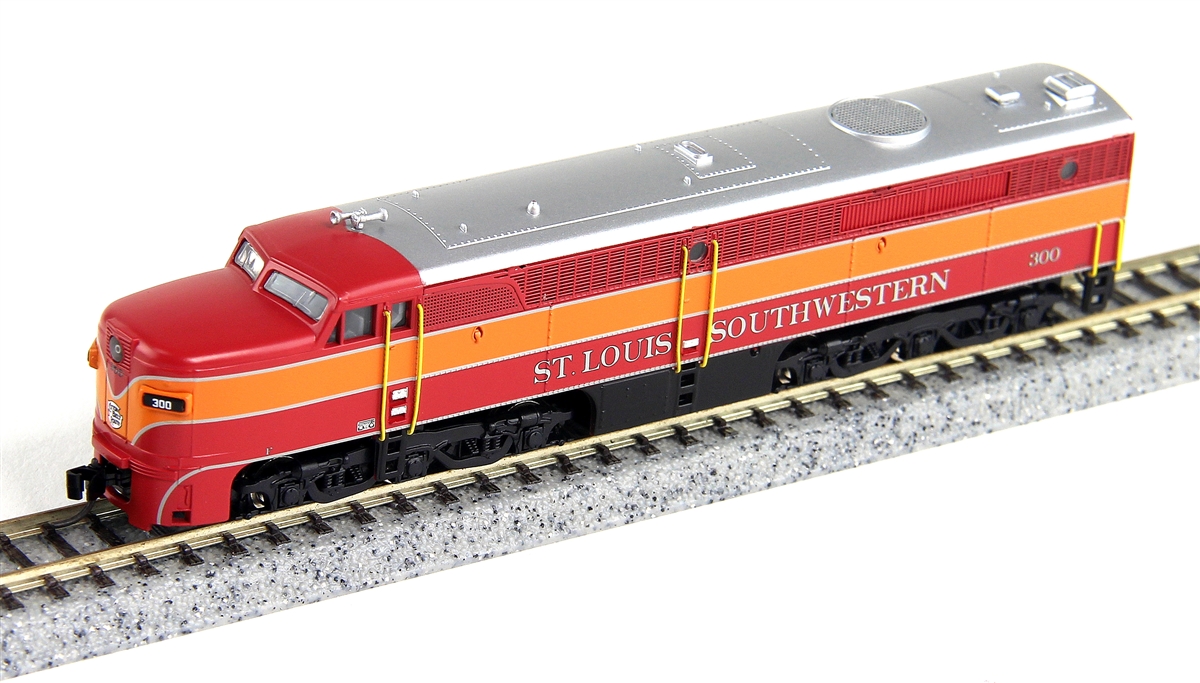
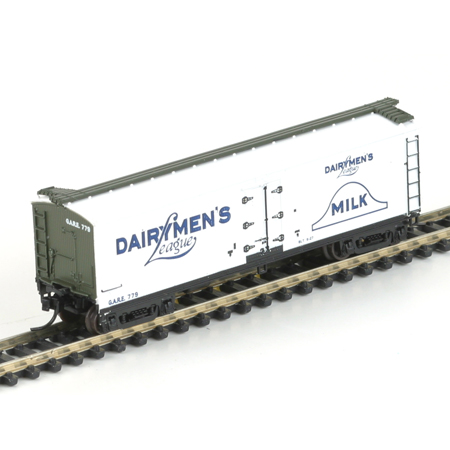
Body Style Information: TYCO's Caboose model is listed throughout the "Brown Box" Era of 1971-1993 carrying the 327 stock number. Though rare in the TYCO number organization, this model is one case where two different items are represented by the same number. For example, TYCO produced a Chessie System example of the both the "Streamline Off-Center Cupola" and "Extended Vision Cupola" Caboose and BOTH models carry the same product number of 327-03. TYCO also did NOT always produced a roadname in both body styles.
From HO-Scale Trains Resource.
From HO-Scale Trains Resource.
Prototype Information: The origins of the railroad caboose appear to date back to the 1840s when Nat Williams, a conductor of the Auburn & Syracuse Railroad (a later affiliate of the New York Central) became fed up with cramped and uncomfortable quarters to do paperwork (a common job of the conductor, whose responsibility is general oversight and control of a train, passenger or freight), which was usually done in either a free space of a passenger car or combine/baggage car. To fix this problem, Williams found an unused boxcar and using a simple box and barrel, as a seat and desk, set up shop in the car to do his duties. Not only did he find out he had plenty of room to work but also figured that he could use the unused space to store tools (flags, lanterns, spare parts, etc.) and other essentials to have on board whenever needed (such things become commonly stored on the caboose).
Perhaps the most striking feature ever applied to the railroad caboose was its cupola. According to the story, conductor T.B. Watson of the Chicago & North Western in the 1860s reportedly used a hole in a boxcar’s roof (which he was using as a caboose) to get a better vantage point of the train ahead. It is said that Watson was amazed by the view afforded from the position being able to not only see the train ahead but also from all sides, and to the rear as well. He apparently convinced C&NW shop forces to construct a type of open observation box onto an existing singe-level caboose with windows all around where one could sit and view their surroundings. The rest, as they say, is history and the common cupola was born.
Steel Cabooses replaced their wood-sheathed brethren after the second world war when the steel glut made the production and maintenance of steel cabooses far more efficient than wooden models. With the advancement of the End-of-Train device, cabooses slowly began to fall out of favor. However, in the early 2000’s, “shoving platforms” began to appear as a place to safely house a crew when a reverse move was required. Instead of riding on the side of a freight car, the crew member now has a safe place to stand, while guiding the rear of a reverse move.
Perhaps the most striking feature ever applied to the railroad caboose was its cupola. According to the story, conductor T.B. Watson of the Chicago & North Western in the 1860s reportedly used a hole in a boxcar’s roof (which he was using as a caboose) to get a better vantage point of the train ahead. It is said that Watson was amazed by the view afforded from the position being able to not only see the train ahead but also from all sides, and to the rear as well. He apparently convinced C&NW shop forces to construct a type of open observation box onto an existing singe-level caboose with windows all around where one could sit and view their surroundings. The rest, as they say, is history and the common cupola was born.
Steel Cabooses replaced their wood-sheathed brethren after the second world war when the steel glut made the production and maintenance of steel cabooses far more efficient than wooden models. With the advancement of the End-of-Train device, cabooses slowly began to fall out of favor. However, in the early 2000’s, “shoving platforms” began to appear as a place to safely house a crew when a reverse move was required. Instead of riding on the side of a freight car, the crew member now has a safe place to stand, while guiding the rear of a reverse move.
Road/Company Information: The Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (reporting mark ATSF), often abbreviated as Santa Fe or AT&SF, was one of the larger railroads in the United States. Chartered in February 1859, the railroad reached the Kansas-Colorado border in 1873 and Pueblo, Colorado, in 1876. To create a demand for its services, the railroad set up real estate offices and sold farm land from the land grants that it was awarded by Congress. Despite the name, its main line never served Santa Fe, New Mexico, as the terrain was too difficult; the town ultimately was reached by a branch line from Lamy.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport, an enterprise that (at one time or another) included a tugboat fleet and an airline (the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway). Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not accessible by rail, and ferryboats on the San Francisco Bay allowed travelers to complete their westward journeys to the Pacific Ocean. The ATSF was the subject of a popular song, Harry Warren & Johnny Mercer's "On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe", written for the film, The Harvey Girls (1946).
The railroad officially ceased operations on December 31, 1996, when it merged with the Burlington Northern Railroad to form the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway.
Read more on Wikipedia.
The Santa Fe was a pioneer in intermodal freight transport, an enterprise that (at one time or another) included a tugboat fleet and an airline (the short-lived Santa Fe Skyway). Its bus line extended passenger transportation to areas not accessible by rail, and ferryboats on the San Francisco Bay allowed travelers to complete their westward journeys to the Pacific Ocean. The ATSF was the subject of a popular song, Harry Warren & Johnny Mercer's "On the Atchison, Topeka and the Santa Fe", written for the film, The Harvey Girls (1946).
The railroad officially ceased operations on December 31, 1996, when it merged with the Burlington Northern Railroad to form the Burlington Northern & Santa Fe Railway.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: The history of TYCO trains can be traced back to John Tyler, a pioneer in HO scale who helped found the Mantua Toy & Metal Products Company in 1926 with other members of his family. They began selling trains under the Mantua name in the 1930s. Early offerings included the powerful Midjet Motor as well as a variety of rolling stock and steam locomotive kits. The shift towards “ready-to-run” (RTR) train sets after World War II led to the creation of the Tyler Manufacturing Company in 1952, better known as TYCO .
Consolidated Foods purchased TYCO in 1970, and manufacturing was shifted from New Jersey to Hong Kong. Consolidated Foods would later change its name to Sara Lee, though Norman Tyler remained as an executive with the new company. This change in ownership ushers in the “brown-box” period for collectors. Prior to 1970, TYCO offered models that reflected fairly accurate prototypes. After 1970, TYCO’s offerings wander into a fantasy world of unprototypical models.
The TYCO model railroad business was bought back by the Tyler family in 1977, who revived them under the Mantua Industries brand. Model train production by TYCO ended in the 1990s, with the final catalog appearance in 1993. The TYCO name continues as a line of radio-controlled cars produced by Mattel.
Many of the TYCO model train products were subsequently manufactured by Mantua and by International Hobby Corporation (IHC). In 2001, Mantua stopped producing its model railroad lines and sold the business to the Model Power company, which continued to sell a few items such as steam engines and freight cars under its Mantua Classics brand. In early 2014, Model Power was acquired by Model Rectifier Corporation (MRC). The company continued to make the Mantua Classics line.
Read more on HO Scale Train Resources and TYCO Brown-Box Era websites.
Consolidated Foods purchased TYCO in 1970, and manufacturing was shifted from New Jersey to Hong Kong. Consolidated Foods would later change its name to Sara Lee, though Norman Tyler remained as an executive with the new company. This change in ownership ushers in the “brown-box” period for collectors. Prior to 1970, TYCO offered models that reflected fairly accurate prototypes. After 1970, TYCO’s offerings wander into a fantasy world of unprototypical models.
The TYCO model railroad business was bought back by the Tyler family in 1977, who revived them under the Mantua Industries brand. Model train production by TYCO ended in the 1990s, with the final catalog appearance in 1993. The TYCO name continues as a line of radio-controlled cars produced by Mattel.
Many of the TYCO model train products were subsequently manufactured by Mantua and by International Hobby Corporation (IHC). In 2001, Mantua stopped producing its model railroad lines and sold the business to the Model Power company, which continued to sell a few items such as steam engines and freight cars under its Mantua Classics brand. In early 2014, Model Power was acquired by Model Rectifier Corporation (MRC). The company continued to make the Mantua Classics line.
Read more on HO Scale Train Resources and TYCO Brown-Box Era websites.
Item created by: luchestr on 2022-05-13 13:01:14. Last edited by Alain LM on 2022-05-26 05:24:43
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.