Model Information: This product first became available in September of 2019.
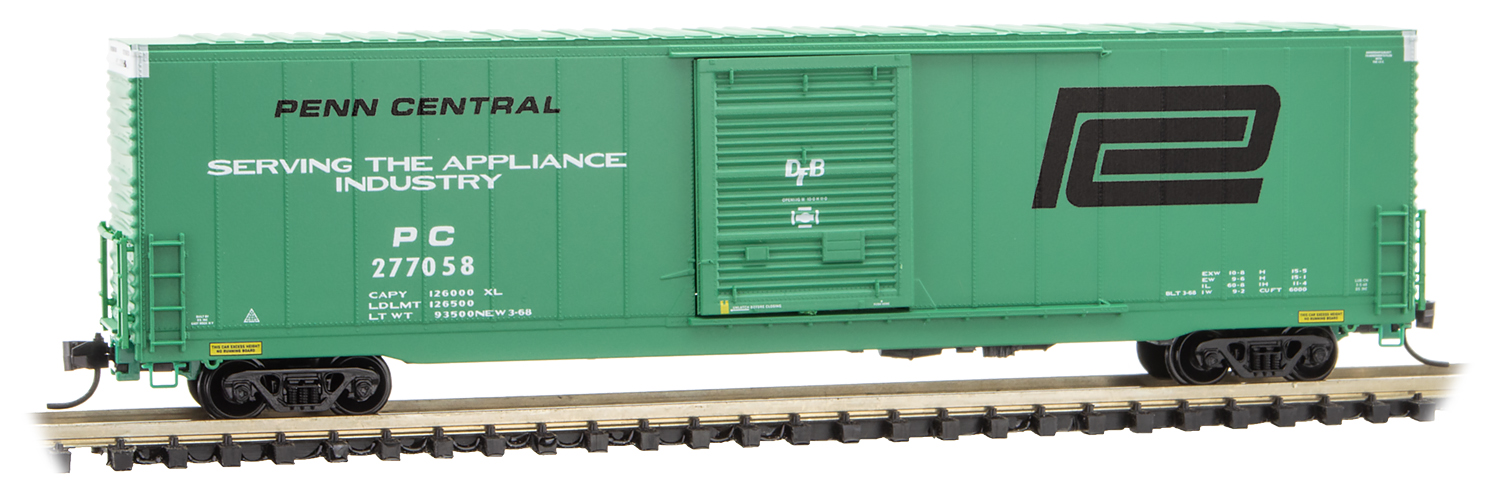
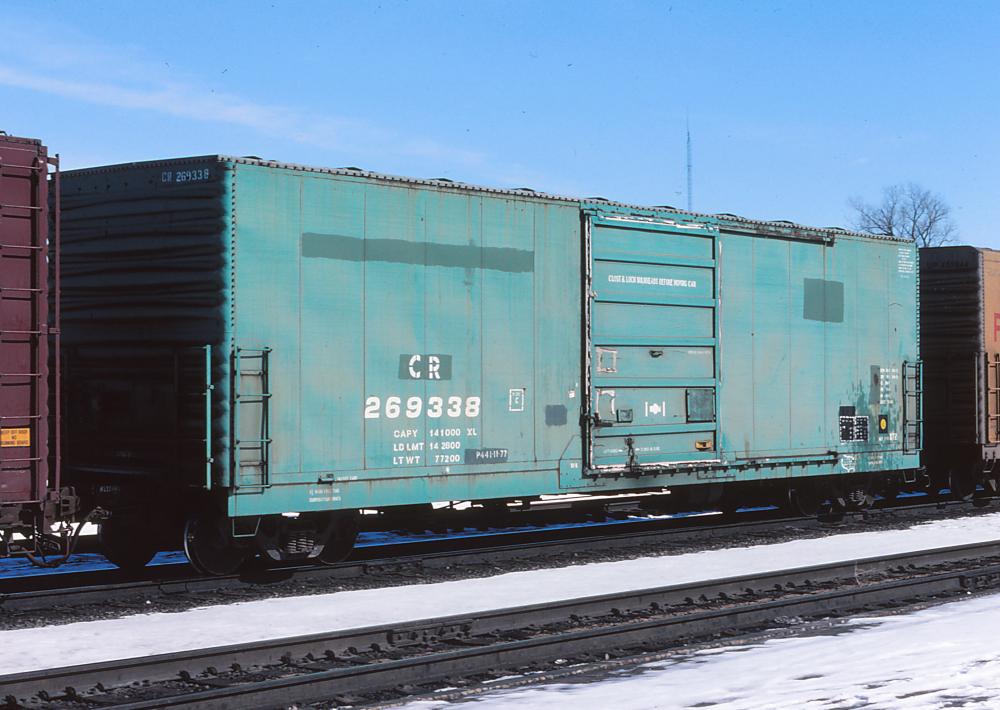
Prototype History: Between 1972 and 1973, Penn Central began purchasing the first of the 50' X72 boxcars from US Railroad Manufacturing (Evans) Blue Island, IL, plant. These cars would eventually find their way to Conrail in 1976, retaining their PC numbering series while getting CR reporting marks. However, many X72's can still be spotted in their original PC green paint scheme and PC reporting marks, though fairly rusted and faded.
There is only one subclass of the X72, the X72A. But as Jim Six points out in his Railroad Model Craftsman article, there appears to be no external distinction between the X72 and X72A. Both cars have welded panel construction, with 6-panel Superior doors. Yet I have photographed one X72, CR 269272, with a 6-panel Superior door with raised X-panels, for which no detail part is available.
The X72 is a general purpose boxcar that can be found in nearly every service, making is a very common boxcar. Some cars are equipped with DF Belt Loaders for assisting in loading and unloading of special equipment, while other cars are equipped with Dual Air Paks for shock control of goods, and pallets. These specially equipped cars are in assigned service to specific industries for specific loading.
There is only one subclass of the X72, the X72A. But as Jim Six points out in his Railroad Model Craftsman article, there appears to be no external distinction between the X72 and X72A. Both cars have welded panel construction, with 6-panel Superior doors. Yet I have photographed one X72, CR 269272, with a 6-panel Superior door with raised X-panels, for which no detail part is available.
The X72 is a general purpose boxcar that can be found in nearly every service, making is a very common boxcar. Some cars are equipped with DF Belt Loaders for assisting in loading and unloading of special equipment, while other cars are equipped with Dual Air Paks for shock control of goods, and pallets. These specially equipped cars are in assigned service to specific industries for specific loading.
Road Name History:  The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American Class I railroad headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, that operated from 1968 until 1976. It was created by the 1968 merger of the Pennsylvania and New York Central railroads. The New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad was added to the merger in 1969; by 1970, the company had filed for what was, at that time, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history.
The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.

The Penn Central was created as a response to challenges faced by all three railroads in the late 1960s. The northeastern quarter of the United States, these railroads' service area, was the most densely populated region of the U.S. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew a high percentage of their revenues from the long-distance shipment of commodities such as coal, lumber, paper and iron ore, Northeastern railroads traditionally depended on a mix of services.
As it turned out, the merged Penn Central was little better off than its constituent roads were before. A merger implementation plan was drawn up, but not carried out. Attempts to integrate operations, personnel and equipment were not very successful, due to clashing corporate cultures, incompatible computer systems and union contracts. Track conditions deteriorated (some of these conditions were inherited from the three merged railroads) and trains had to be run at reduced speeds. This meant delayed shipments and personnel working a lot of overtime. As a result, operating costs soared. Derailments and wrecks became frequent, particularly in the midwest.
The American financial system was shocked when after only two years of operations, the Penn Central Transportation company was put into bankruptcy on June 21, 1970. It was the largest corporate bankruptcy in American history at that time. Although the Penn Central Transportation Company was put into bankruptcy, its parent Penn Central Company was able to survive.
The Penn Central continued to operate freight service under bankruptcy court protection. After private-sector reorganization efforts failed, Congress nationalized the Penn Central under the terms of the Railroad Revitalization and Regulatory Reform Act of 1976. The new law folded six northeastern railroads, the Penn Central and five smaller, failed lines, into the Consolidated Rail Corporation, commonly known as Conrail. The act took effect on April 1, 1976.
Read more on Wikipedia.
Brand/Importer Information: Eastern Seaboard Models was founded in 1987. They are a manufacturer of N scale reproductions of North American eastern railroad prototypes. The have both decorated other manufacturers' models as well as designed body styles of their own. They are located at PO Box 301, Waldwick, New Jersey 07463-0301 U.S.A.
Their 2016 lineup includes ready-to-run gondolas, well cars, hoppers, tank cars and boxcars. They also produce craftsman quality kits in their "Made in America" series. ESM products may be purchased directly from their website.
Their 2016 lineup includes ready-to-run gondolas, well cars, hoppers, tank cars and boxcars. They also produce craftsman quality kits in their "Made in America" series. ESM products may be purchased directly from their website.
Item created by: gdm on 2019-09-29 16:46:38. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-05-21 15:37:10
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.