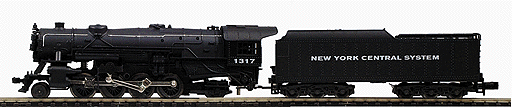
Specific Item Information: Steam 2-8-2 Heavy Mikado w/Long-Distance Tender Powered -- New York Central
Model Information: This model was first developed by Rivarossi for Atlas and released in 1969. The model uses much the same design as Rivarossi's earlier 4-6-2 and 0-8-0 models. The first several releases were models of the USRA light Mikado. In 1982, a version was created to model the Heavy Mikado. Atlas was the sole importer of the early version through 1977. After that Con-Cor started importing them, and it at under Con-Cor's request that the 'Heavy' version was developed. Con-Cor continued to import these models (with no significant changes) through 2006 when Rivarossi went bankrupt.
Compared with the later Kato-made steamers of the 1980s, these locomotives are not very good. They use a fairly wonky electrical pickup scheme which may require some fiddling in order to produce reliable current. They don't have much in the way of shell detail either.
Compared with the later Kato-made steamers of the 1980s, these locomotives are not very good. They use a fairly wonky electrical pickup scheme which may require some fiddling in order to produce reliable current. They don't have much in the way of shell detail either.
DCC Information: Don't even think about it.
Prototype History: The Heavy Mikado was "conceived" under the auspices of the United States Railway Administration (USRA), an agency established during WWI to regulate the railroad industry during the war.
One of the first undertakings of the USRA was to develop locomotive (and rolling stock) designs that the railroads could share.
This "common design" program was highly successful in streamlining production, and many USRA engines were used long after the war was over, essentially "outliving" the agency that conceived them.
The 2-8-2 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and one trailing axle. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, or shortened to just "Mike". The USRA ultimately created 12 different steam locomotive designs, including both the Heavy Mikado and Light Mikado. Both the Light and Heavy Mikado used the same 63" drivers and running gear, but the Heavy Mike had a fatter boiler and put out more pounds on the drivers. This resulted in a more powerful locomotive.
Under the USRA's watch, 233 Heavy Mikados were built. Including copies built later, the total number of Heavy Mikes was 957 units, purchased originally by 23 different railroads, primarily in freight service. Some Mikado steam engine are still in service today, employed mostly for tourist or railfan trips.
The 2-8-2 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and one trailing axle. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, or shortened to just "Mike". The USRA ultimately created 12 different steam locomotive designs, including both the Heavy Mikado and Light Mikado. Both the Light and Heavy Mikado used the same 63" drivers and running gear, but the Heavy Mike had a fatter boiler and put out more pounds on the drivers. This resulted in a more powerful locomotive.
Under the USRA's watch, 233 Heavy Mikados were built. Including copies built later, the total number of Heavy Mikes was 957 units, purchased originally by 23 different railroads, primarily in freight service. Some Mikado steam engine are still in service today, employed mostly for tourist or railfan trips.
Road Name History: The New York Central Railroad (reporting mark NYC), known simply as the New York Central in its publicity, was a railroad operating in the Northeastern United States. Headquartered in New York City, the railroad served most of the Northeast, including extensive trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, and Massachusetts, plus additional trackage in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Con-Cor has been in business since 1962. Many things have changed over time as originally they were a complete manufacturing operation in the USA and at one time had upwards of 45 employees. They not only designed the models,but they also built their own molds, did injection molding, painting, printing and packaging on their models.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-08-20 21:30:51
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.