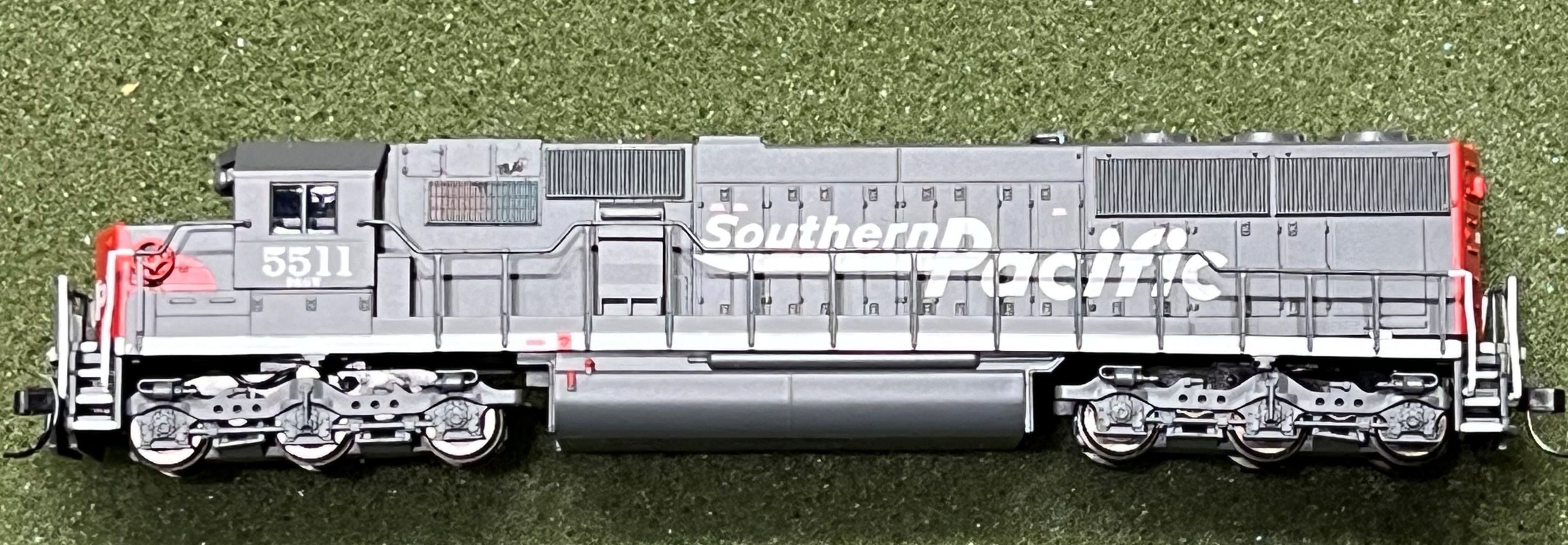
Series Information:
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:Early Gold Series equipped with ESU’s Exclusive "Full Throttle" features for ultimate realism in prototype running.
Over 20 sound effects are available, including engine start-up and shutdown, prime mover sounds through all eight notches, bell, air horn, air compressor, dynamic brakes and more.
There are up to 16 user-selectable horns, 2 user-selectable bells, and 2 user-selectable synchronized brake squeals.
2024 Releases feature Soundtraxx Tsunami Decoder NMRA 21-pin plug.
DCC OPERATION FEATURES:
- Supports all DCC-programming modes
- DCC includes RailCom and RailComPlus, with 14, 28 or 128 speed steps and with 2-digit and 4-digit addressing.
- Flexible mapping of function keys F0 to F28.
- A total of 6 DCC function outputs are available, and all can be function mapped (disable, brightness, light effects) individually
- Follows all NMRA DCC standards and recommended practices.
Model Information: Atlas introduced the SD60 in 1998. The SD50 and SD60M followed in 1999. In 2002 they revised the SD60M and SD50. In 2005, Atlas revised the SD60. All three models (SD60, SD60M and SD50) share the same mechanism and differ only in shell detailing. These models also come with uninstalled detail parts such as snow-plow and winterization hatches. These details must be installed by the owner.
The revised versions all carry typical post-2000 mechanisms. Therefore, we see features such as dial flywheels, all-wheel pickup and drive, blackened metal wheels, bi-directional lighting, a split-frame DCC-Ready chassis and easily-swappable body-mount couplers. The revised version feature Atlas' slow-speed motor, golden white LEDs and nicely painted two-tone handrails. Yes, they run very nicely.
The revised versions all carry typical post-2000 mechanisms. Therefore, we see features such as dial flywheels, all-wheel pickup and drive, blackened metal wheels, bi-directional lighting, a split-frame DCC-Ready chassis and easily-swappable body-mount couplers. The revised version feature Atlas' slow-speed motor, golden white LEDs and nicely painted two-tone handrails. Yes, they run very nicely.
DCC Information: The revised version of this model is DCC ready. It is available either in DC or DCC-equipped, with Lenz LE062XF for earlier runs, and with NCE N12A1 for more recent ones.
Models accept the following after market plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A1: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale SD60, SD60M, SD50 and others.
- TCS ALD4: Four Function decoder, for Atlas Long length Drop-in.
- NCE N12A1: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas SD50, SD60M, SD60.
Models accept the following after market plug-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163A1: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Atlas N-Scale SD60, SD60M, SD50 and others.
- TCS ALD4: Four Function decoder, for Atlas Long length Drop-in.
- NCE N12A1: Plug and play decoder for N-Scale Atlas SD50, SD60M, SD60.
Prototype History: The SD50 was produced in response to increasingly tough competition from GE Transportation Systems, whose Dash 7 line was proving quite successful with railroads. While EMD's SD40-2 was a reliable and trusted product, GE's line included locomotives up to 3,600 hp (2,685 kW) with more modern technology, as well as very competitive finance and maintenance deals. EMD responded throughout the SD50 program by offering discounts on large orders.
GM-EMD had previously produced 3,600 hp (2,685 kW) locomotives, the SD45 and later SD45-2, but these used huge, 20-cylinder engines with high fuel consumption, and had reliability problems when first introduced. Demand for the 45 series dropped sharply after the 1970s fuel crisis. The SD50 used an updated version of the V16 645 used in the SD40-2, uprated to 3,500 hp (2,600 kW)- and later 3,600 hp (2,685 kW) - at 950 rpm from 3,000 hp (2,240 kW) at 900 rpm. This proved to be a step too far; the 50 series models were plagued by engine and electrical system problems which harmed both sales and the reputation of EMD.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
GM-EMD had previously produced 3,600 hp (2,685 kW) locomotives, the SD45 and later SD45-2, but these used huge, 20-cylinder engines with high fuel consumption, and had reliability problems when first introduced. Demand for the 45 series dropped sharply after the 1970s fuel crisis. The SD50 used an updated version of the V16 645 used in the SD40-2, uprated to 3,500 hp (2,600 kW)- and later 3,600 hp (2,685 kW) - at 950 rpm from 3,000 hp (2,240 kW) at 900 rpm. This proved to be a step too far; the 50 series models were plagued by engine and electrical system problems which harmed both sales and the reputation of EMD.
From Wikipedia
Read more on American-Rails.com
Road Name History:  The Southern Pacific Transportation Company (reporting mark SP), earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually called the Southern Pacific or (from the railroad's initials) Espee, was an American Class I railroad. It was absorbed in 1988 by the company that controlled the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad and eight years later became part of the Union Pacific Railroad.
The Southern Pacific Transportation Company (reporting mark SP), earlier Southern Pacific Railroad and Southern Pacific Company, and usually called the Southern Pacific or (from the railroad's initials) Espee, was an American Class I railroad. It was absorbed in 1988 by the company that controlled the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad and eight years later became part of the Union Pacific Railroad.
The railroad was founded as a land holding company in 1865, later acquiring the Central Pacific Railroad by lease. By 1900 the Southern Pacific Company was a major railroad system incorporating many smaller companies, such as the Texas and New Orleans Railroad and Morgan's Louisiana and Texas Railroad. It extended from New Orleans through Texas to El Paso, across New Mexico and through Tucson, to Los Angeles, through most of California, including San Francisco and Sacramento. Central Pacific lines extended east across Nevada to Ogden, Utah, and reached north through Oregon to Portland. Other subsidiaries eventually included the St. Louis Southwestern Railway (Cotton Belt), the Northwestern Pacific Railroad at 328 miles (528 km), the 1,331 miles (2,142 km) Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico, and a variety of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge routes.
In 1929 SP/T&NO operated 13848 route-miles not including Cotton Belt, whose purchase of the Golden State Route circa 1980 nearly doubled its size to 3,085 miles (4,965 km), bringing total SP/SSW mileage to around 13,508 miles (21,739 km).
By the 1980s route mileage had dropped to 10,423 miles (16,774 km), mainly due to the pruning of branch lines. In 1988 the Southern Pacific was taken over by D&RGW parent Rio Grande Industries. The combined railroad kept the Southern Pacific name due to its brand recognition in the railroad industry and with customers of both constituent railroads. Along with the addition of the SPCSL Corporation route from Chicago to St. Louis, the total length of the D&RGW/SP/SSW system was 15,959 miles (25,684 km).
By 1996 years of financial problems had dropped SP's mileage to 13,715 miles (22,072 km), and it was taken over by the Union Pacific Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The railroad was founded as a land holding company in 1865, later acquiring the Central Pacific Railroad by lease. By 1900 the Southern Pacific Company was a major railroad system incorporating many smaller companies, such as the Texas and New Orleans Railroad and Morgan's Louisiana and Texas Railroad. It extended from New Orleans through Texas to El Paso, across New Mexico and through Tucson, to Los Angeles, through most of California, including San Francisco and Sacramento. Central Pacific lines extended east across Nevada to Ogden, Utah, and reached north through Oregon to Portland. Other subsidiaries eventually included the St. Louis Southwestern Railway (Cotton Belt), the Northwestern Pacific Railroad at 328 miles (528 km), the 1,331 miles (2,142 km) Southern Pacific Railroad of Mexico, and a variety of 3 ft (914 mm) narrow gauge routes.
In 1929 SP/T&NO operated 13848 route-miles not including Cotton Belt, whose purchase of the Golden State Route circa 1980 nearly doubled its size to 3,085 miles (4,965 km), bringing total SP/SSW mileage to around 13,508 miles (21,739 km).
By the 1980s route mileage had dropped to 10,423 miles (16,774 km), mainly due to the pruning of branch lines. In 1988 the Southern Pacific was taken over by D&RGW parent Rio Grande Industries. The combined railroad kept the Southern Pacific name due to its brand recognition in the railroad industry and with customers of both constituent railroads. Along with the addition of the SPCSL Corporation route from Chicago to St. Louis, the total length of the D&RGW/SP/SSW system was 15,959 miles (25,684 km).
By 1996 years of financial problems had dropped SP's mileage to 13,715 miles (22,072 km), and it was taken over by the Union Pacific Railroad.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: CMK on 2021-05-14 11:29:31. Last edited by Alain LM on 2024-11-04 04:02:07
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.