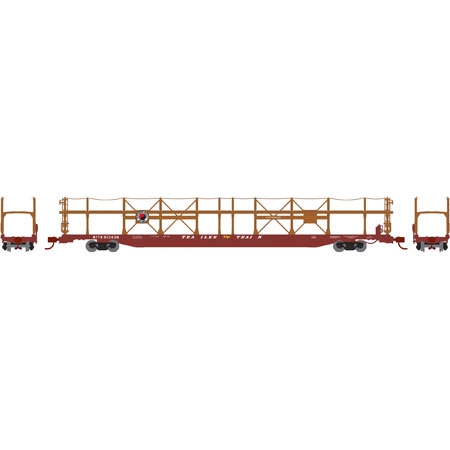
Model Information: New road numbers;
Era: 1941+;
Three road numbers;
Working drop ends. Gently lift up and push inward to fold ends down;
Factory installed wire grab irons;
Interior detailing;
Bettendorf trucks;
Fully-assembled and ready-to-run out of the box;
Accurately painted and printed;
Die cast body and underframe;
Separately applied brake wheel;
Machined metal wheels;
Screw mounted trucks;
McHenry operating knuckle couplers;
Weighted for trouble free operation;
Clear plastic jewel box for convenient storage;
Operates on Code 55 and 80 rail;
Minimum radius: 9 3/4";
Recommended radius: 11"
Prototype History: Generally used to haul scrap metal and loose bulk materials, gondola cars vary in length and side heights. Mill Gondola cars are more commonly used for high-density commodities and have a flat bottom while regular Gondola cars are most commonly used for coal or crushed aggregates and can have a flat or tub bottom configuration.
Steel-sided 65' mill gondolas date back to at least the 1940s, however specialized rib-sided "mill" gondolas are a relatively modern design. These cars are intended for use with the steel trade, and they are used to transport just about anything that can be loaded using an overheard crane. They date from the 1970s forward.
Steel-sided 65' mill gondolas date back to at least the 1940s, however specialized rib-sided "mill" gondolas are a relatively modern design. These cars are intended for use with the steel trade, and they are used to transport just about anything that can be loaded using an overheard crane. They date from the 1970s forward.
Road Name History: The EJ&E dates from 1888. For most of its history, it was owned by US Steel whose Gary Works is near the east end of the line. Another company owns the mill now.
The EJ&E traces a wide arc around the Chicago area between 30 and 40 miles from the city center from Waukegan on the north, around Walker and Joliet, then east as far as Porter, Indiana. Because of this, the EJ&E was known for years as “The Chicago Outer Belt.” It also had the nickname, “The J”.
EJ&E’s two biggest missions have been moving steel and acting as a transfer road for all of Chicago’s Class 1’s and shortlines. As a result, the line was heavily trafficked with 100 locomotives required to serve just 230 route miles. In addition, EJ&E had over 10,000 freight cars, a huge fleet for a line that size.
In the early diesel days, EJ&E stuck mostly with Baldwin and EMD with a few Alco RS2’s thrown in. The J had more Baldwin center cab transfer engines (DT 6-6-2000) than anyone else, in fact more than just about everyone else combined. Ballasted EMD SD7’s painted in green over orange were also used in transfer service. EMD NW2’s were the primary switchers. In 1970, the Baldwins were replaced by EMD SD38-2’s, delivered with dual controls to they could just as easily run long hood forward. By that time, EJ&E had gone to solid orange with silver trucks and fuel tanks with various striping and logo placement variations over the years. They would also toy with gold and yellow and green and yellow schemes.
In 2009 the Elgin Joliet & Eastern was acquired by Canadian National in order to link their former Wisconsin Central, Illinois Central, Chicago Central & Pacific, and Grand Trunk Western lines. These lines approached the city from different directions and had required trackage rights and terminal roads to reach each other so acquiring the EJ&E was a logical move.
The EJ&E traces a wide arc around the Chicago area between 30 and 40 miles from the city center from Waukegan on the north, around Walker and Joliet, then east as far as Porter, Indiana. Because of this, the EJ&E was known for years as “The Chicago Outer Belt.” It also had the nickname, “The J”.
EJ&E’s two biggest missions have been moving steel and acting as a transfer road for all of Chicago’s Class 1’s and shortlines. As a result, the line was heavily trafficked with 100 locomotives required to serve just 230 route miles. In addition, EJ&E had over 10,000 freight cars, a huge fleet for a line that size.
In the early diesel days, EJ&E stuck mostly with Baldwin and EMD with a few Alco RS2’s thrown in. The J had more Baldwin center cab transfer engines (DT 6-6-2000) than anyone else, in fact more than just about everyone else combined. Ballasted EMD SD7’s painted in green over orange were also used in transfer service. EMD NW2’s were the primary switchers. In 1970, the Baldwins were replaced by EMD SD38-2’s, delivered with dual controls to they could just as easily run long hood forward. By that time, EJ&E had gone to solid orange with silver trucks and fuel tanks with various striping and logo placement variations over the years. They would also toy with gold and yellow and green and yellow schemes.
In 2009 the Elgin Joliet & Eastern was acquired by Canadian National in order to link their former Wisconsin Central, Illinois Central, Chicago Central & Pacific, and Grand Trunk Western lines. These lines approached the city from different directions and had required trackage rights and terminal roads to reach each other so acquiring the EJ&E was a logical move.
Brand/Importer Information: Athearn's history began in 1938, when its founder-to-be, Irvin Athearn, started an elaborate O scale layout in his mother's house. After placing an ad selling the layout, and receiving much response to it, Irv decided that selling model railroads would be a good living. He sold train products out of his mother's house through most of the 1940s. After becoming a full-time retailer in 1946, Irv opened a separate facility in Hawthorne, California in 1948, and that same year he branched into HO scale models for the first time.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Athearn acquired the Globe Models product line and improved upon it, introducing a comprehensive array of locomotive, passenger and freight car models. Improvements included all-wheel drive and electrical contact. One innovation was the "Hi-Fi" drive mechanism, employing small rubber bands to transfer motion from the motor spindle to the axles. Another was the double-ended ring magnet motor, which permitted easy connection to all-wheel-drive assemblies. Athearn was also able to incorporate flywheels into double-ended drives.
The company produced a model of the Boston & Maine P4 class Pacific steam locomotive which incorporated a cast zinc alloy base and thermoplastic resin superstructure. It had a worm drive and all power pickup was through the bipolar trucks that carried the tender. This item was discontinued after the Wilson motor was no longer available, and was not redesigned for a more technologically advanced motor.
Athearn's car fleet included shorter-than-scale interpretations of passenger cars of Southern Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe Railroad prototypes. The company also offered a variety of scale-length freight cars with sprung and equalized trucks. The cars could be obtained in simple kit form, or ready-to-run in windowed display boxes. The comprehensive scope of the product line contributed to the popularity of HO as a model railroad scale, due to the ready availability of items and their low cost.
Irv Athearn died in 1991. New owners took control in 1994, but continued to follow Athearn's commitment to high-quality products at reasonable prices. Athearn was bought in 2004 by Horizon Hobby. Athearn was then moved from its facility in Compton to a new facility in Carson, California. In mid-2009, all remaining US production was moved to China and warehousing moved to parent Horizon Hobby. Sales and product development was relocated to a smaller facility in Long Beach, California.
Read more on Wikipedia and Athearn website.
Item created by: Jenna on 2019-10-25 15:17:46. Last edited by CMK on 2020-06-01 03:31:20
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.