Caboose N Scale molds, was acquired by Fox Valley, who has since produced at least one run of these cars. The recent Fox Valley releases (2017) have redone the underframe to carry body-mount couplers and blackened metal wheels - which is very nice to see and makes this model a 3rd generation piece of rolling stock.
Prototype History: Manufactured from 1966 through 1971 by Pullman Standard, the 4,740 Cu. Ft. Hoppers were considered the 'Standard of the Industry' at the time. Well over 13,000 cars were owned by numerous railroads and private companies during this time. Today, many of the cars are still in service under new ownership due to mergers and the constant changes of lessees and private owners. Features unique to this car include the 16 vertical posts on the car side, a flat roof with 4 center through hatches.
The 4,740 and 4,750 designs are often mistaken for each other, although the 4,750 has two more panels.
The 4,740 and 4,750 designs are often mistaken for each other, although the 4,750 has two more panels.
Road Name History: The Illinois Terminal has one of the most complicated histories for a railroad its size that I’ve ever seen. So without going into too much detail, the IT was established in 1890 when future US President William McKinley bought a streetcar line in the Champaign-Urbana, Illinois area. Within 20 years, he had an electrified interurban passenger and freight system linking Peoria, Bloomington, Danville, Champaign-Urbana, Decatur and Springfield with St. Louis. At its zenith, there was nearly 500 miles of line which included bypasses to keep the freight trains out of the city streets.
In 1904, McKinley went off to Congress and the Illinois Terminal became the Illinois Traction Company until the name reverted in 1937. The interurban passenger operations were significant and outlasted most other Midwestern lines. They were one of only 3 interurban lines in the country to operate sleepers. The principle sleeper route was between Peoria and St. Louis, which had no competition from the local steam roads. At the dawn of the Depression, IT had 124 interurban passenger cars, 22 steam locomotives, and 51 electric freight locomotives.
After the war, passenger service began to wane. By ’56, the intercity passenger service was gone and the last St. Louis area suburban service disappeared two years later. Diesels had begun to arrive in 1950, and by 1955, they had replaced steam and electrics in freight service. The earliest diesels were delivered in black with white trim which was later replaced with variations of bright green and yellow with silver trucks for the remainder of the line’s history.
Now just a hint of IT’s strange corporate machinations: in 1954, the Illinois-Missouri Terminal Railway was incorporated by B&O, C&EI, CB&Q, GM&O, Litchfield & Madison (later C&NW), IC, NKP, Frisco, and Wabash. The I-MT bought the IT 2 years later. The IT was then renamed “Liquidating Terminal” and the I-MT was renamed “Illinois Terminal.” NYC and RI would also buy slices of this IT. This was all for the purpose of providing neutral switching access in the St. Louis - Alton industrial belt for all of the city’s Class 1 carriers. Ironically, a decade before, the IT had been officially named “Liquidating Railway” and “Purchaser Railroad” for the brief period it took to transfer ownership at that time.
By 1980, IT had swapped nearly two thirds of their original mainline trackage for trackage rights on parallel Class 1’s rather than trying to upgrade their own. The freight was handled with 46 diesels with half a dozen SD39’s taking on the heaviest jobs. They also had over 2,600 freight cars. In 1981, the Illinois Terminal was purchased by Norfolk & Western and merged out of existence in 1982.
In 1904, McKinley went off to Congress and the Illinois Terminal became the Illinois Traction Company until the name reverted in 1937. The interurban passenger operations were significant and outlasted most other Midwestern lines. They were one of only 3 interurban lines in the country to operate sleepers. The principle sleeper route was between Peoria and St. Louis, which had no competition from the local steam roads. At the dawn of the Depression, IT had 124 interurban passenger cars, 22 steam locomotives, and 51 electric freight locomotives.
After the war, passenger service began to wane. By ’56, the intercity passenger service was gone and the last St. Louis area suburban service disappeared two years later. Diesels had begun to arrive in 1950, and by 1955, they had replaced steam and electrics in freight service. The earliest diesels were delivered in black with white trim which was later replaced with variations of bright green and yellow with silver trucks for the remainder of the line’s history.
Now just a hint of IT’s strange corporate machinations: in 1954, the Illinois-Missouri Terminal Railway was incorporated by B&O, C&EI, CB&Q, GM&O, Litchfield & Madison (later C&NW), IC, NKP, Frisco, and Wabash. The I-MT bought the IT 2 years later. The IT was then renamed “Liquidating Terminal” and the I-MT was renamed “Illinois Terminal.” NYC and RI would also buy slices of this IT. This was all for the purpose of providing neutral switching access in the St. Louis - Alton industrial belt for all of the city’s Class 1 carriers. Ironically, a decade before, the IT had been officially named “Liquidating Railway” and “Purchaser Railroad” for the brief period it took to transfer ownership at that time.
By 1980, IT had swapped nearly two thirds of their original mainline trackage for trackage rights on parallel Class 1’s rather than trying to upgrade their own. The freight was handled with 46 diesels with half a dozen SD39’s taking on the heaviest jobs. They also had over 2,600 freight cars. In 1981, the Illinois Terminal was purchased by Norfolk & Western and merged out of existence in 1982.
Brand/Importer Information: The Freight Yard was a hobby shop that did custom decoration and special runs of other manufacturers' N Scale products. It sold its custom products under several brands or collections: Premiere Editions, by The Freight Yard and Dreams Design.
It was located in Anaheim, California and then moved to 2006 in Phoenix, Arizona.
Established in the late 1980s, it stopped business under this name by the end of the 2000s.
The Freight Yard was owned and operated by Darren J. Cohen. Darren is now operating North Valley Trains.
The Freight Yard / Premiere Editions runs are usually available in series of two to twelve different numbers (suffixed A to M, with I not used).
The first two digits of the stock number correspond to the release year (9x being 199x, and 2x being 200x).
It was located in Anaheim, California and then moved to 2006 in Phoenix, Arizona.
Established in the late 1980s, it stopped business under this name by the end of the 2000s.
The Freight Yard was owned and operated by Darren J. Cohen. Darren is now operating North Valley Trains.
The Freight Yard / Premiere Editions runs are usually available in series of two to twelve different numbers (suffixed A to M, with I not used).
The first two digits of the stock number correspond to the release year (9x being 199x, and 2x being 200x).
Manufacturer Information: While they were in business, Red Caboose split its production runs between the US and China. Which models were produced where was a function of which body style and which run. Furthermore, which Chinese company was used for production is something we would love to find out.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2022-06-21 12:13:09. Last edited by Alain LM on 2022-09-25 05:41:25
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.