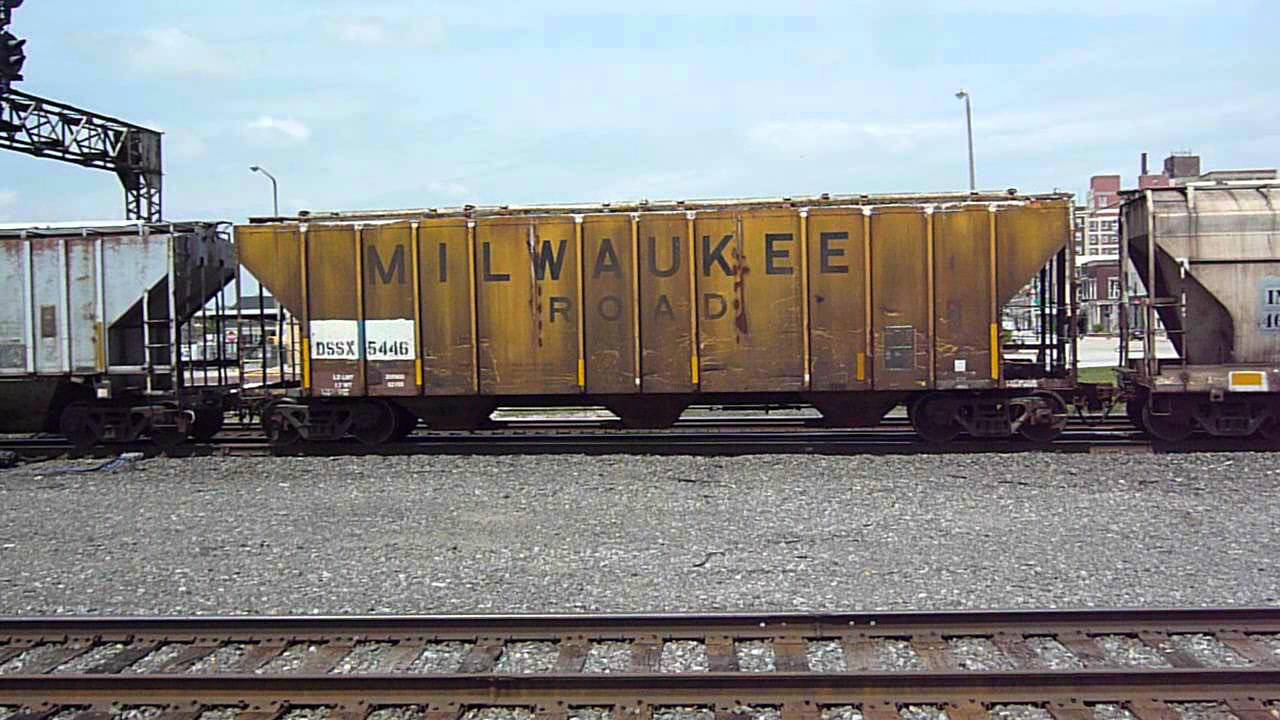Specific Item Information: Release 2
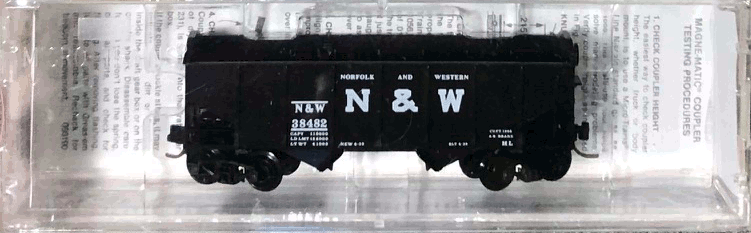
Designed from builder drawings and field measurements, the Pullman-Standard 4785cf Covered Hopper is perfect for modelers from the 1960s until today. Since the beginning, these cars have crisscrossed North America running in singles and groups in mixed freight trains. The Rivet Counter series model features different roof hatch, outlet gate, and, and end “cage” support variations per roadname and production group.
Designed from builder drawings and field measurements, the Pullman-Standard 4785cf Covered Hopper is perfect for modelers from the 1960s until today. Since the beginning, these cars have crisscrossed North America running in singles and groups in mixed freight trains. The Rivet Counter series model features different roof hatch, outlet gate, and, and end “cage” support variations per roadname and production group.
Model Information: One of the larger sizes offered in the Pullman-Standard covered hopper catalog, the PS-2CD 4785 cubic foot design could be optimized for a variety of commodities, from grain products, to chemical or mineral ladings. Introduced in 1967 and built at their Butler, PA plant, the basic design would see refinements to its basic design over its five-year production span. The end “cages” of the cars would change over this period, with revisions to the end grab iron and support arrangements. Later production would also feature tall shear plates as part of the end sills, adding another visual distinction to this family of cars.
Prototype History: Like their PS-1 boxcars, PS-5 gondolas and other car designs, Pullman Standard applied the PS-2 classification to all of its covered hoppers. Pullman Standard built covered hoppers in many sizes and configurations. But say “PS-2” to railfans and it is this particular car that usually first comes to mind. The 2003 cubic foot car was one of the first, smallest and prolific of the PS-2 cars.
Pullman began building its standardized freight car designs with the PS-1 boxcar in 1947. Next up would be a standard covered hopper – hence PS-2 – shortly thereafter. Although covered hoppers are among the most common cars on the rails today, in 1947 they were a rarity. The PS-2’s primary competition wasn’t other covered hopper designs but boxcars. Grain, cement, sand and dried chemicals were carried mostly in boxcars prior to the 1950s either in sacks and bags or poured in bulk through hatches in the roof. The theory here was that it made more sense to utilize a single car for a variety of products. The car could carry bags of cement one way and then cut lumber the other. Of course a car that could do many things often couldn’t do many of them well.
Pullman began building its standardized freight car designs with the PS-1 boxcar in 1947. Next up would be a standard covered hopper – hence PS-2 – shortly thereafter. Although covered hoppers are among the most common cars on the rails today, in 1947 they were a rarity. The PS-2’s primary competition wasn’t other covered hopper designs but boxcars. Grain, cement, sand and dried chemicals were carried mostly in boxcars prior to the 1950s either in sacks and bags or poured in bulk through hatches in the roof. The theory here was that it made more sense to utilize a single car for a variety of products. The car could carry bags of cement one way and then cut lumber the other. Of course a car that could do many things often couldn’t do many of them well.
Road Name History:  The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: ScaleTrains.com, Inc. is an upstart HO and N Scale model manufacturer that was founded by a team with more than 125 years of accumulated experience in the model railroad hobby and industry.
ScaleTrains is specifically focused on the tiny details in the printing and quality of the construction. The four friends who founded the company are all avid modelers themselves. Their factory is located in Tennessee. Unlike most other companies, they offer a range of different levels of complexity in their offerings so as to be able to provide products for both the budget-conscious collector as well as the detail-focused model enthusiast without compromising on quality for either.
They range covers the following, by increasing level of detailing:
ScaleTrains is specifically focused on the tiny details in the printing and quality of the construction. The four friends who founded the company are all avid modelers themselves. Their factory is located in Tennessee. Unlike most other companies, they offer a range of different levels of complexity in their offerings so as to be able to provide products for both the budget-conscious collector as well as the detail-focused model enthusiast without compromising on quality for either.
They range covers the following, by increasing level of detailing:
- Operator™ trains are built for modelers who enjoy running high-quality, realistic trains at an affordable price. Designed from builder’s drawings and photographs, Operator models have fewer factory-applied parts and simplified printing. For added versatility, super-detail parts are available separately.
- The Rivet Counter™ line strives to create the most accurately detailed models imaginable. The real-world counterpart is meticulously researched to ensure prototype fidelity. Each model features numerous factory applied parts including roadname and road number specific details whenever possible.
- Museum Quality™ models are historically accurate replicas of the most famous locomotives in North American railroading history. Exhaustive research and a commitment to perfection combine to create the ultimate scale model. Museum Quality trains establish new standards which make them just as legendary as the original.
Item created by: CMK on 2020-01-23 11:36:53. Last edited by CMK on 2020-05-12 10:21:35
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.