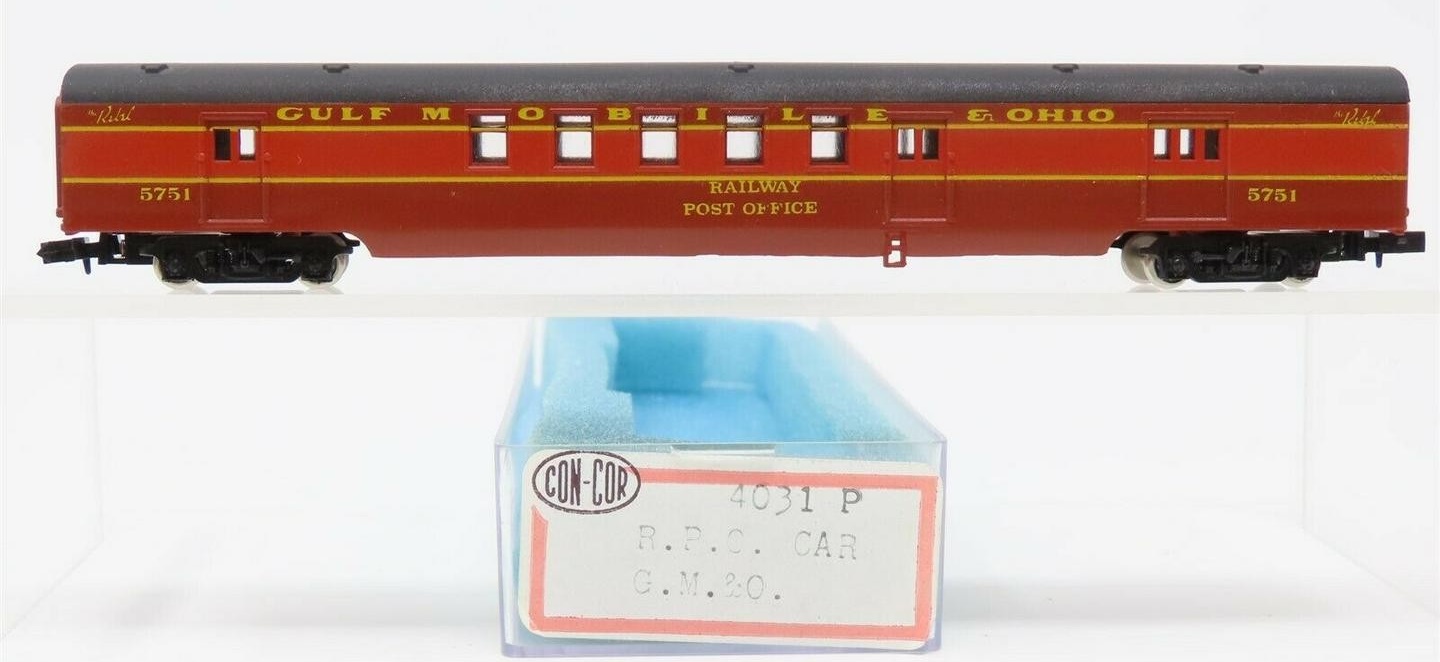
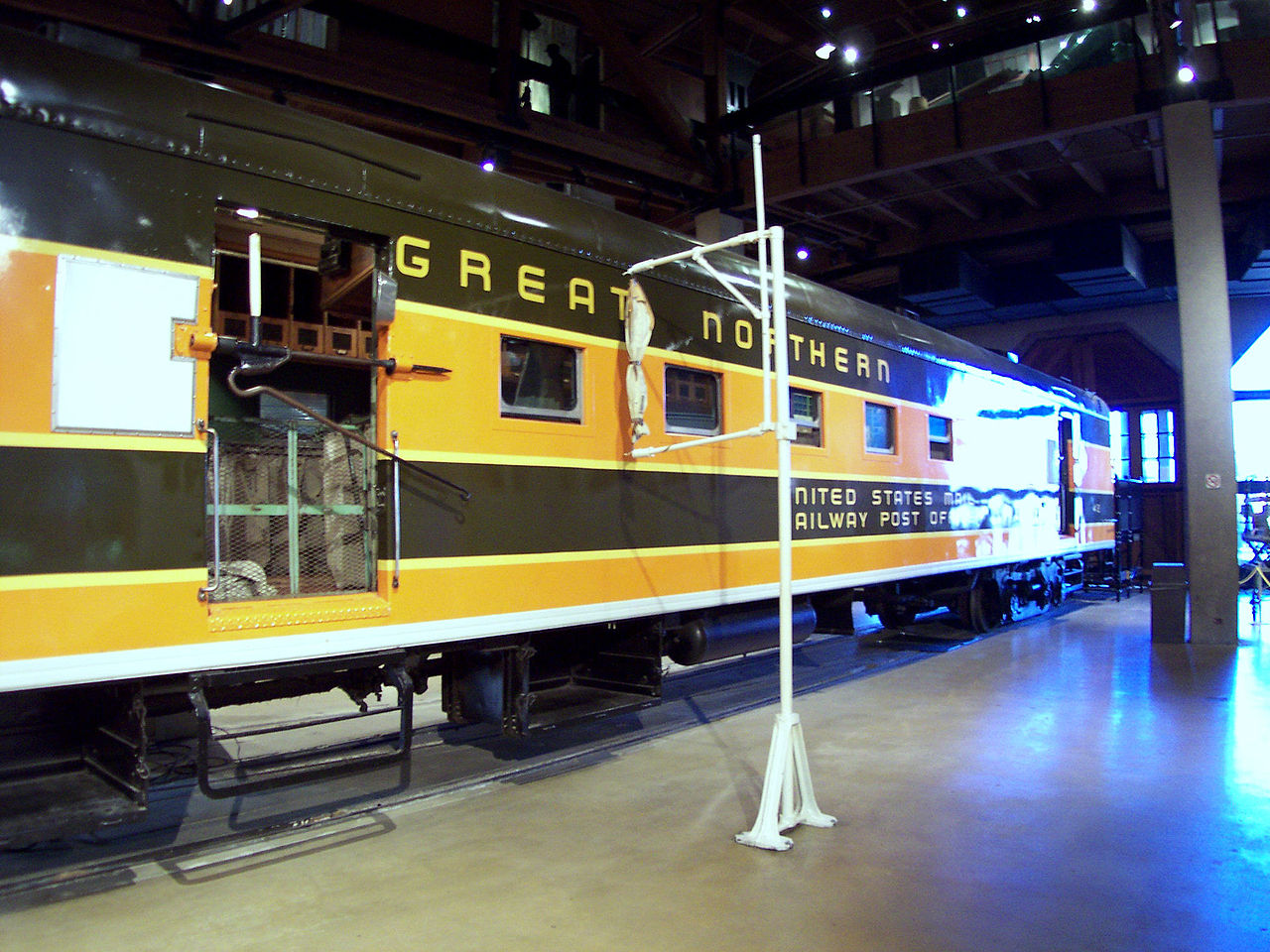
Model Information: This model was designed by Con-Cor in the 1970s. It is modeled after the AC&F RPO built for GN in 1950-51 as series 37-42. It has a 60’ RPO compartment, with 5 windows in the middle of the car, and 3 doors The double windows on the model are however different from the prototype, that are smaller single windows.
The molds were damaged at some point, so the production of this model stopped definitively by end of the 1980s. Con-Cor redesigned a new RPO, modeled after a Pullman Standard build for the GN; the newer RPO (still produced) has only 3 double-windows, located at one end of the car, and only 2 doors.
The molds were damaged at some point, so the production of this model stopped definitively by end of the 1980s. Con-Cor redesigned a new RPO, modeled after a Pullman Standard build for the GN; the newer RPO (still produced) has only 3 double-windows, located at one end of the car, and only 2 doors.
Prototype History: In the post-war period, passenger rail service boomed. In order to increase efficiency, the railroads set to replacing their old wood, steel and concrete heavyweight passenger cars with newer lightweight, streamlined cars. The new cars were made from stainless steel, aluminum and Cor-Ten steel. These cars required less motive power to pull and were cheaper to manufacture. Production was also concentrated in a few manufacturers rather than each railroad making its own. This led to standardization which further reduced costs. The new "lightweight" cars were also given "streamlined" designs to make them more visually appealing. Budd, Pullman Standard and ACF were all well known manufacturers of these cars.
A railway post office, commonly abbreviated as RPO, was a railroad car that was normally operated in passenger service as a means to sort mail en route, in order to speed delivery. The RPO was staffed by highly trained Railway Mail Service postal clerks, and was off-limits to the passengers on the train.
This particular prototype represents the AC&F RPO-baggage built for GN in 1950-51 as series 37-42. It has a 60’ RPO compartment, with 5 windows and 2 doors, and a third door for the storage / baggage section. See here for more details.
Read more about RPOs on Wikipedia
A railway post office, commonly abbreviated as RPO, was a railroad car that was normally operated in passenger service as a means to sort mail en route, in order to speed delivery. The RPO was staffed by highly trained Railway Mail Service postal clerks, and was off-limits to the passengers on the train.
This particular prototype represents the AC&F RPO-baggage built for GN in 1950-51 as series 37-42. It has a 60’ RPO compartment, with 5 windows and 2 doors, and a third door for the storage / baggage section. See here for more details.
Read more about RPOs on Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The GM&O was the product of the 1940 merger of Gulf Mobile & Northern and the Mobile & Ohio. During these early years, the GM&O consisted of a route from St. Louis south to Jackson, Tennessee where it then split into 2 routes to the port of Mobile, Alabama. In addition, there were routes to Memphis, Tennessee; Jackson, Mississippi; and Birmingham and Montgomery, Alabama. GM&O also served New Orleans and Paducah via trackage rights. The merger was championed by Ike Tigrett from the GM&N and Ike would lead the GM&O for most of its history.
The GM&O was the product of the 1940 merger of Gulf Mobile & Northern and the Mobile & Ohio. During these early years, the GM&O consisted of a route from St. Louis south to Jackson, Tennessee where it then split into 2 routes to the port of Mobile, Alabama. In addition, there were routes to Memphis, Tennessee; Jackson, Mississippi; and Birmingham and Montgomery, Alabama. GM&O also served New Orleans and Paducah via trackage rights. The merger was championed by Ike Tigrett from the GM&N and Ike would lead the GM&O for most of its history.
In 1947, GM&O acquired the Alton Railroad. This linked Chicago and Peoria with St. Louis and Kansas City. This acquisition made GM&O a Great Lakes to the Gulf carrier and pushed the mileage up over 2,700. GM&O tried to sell the Kansas City line in the 50’s to Santa Fe and Burlington but there was tremendous pressure from other lines to keep Santa Fe out of St. Louis. In the end, GM&O kept the route and Burlington got trackage rights on a portion of it to shorten its own route.
GM&O dieselized early with the last steam locomotive retired in 1949. The first generation freight diesel fleet included Alco switchers, road switchers (all of which were long-hood-forward,) and FA series cab units and EMD F units. For passenger service, GM&O had power from both Alco and EMD. Everything was painted red and maroon with gold lettering. Both Alton and GM&N had used red in the past so this was appropriate. The oddball of the fleet was #1900, a cab unit model 4-S built by Ingalls Shipbuilding. It was the only locomotive Ingalls would ever build.
The 60’s brought fleets of GP30’s and 35’s. These were delivered on Alco trucks from traded in FA’s and wore a new black and white paint scheme designed by EMD. A few years later, more new power arrived from EMD, this time GP38’s and SD40’s wearing two variations of red and white. First generation diesels still on the roster received solid red or maroon in some cases. The diesel fleet consisted of around 260 units.
As for passenger service, The Rebels ran south of St. Louis with a train each to New Orleans and Mobile. Seven trains a day connected St. Louis and Chicago – more than all other railroads combined between those cities. These included the Abraham Lincoln, Ann Rutledge, and Alton Limited. They also had a single daily Chicago commuter train called The Plug. Amtrak took over three of the Chicago – St. Louis departures in 1971.
By contemporary accounts, GM&O was a class operation with a thin layer of responsive management, esprit de corps in the ranks, and good track - all of this despite serving one of the poorest regions of the country. As the 1960s drew to a close, GM&O faced the impending retirement of the original management team. Because the management layer was so thin, there were few young up-and-comers being groomed to take their places. So, to protect the shareholders, GM&O began shopping for merger partners. In 1972, Gulf Mobile & Ohio merged with Illinois Central to form Illinois Central Gulf.

In 1947, GM&O acquired the Alton Railroad. This linked Chicago and Peoria with St. Louis and Kansas City. This acquisition made GM&O a Great Lakes to the Gulf carrier and pushed the mileage up over 2,700. GM&O tried to sell the Kansas City line in the 50’s to Santa Fe and Burlington but there was tremendous pressure from other lines to keep Santa Fe out of St. Louis. In the end, GM&O kept the route and Burlington got trackage rights on a portion of it to shorten its own route.
GM&O dieselized early with the last steam locomotive retired in 1949. The first generation freight diesel fleet included Alco switchers, road switchers (all of which were long-hood-forward,) and FA series cab units and EMD F units. For passenger service, GM&O had power from both Alco and EMD. Everything was painted red and maroon with gold lettering. Both Alton and GM&N had used red in the past so this was appropriate. The oddball of the fleet was #1900, a cab unit model 4-S built by Ingalls Shipbuilding. It was the only locomotive Ingalls would ever build.
The 60’s brought fleets of GP30’s and 35’s. These were delivered on Alco trucks from traded in FA’s and wore a new black and white paint scheme designed by EMD. A few years later, more new power arrived from EMD, this time GP38’s and SD40’s wearing two variations of red and white. First generation diesels still on the roster received solid red or maroon in some cases. The diesel fleet consisted of around 260 units.
As for passenger service, The Rebels ran south of St. Louis with a train each to New Orleans and Mobile. Seven trains a day connected St. Louis and Chicago – more than all other railroads combined between those cities. These included the Abraham Lincoln, Ann Rutledge, and Alton Limited. They also had a single daily Chicago commuter train called The Plug. Amtrak took over three of the Chicago – St. Louis departures in 1971.
By contemporary accounts, GM&O was a class operation with a thin layer of responsive management, esprit de corps in the ranks, and good track - all of this despite serving one of the poorest regions of the country. As the 1960s drew to a close, GM&O faced the impending retirement of the original management team. Because the management layer was so thin, there were few young up-and-comers being groomed to take their places. So, to protect the shareholders, GM&O began shopping for merger partners. In 1972, Gulf Mobile & Ohio merged with Illinois Central to form Illinois Central Gulf.
Brand/Importer Information: Con-Cor has been in business since 1962. Many things have changed over time as originally they were a complete manufacturing operation in the USA and at one time had upwards of 45 employees. They not only designed the models,but they also built their own molds, did injection molding, painting, printing and packaging on their models.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2020-11-11 13:35:40. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-11-11 13:38:25
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.