Model Information: This model was developed by Delaware Valley Freight Car Corporation. The tooling was purchased by Bowser in 1998 and has been re-released several times since it was acquired. The body style has also been sold by Eastern Seaboard Models under the ESM branding. The model is available in both 3-Bay and 6-Bay variations.
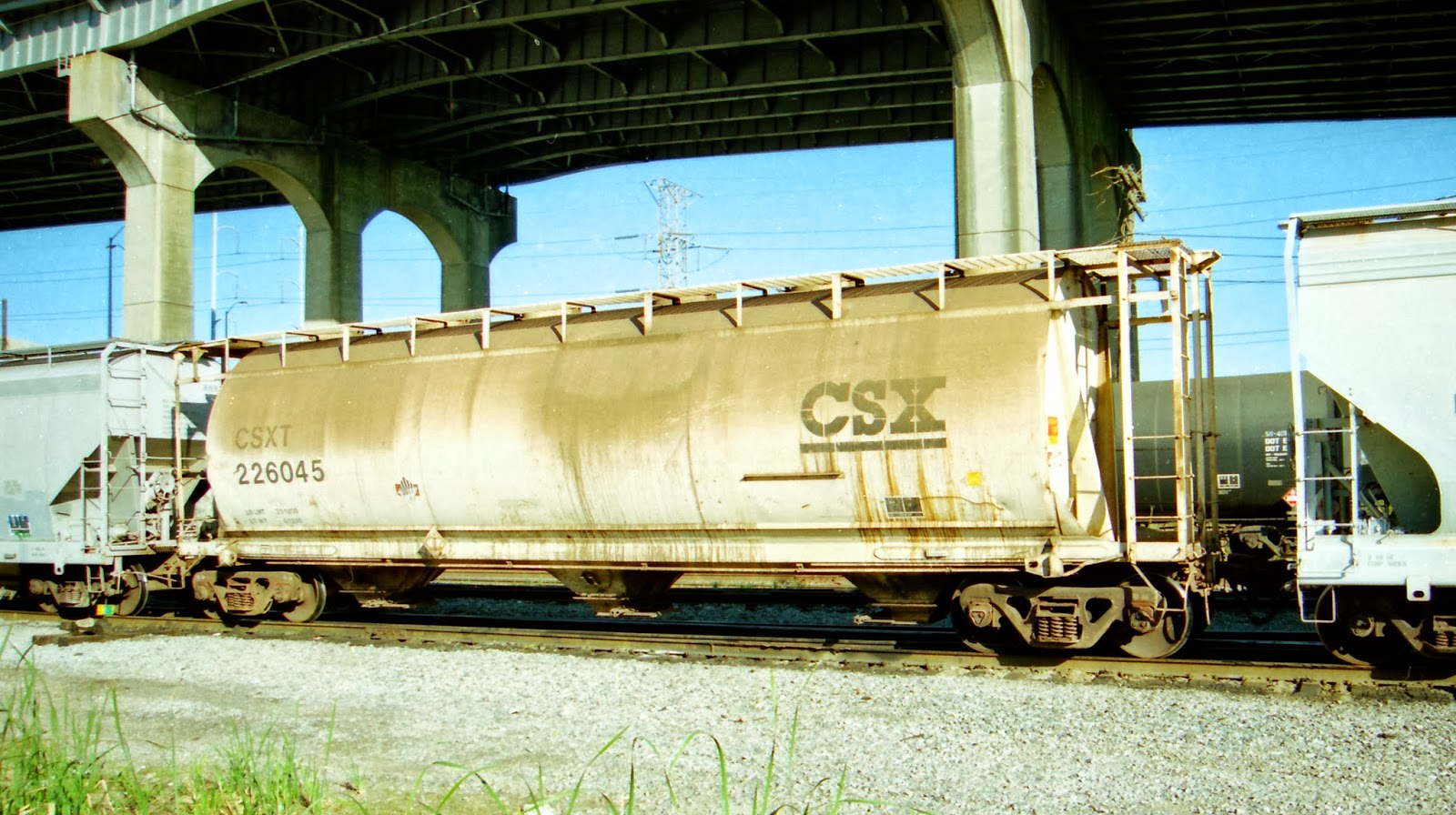
Prototype History: ACF introduced their roundish cylindrical hoppers in the early 1960s. The cars differed greatly from the ribbed sided hoppers of the era. They have been made in 3-bay and 6-bay variations. These cylindrical hoppers were superseded on ACF’s production line by the Centerflow in 1964, a revolutionary design that influenced later covered hopper types. In the late 60s or early 70s Canada came out with 4-bay covered hoppers that appear to be derived from ACF’s pre-Centerflow cylindrical hoppers. These cars were used by CN, CP and various smaller Canadian shippers. There is some question as to why the Canadian builder based their design off the older cylindrical and not ACF’s newer Centerflow. It was likely a patent issue and copying it could have triggered legal action against the Canadian builders. There are also certain structural design differences between the cylindrical and centerflow cars and perhaps the decision to copy the cylindrical was based on the greater volume capacity of the cylindrical design.
Road Name History: The New York Central Railroad (reporting mark NYC), known simply as the New York Central in its publicity, was a railroad operating in the Northeastern United States. Headquartered in New York City, the railroad served most of the Northeast, including extensive trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, and Massachusetts, plus additional trackage in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: On May 1, 1961, Bowser was purchased by Lewis and Shirlee English and moved from Redlands, CA to their basement in Muncy, PA. The original Bowser Manufacturing Co first advertised in the model railroad magazines in November 1948. At that time, the company had only one (HO Scale) engine, the Mountain, which had a cast brass boiler that is no longer available. It was sometime later that Bowser (Redlands) developed the NYC K-11 and the UP Challenger. The molds were made by K. Wenzlaff who introduced himself at the MRIA Show in Pasadena, CA in 1985 These two locomotives are still current production.
Bowser entered into N Scale in 1998 with their acquisition of the Delaware Valley Car Company, a manufacturer of N scale freight cars.
Bowser entered into N Scale in 1998 with their acquisition of the Delaware Valley Car Company, a manufacturer of N scale freight cars.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-08-30 10:56:15
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.