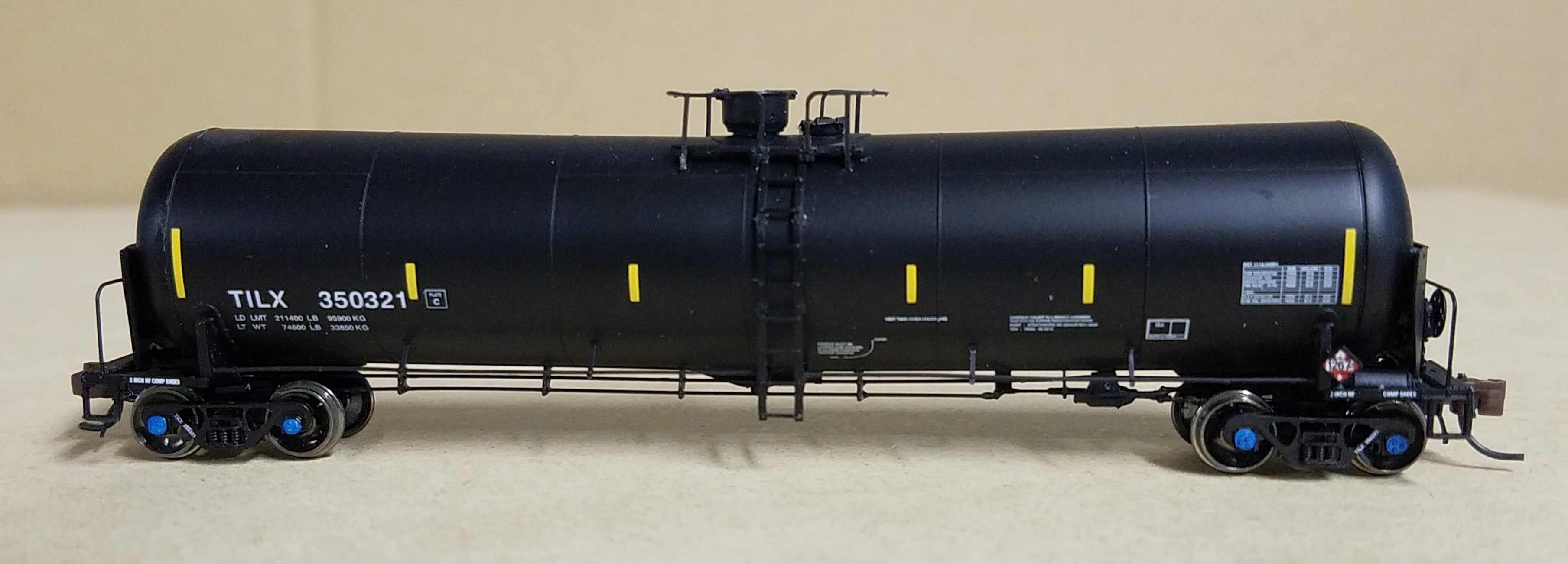
Model Information: Model: Introduction: October 2009. ERA: 1960s to present (depending on road name). Three bodies available: C-50-7, C-50-8 and C-50-9
Features: Body mounted McHenry knuckle spring couplers,Weighted for optimum performance, Partial interior, Separately applied wire grab irons, New truck tooling including axle mounted generator, End walkway tread, Etched window screens included, Finely detailed end railing and brake wheel, Fully detailed underbody, Window glazing, Plastic/etched roof detail (antenna, marker light, smoke jack and vent) when appropriate per prototype.
Features: Body mounted McHenry knuckle spring couplers,Weighted for optimum performance, Partial interior, Separately applied wire grab irons, New truck tooling including axle mounted generator, End walkway tread, Etched window screens included, Finely detailed end railing and brake wheel, Fully detailed underbody, Window glazing, Plastic/etched roof detail (antenna, marker light, smoke jack and vent) when appropriate per prototype.
Prototype History: In a bay window caboose, the crew monitoring the train sits in the middle of the car in a section of wall that projects from the side of the caboose. The windows set into these extended walls resemble architectural bay windows, so the caboose type is called a bay window caboose. This type afforded a better view of the side of the train and eliminated the falling hazard of the cupola. The bay window gained favor with many railroads because it eliminated the need for additional clearances in tunnels and overpasses. On the west coast, the Milwaukee Road and the Northern Pacifc Railway used these cars, converting over 900 roof top cabooses to bay window cabooses in the late 1930's. Milwaukee Road rib-side window cabooses are preserved at New Libson, Wisconsin, the Illinois Railway Museum, the Mt. Rainer Scenic Railroad, and Cedarburg, Wisconsin.
When the shift was made from wooden to steel caboose construction, a new type of caboose also arrived. The new caboose design replaced the traditional roof-mounted “cupola” with “bay-windows” attached to the sides of the caboose. As freight cars grew taller, the effectiveness of cupolas as practical observation points was diminished. This was especially true on lines that suffered from low clearances and were incapable of making cupolas high enough to see over the top of the tallest freight cars. Cabooses were prone to rough handling, and many a trainman was knocked out of his perch in the cupola and injured when he fell. The new caboose design was safer as well as more effective.
When the shift was made from wooden to steel caboose construction, a new type of caboose also arrived. The new caboose design replaced the traditional roof-mounted “cupola” with “bay-windows” attached to the sides of the caboose. As freight cars grew taller, the effectiveness of cupolas as practical observation points was diminished. This was especially true on lines that suffered from low clearances and were incapable of making cupolas high enough to see over the top of the tallest freight cars. Cabooses were prone to rough handling, and many a trainman was knocked out of his perch in the cupola and injured when he fell. The new caboose design was safer as well as more effective.
Road Name History: The New York Central Railroad (reporting mark NYC), known simply as the New York Central in its publicity, was a railroad operating in the Northeastern United States. Headquartered in New York City, the railroad served most of the Northeast, including extensive trackage in the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, and Massachusetts, plus additional trackage in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St.Louis in the midwest along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Detroit. NYC's Grand Central Terminal in New York City is one of its best known extant landmarks.
1853 company formation: Albany industrialist and Mohawk Valley Railroad owner Erastus Corning managed to unite ten railroads together into one system, and on March 17, 1853 executives and stockholders of each company agreed to merge. The merger was approved by the state legislature on April 2, and by May 17, 1853 the New York Central Railroad was formed.
In 1867 Vanderbilt acquired control of the Albany to Buffalo running NYC. On November 1, 1869 he merged the NYC with his Hudson River Railroad into the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad. Vanderbilt's other lines were operated as part of the NYC.
In 1914, the operations of eleven subsidiaries were merged with the New York Central & Hudson River Railroad, re-forming the New York Central Railroad. From the beginning of the merge, the railroad was publicly referred to as the New York Central Lines. In the summer of 1935, the identification was changed to the New York Central System.
In 1968 the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central (the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad joined in 1969). That company went bankrupt in 1970 and was taken over by the federal government and merged into Conrail in 1976. Conrail was broken up in 1998, and portions of its system was transferred to the newly formed New York Central Lines LLC, a subsidiary leased to and eventually absorbed by CSX and Norfolk Southern. Those companies' lines included the original New York Central main line, but outside that area it included lines that were never part of the New York Central system. CSX was able to take one of the most important main lines in the nation, which runs from New York City and Boston to Cleveland, Ohio, as part of the Water Level Route, while Norfolk Southern gained the Cleveland, Ohio to Chicago, Illinois portion of the line called the Chicago line.
At the end of 1925, the New York Central System operated 11,584 miles (18,643 km) of road and 26,395 miles (42,479 km) of track; at the end of 1967 the mileages were 9,696 miles (15,604 km) and 18,454 miles (29,699 km).
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Athearn's history began in 1938, when its founder-to-be, Irvin Athearn, started an elaborate O scale layout in his mother's house. After placing an ad selling the layout, and receiving much response to it, Irv decided that selling model railroads would be a good living. He sold train products out of his mother's house through most of the 1940s. After becoming a full-time retailer in 1946, Irv opened a separate facility in Hawthorne, California in 1948, and that same year he branched into HO scale models for the first time.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2021-02-11 14:35:55
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.