Series Information: A collection released by Con-Cor
Model Information: Originally, Con-cor contracted with Kato of Japan to produce this model. It was first released in 1973, though it does not appear in the 1973 JMC catalog. Con-Cor later moved this tooling to China and re-released the model in 1997 under their "Rail Baron Collection" branding. The mechanism is shared with the Kato-made Gas Turbine models introduced in 1975.
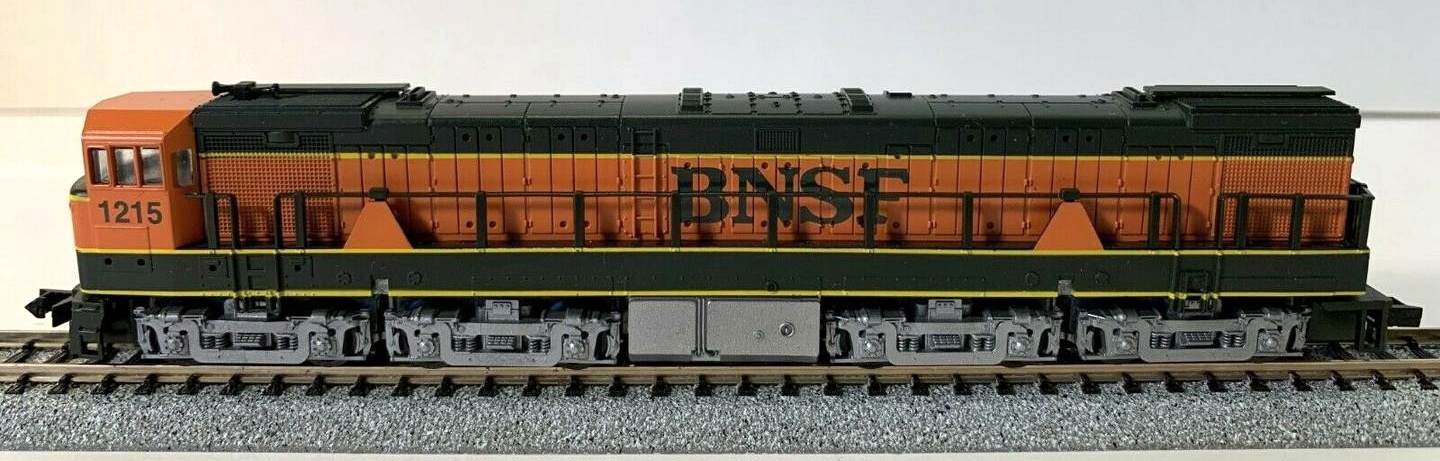
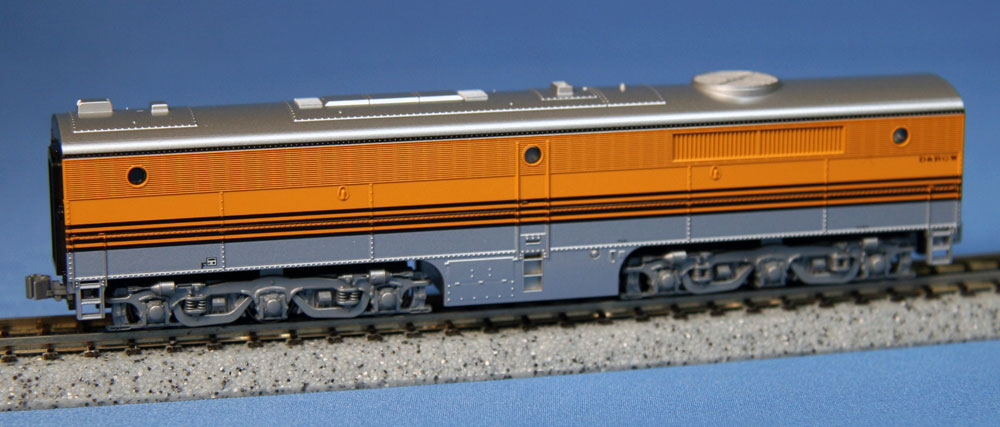
This locomotive was owned only by Union Pacific and Southern Pacific; Con-Cor however released it in several other paint schemes, that are pure fantasies.
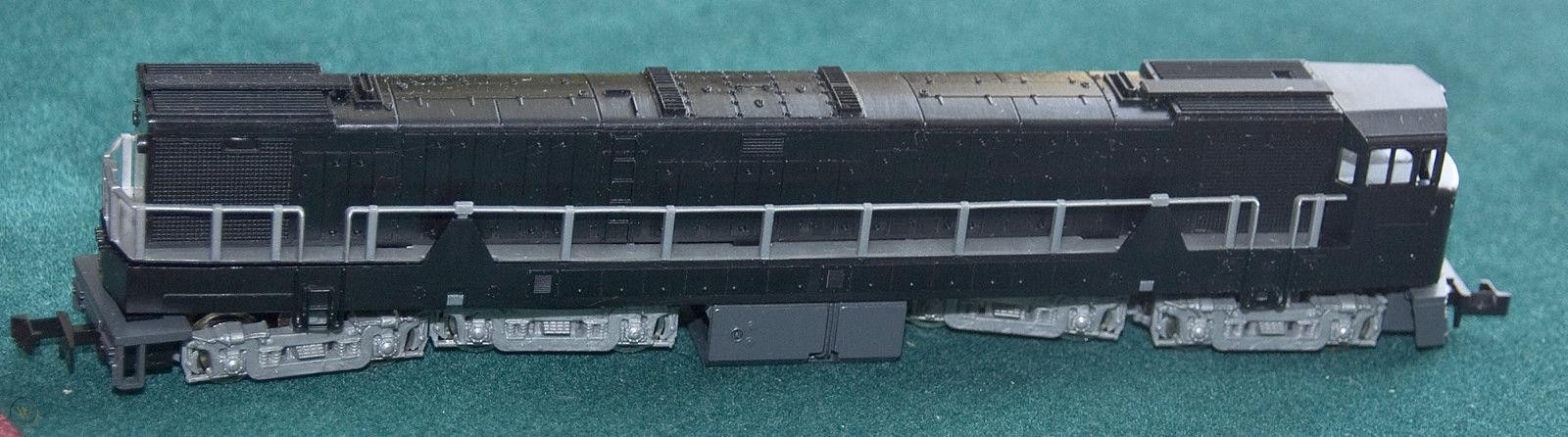
This model has been re-run several times in different road names using the same stock number.
This locomotive was owned only by Union Pacific and Southern Pacific; Con-Cor however released it in several other paint schemes, that are pure fantasies.
This model has been re-run several times in different road names using the same stock number.
DCC Information: No provision for DCC in either release.
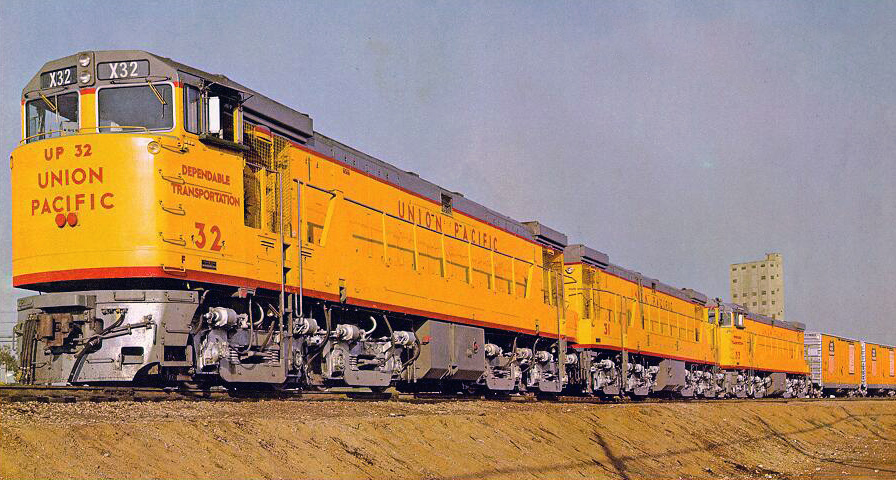
Prototype History: The GE U50 was an eight-axle, in B-B-B-B configuration, 5,000 hp (3,700 kW) road switcher diesel-electric locomotive built by General Electric. They were twin-engined locomotives, combining two 2,500 hp (1,900 kW) diesel engines.
The U50 was built in response to the Union Pacific Railroad's requirement, issued in the early 1960s, for a 15,000 hp (11,200 kW) 3-unit locomotive intended to replace the turbines. The design was effectively two U25B locomotives on a single frame; each diesel engine and generator powered only the two trucks at the same end.
26 U50 have been produced, 23 for UP and 3 for SP. They were all scrapped by 1977.
Read more on Wikipedia and American-Rails.com
The U50 was built in response to the Union Pacific Railroad's requirement, issued in the early 1960s, for a 15,000 hp (11,200 kW) 3-unit locomotive intended to replace the turbines. The design was effectively two U25B locomotives on a single frame; each diesel engine and generator powered only the two trucks at the same end.
26 U50 have been produced, 23 for UP and 3 for SP. They were all scrapped by 1977.
Read more on Wikipedia and American-Rails.com
Road Name History: The BNSF Railway (reporting mark BNSF) is one of the largest freight railroad networks in North America, second to the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) (its primary competitor for Western U.S. freight), and is one of seven North American Class I railroads. It has 48,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide high-speed links between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.[2] The BNSF and UP have a duopoly on all transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western U.S. and share trackage rights over thousands of miles of track.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
Brand/Importer Information: Con-Cor has been in business since 1962. Many things have changed over time as originally they were a complete manufacturing operation in the USA and at one time had upwards of 45 employees. They not only designed the models,but they also built their own molds, did injection molding, painting, printing and packaging on their models.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2021-09-26 13:33:54. Last edited by Alain LM on 2021-09-26 13:40:21
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.