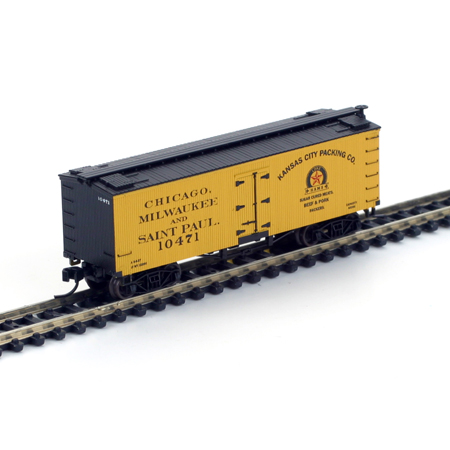
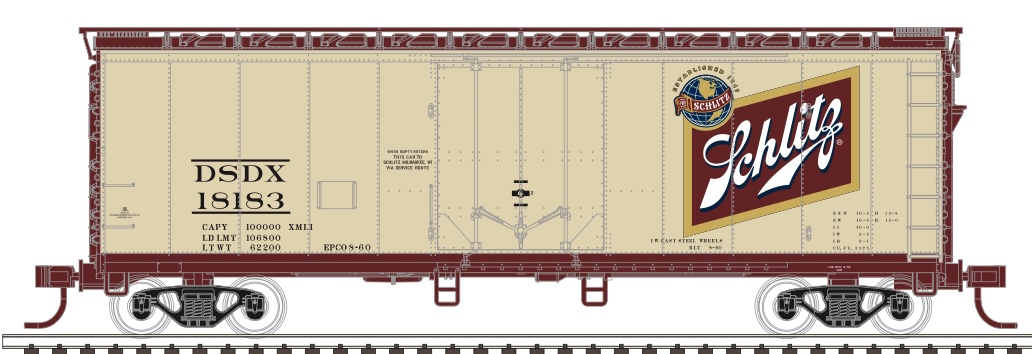
Model Information: Atlas first released this model in 1976. It was originally produced in their New Jersey factor. It replaced a similar model made by Roco for Atlas from 1967 - 1975. The American-made Atlas tooling was launched with an amazing 24 different road names. In the 1997 Atlas catalog, this model is referred to as a 40' Plugdoor Boxcar. However, the earlier Roco model had been referred to alternatively as a "Reefer" (1967, 1969 and 1971) as well as a "40' Insulated Plugdoor" (1975). Sometime in the 1990s, the tooling was moved to China. From September 2006 onward, this model was considered part of the 'Trainman' product line.
Prototype History: Plug-Door boxcars are usually insulated and typically carry products such as canned goods that require protection from extremes of temperature but do not require refrigeration. Plug-style doors were normally used to ensure a tight seal in the insulation. Designed for transport of both perishables and large loads, plug doors allowed box cars to be sealed from outside dust and dirt. Cars like these were manufactured during the 50s and 60s.
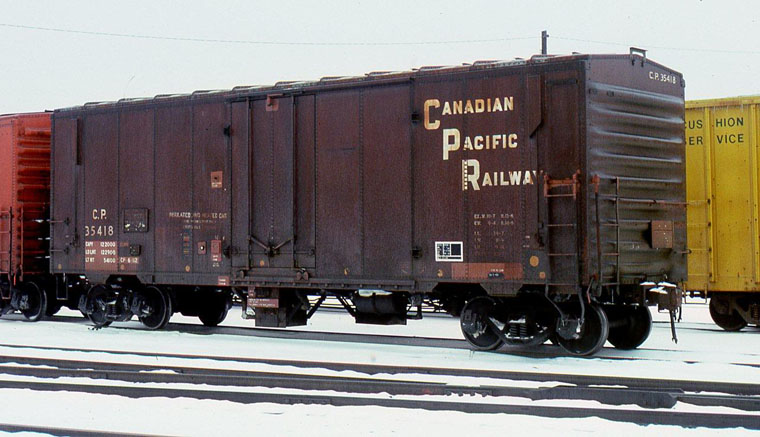
Whether you consider this a reefer or a boxcar is a matter for angel-pinhead-counters. There seems to be a bit of a blurry line during the transition era between the idea of a steel ice reefer and an insulated boxcar. I guess an ice reefer was meant to hold ice for cooling but I doubt this is a cut-and-dry distinction. Modern "mechanical" reefers are a different breed as they contain a refrigeration unit which quite distinctly sets them apart from "boxcars".
Whether you consider this a reefer or a boxcar is a matter for angel-pinhead-counters. There seems to be a bit of a blurry line during the transition era between the idea of a steel ice reefer and an insulated boxcar. I guess an ice reefer was meant to hold ice for cooling but I doubt this is a cut-and-dry distinction. Modern "mechanical" reefers are a different breed as they contain a refrigeration unit which quite distinctly sets them apart from "boxcars".
Road Name History: The Joseph Schlitz Brewing Company was an American brewery based in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and once the largest producer of beer in the United States. Its namesake beer, Schlitz (pronunciation: /ˈʃlɪts/), was known as "The beer that made Milwaukee famous" and was advertised with the slogan "When you're out of Schlitz, you're out of beer". Schlitz first became the largest beer producer in the US in 1902 and enjoyed that status at several points during the first half of the twentieth century, exchanging the title with Anheuser-Busch multiple times during the 1950s.
The company was founded by August Krug in 1849 but acquired by Joseph Schlitz in 1858. Schlitz was bought by Stroh Brewery Company in 1982 and subsequently sold along with the rest of Stroh's assets to Pabst Brewing Company in 1999. Pabst now produces the recently relaunched "Schlitz Gusto" beer and Old Milwaukee.
On November 13, 2014, Pabst announced that it had completed its sale to Blue Ribbon Intermediate Holdings, LLC. Blue Ribbon is a partnership between American beer entrepreneur Eugene Kashper and TSG Consumer Partners, a San Francisco?based private equity firm. Prior reports suggested the price agreed upon was around $700 million.
From Wikipedia
The company was founded by August Krug in 1849 but acquired by Joseph Schlitz in 1858. Schlitz was bought by Stroh Brewery Company in 1982 and subsequently sold along with the rest of Stroh's assets to Pabst Brewing Company in 1999. Pabst now produces the recently relaunched "Schlitz Gusto" beer and Old Milwaukee.
On November 13, 2014, Pabst announced that it had completed its sale to Blue Ribbon Intermediate Holdings, LLC. Blue Ribbon is a partnership between American beer entrepreneur Eugene Kashper and TSG Consumer Partners, a San Francisco?based private equity firm. Prior reports suggested the price agreed upon was around $700 million.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-09-14 13:58:41
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.