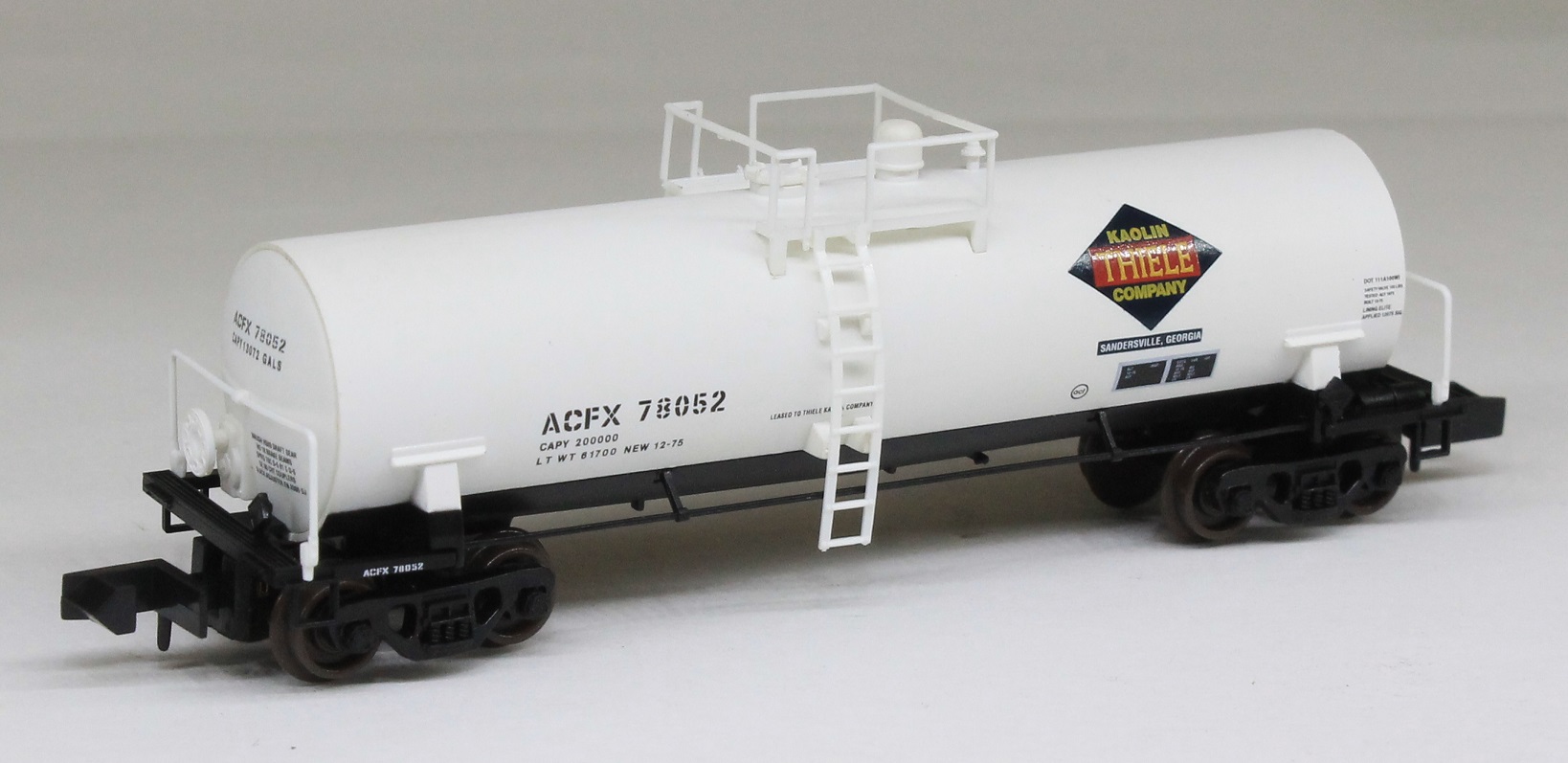
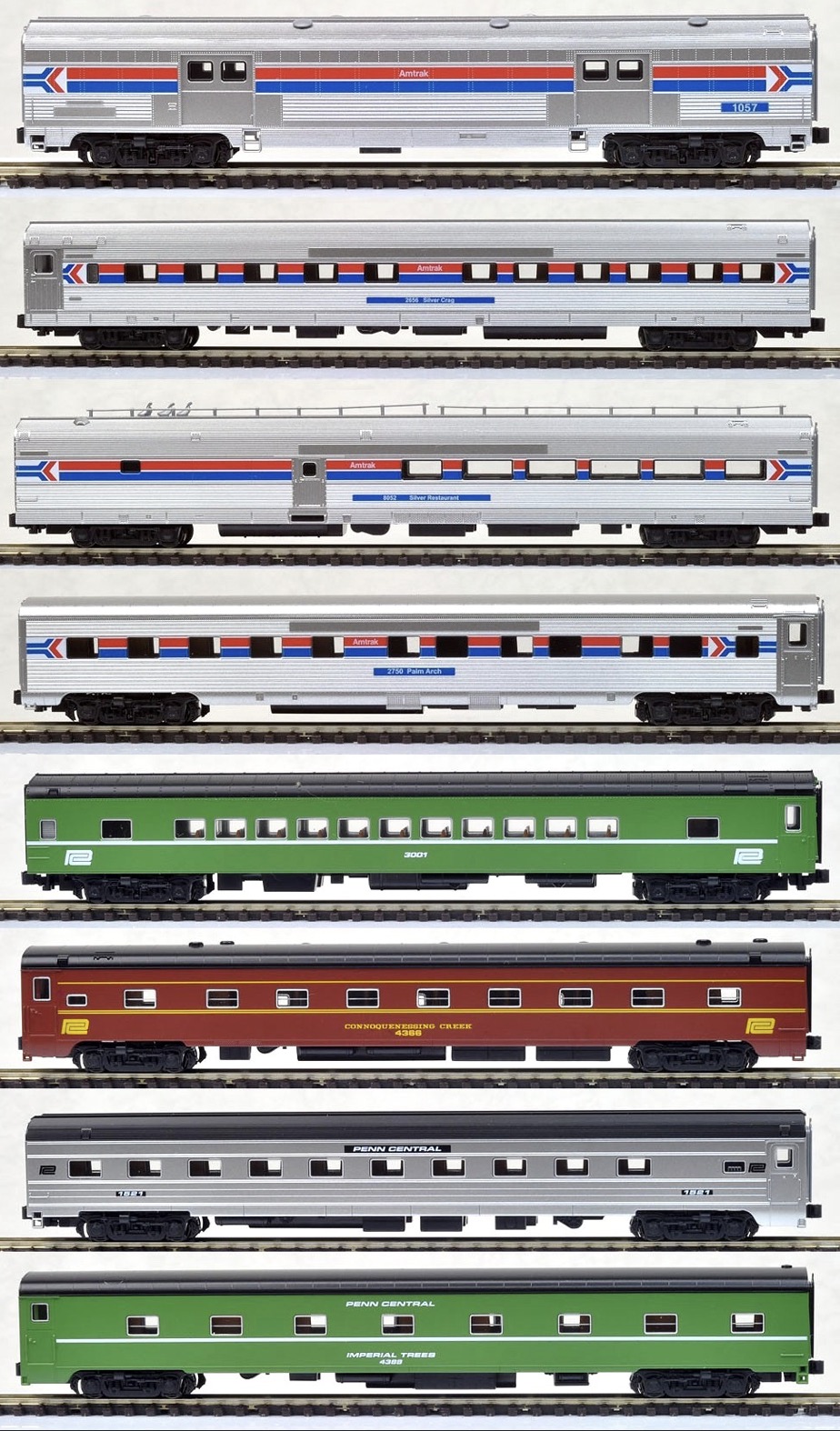
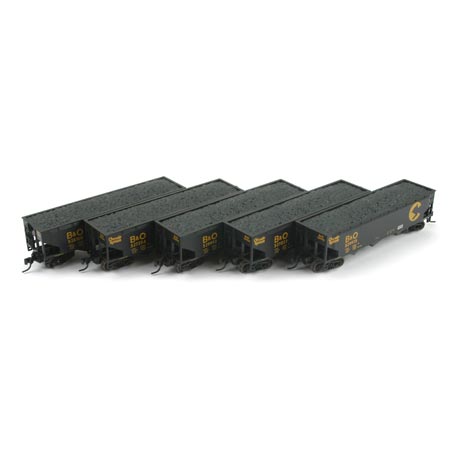
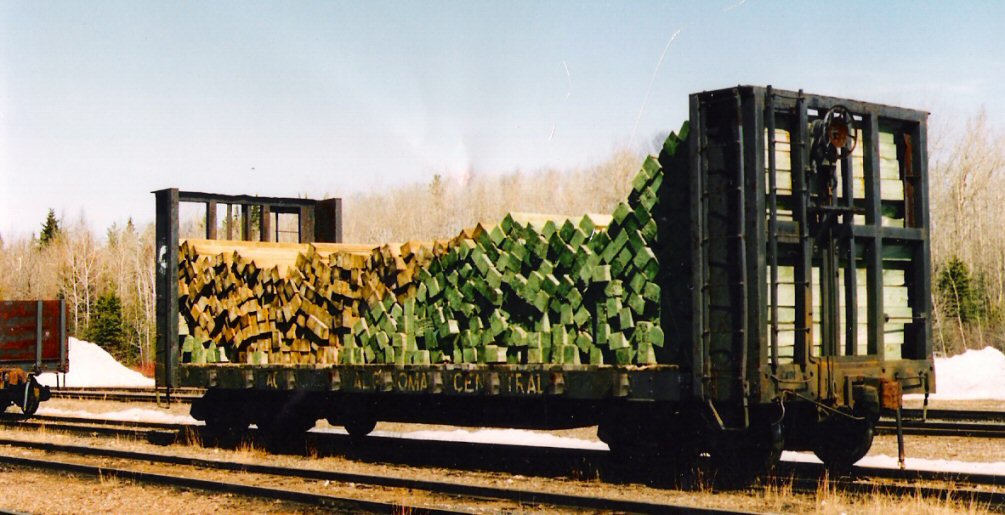
Model Information: This is one of Atlas' Chinese-made toolings. It served as the replacement for the earlier Roco-made bulkhead flatcars from the 1960s and 1970s. This model is somewhat more detailed than the earlier Roco model It first appears in the Atlas 2000 catalog with two undecorated versions (open vs closed ends) and six different road names, each with multiple numbers. The price for the decorated version in 2000 was $13.95 and $9.95 for the two undecorated models.
Prototype History: Pulpwood is not a specific type of wood, but actually tree limbs that are cut to a specified length, then turned into wood pulp and used in the paper industry. Early paper making had the trees near the paper plant. As timber resources were diminished, the need for transporting pulpwood began to rise. Railroads were seen as an efficient method of transporting pulpwood. Pulpwood in the Southeast and Northeast is generally cut into four-foot or less lengths and loaded onto "V-deck" bulkhead flat cars.
In the early 1950s General Steel Castings, produced a "V-deck" design.
Another notable manufacturer of pulpwood flat cars was the Southern Iron & Equipment Company (SIECO) that manufactured this type of car in the 1960s and 1970s, with over 800 delivered in the early 1979’s to the Southern Railway, alone.
In the early 1950s General Steel Castings, produced a "V-deck" design.
Another notable manufacturer of pulpwood flat cars was the Southern Iron & Equipment Company (SIECO) that manufactured this type of car in the 1960s and 1970s, with over 800 delivered in the early 1979’s to the Southern Railway, alone.
Road Name History:  The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (reporting marks C&O, CO) was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond to the Ohio River by 1873, where the railroad town (and later city) of Huntington, West Virginia was named for him.
The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (reporting marks C&O, CO) was a Class I railroad formed in 1869 in Virginia from several smaller Virginia railroads begun in the 19th century. Led by industrialist Collis P. Huntington, it reached from Virginia's capital city of Richmond to the Ohio River by 1873, where the railroad town (and later city) of Huntington, West Virginia was named for him.
Tapping the coal reserves of West Virginia, the C&O's Peninsula Extension to new coal piers on the harbor of Hampton Roads resulted in the creation of the new City of Newport News. Coal revenues also led the forging of a rail link to the Midwest, eventually reaching Columbus, Cincinnati and Toledo in Ohio and Chicago, Illinois.
By the early 1960s the C&O was headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio, USA. In 1972, under the leadership of Cyrus Eaton, it became part of the Chessie System, along with the Baltimore and Ohio and Western Maryland Railway. The Chessie System was later combined with the Seaboard Coast Line and Louisville and Nashville, both the primary components of the Family Lines System, to become a key portion of CSX Transportation (CSXT) in the 1980s. A substantial portion of Conrail was added in 1999.
C&O's passenger services ended in 1971 with the formation of Amtrak. Today Amtrak's tri-weekly Cardinal passenger train follows the historic and scenic route of the C&O through the New River Gorge in one of the more rugged sections of the Mountain State. The rails of the former C&O also continue to transport intermodal and freight traffic, as well as West Virginia bituminous coal east to Hampton Roads and west to the Great Lakes as part of CSXT, a Fortune 500 company which was one of seven Class I railroads operating in North America at the beginning of the 21st century.
At the end of 1970 C&O operated 5067 miles of road on 10219 miles of track, not including WM or B&O and its subsidiaries.
Read more on Wikipedia.

Tapping the coal reserves of West Virginia, the C&O's Peninsula Extension to new coal piers on the harbor of Hampton Roads resulted in the creation of the new City of Newport News. Coal revenues also led the forging of a rail link to the Midwest, eventually reaching Columbus, Cincinnati and Toledo in Ohio and Chicago, Illinois.
By the early 1960s the C&O was headquartered in Cleveland, Ohio, USA. In 1972, under the leadership of Cyrus Eaton, it became part of the Chessie System, along with the Baltimore and Ohio and Western Maryland Railway. The Chessie System was later combined with the Seaboard Coast Line and Louisville and Nashville, both the primary components of the Family Lines System, to become a key portion of CSX Transportation (CSXT) in the 1980s. A substantial portion of Conrail was added in 1999.
C&O's passenger services ended in 1971 with the formation of Amtrak. Today Amtrak's tri-weekly Cardinal passenger train follows the historic and scenic route of the C&O through the New River Gorge in one of the more rugged sections of the Mountain State. The rails of the former C&O also continue to transport intermodal and freight traffic, as well as West Virginia bituminous coal east to Hampton Roads and west to the Great Lakes as part of CSXT, a Fortune 500 company which was one of seven Class I railroads operating in North America at the beginning of the 21st century.
At the end of 1970 C&O operated 5067 miles of road on 10219 miles of track, not including WM or B&O and its subsidiaries.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: james13pugh on 2022-04-20 16:30:11
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.