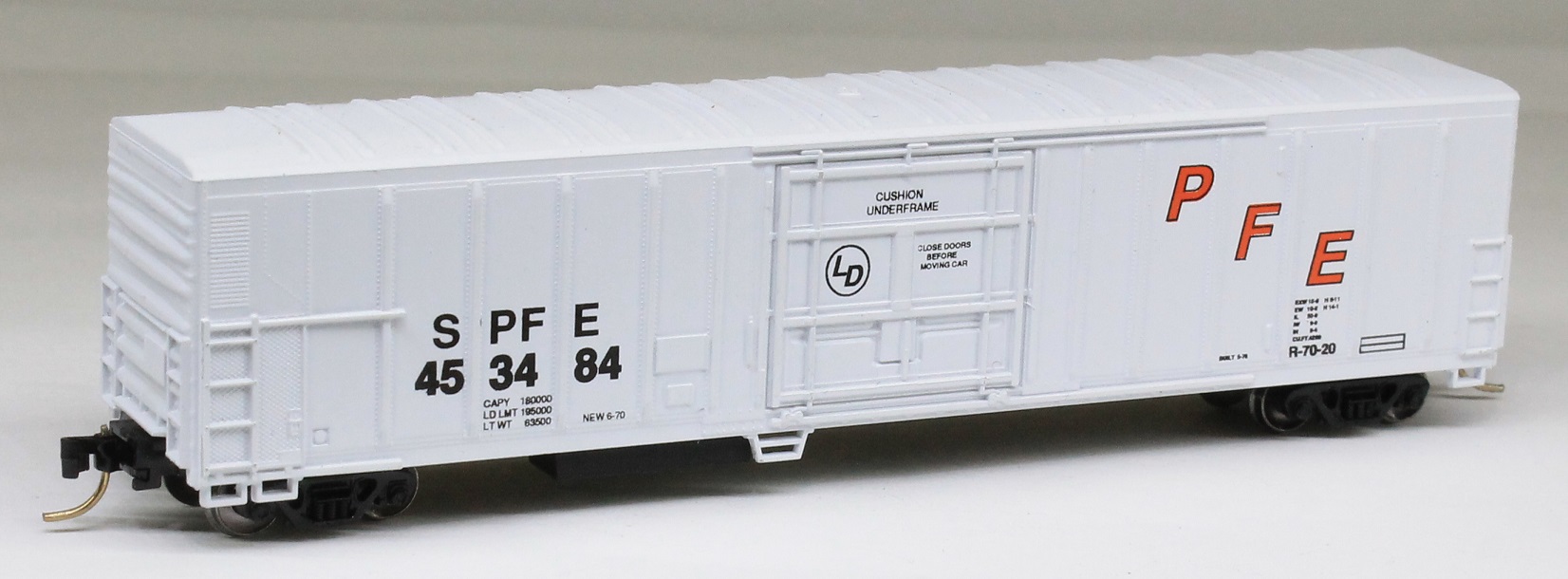
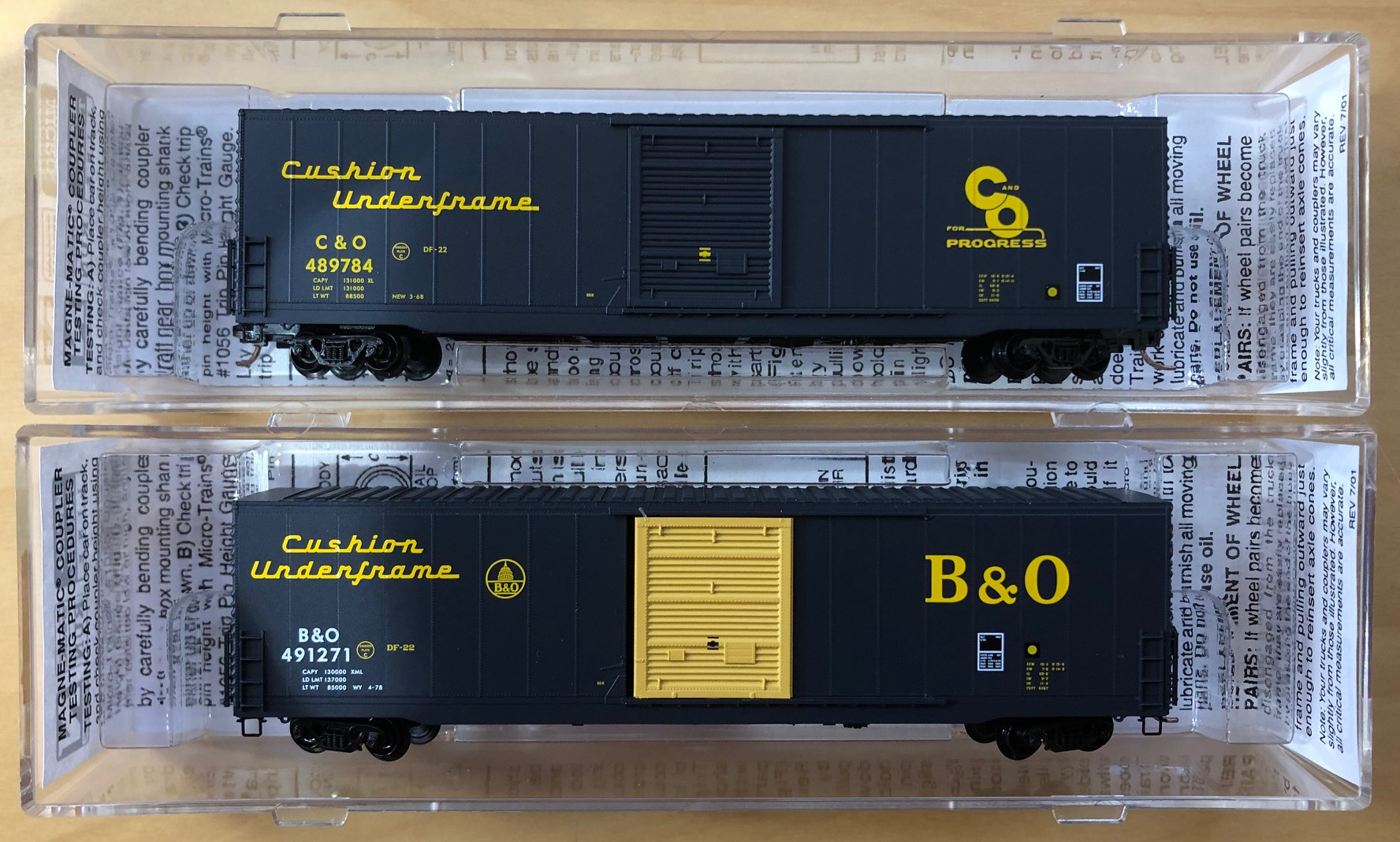
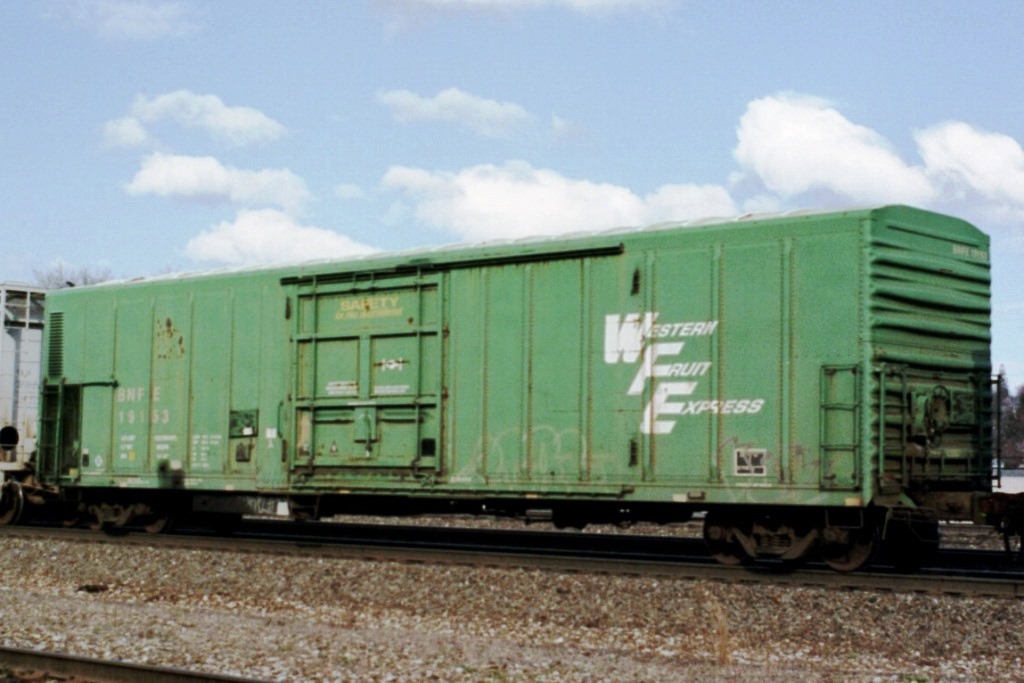
Model Information: This tooling was created by MDC and later acquired by Athearn in 2004. The models are based on the Pacific Fruit Express R-70-20 to R-70-24 class of reefers. The MDC versions were usually sold in kit form, though more recent releases were in RTR format. The MDC releases included Rapido couplers and blackened metal wheels.
The most recent releases from Athearn have the following features: Razor sharp printing and painting; Weighted for optimum performance; Body mounted McHenry scale knuckle spring couplers installed; Machined 33” metal wheels; Window packaging for easy viewing; Interior plastic blister safely holds the model for convenient storage; Minimum radius: 10”.
The most recent releases from Athearn have the following features: Razor sharp printing and painting; Weighted for optimum performance; Body mounted McHenry scale knuckle spring couplers installed; Machined 33” metal wheels; Window packaging for easy viewing; Interior plastic blister safely holds the model for convenient storage; Minimum radius: 10”.
Prototype History: Pacific Car and Foundry responded to the railroad’s migration from ice stored in bunkers as a primary cooling system to the diesel mechanical systems. The mechanical reefers could keep a more regular temperature, often times colder then what the ice bunker cars could at the time. Initially mechanical reefers were used primarily in frozen food service. This would soon change as mechanical refrigeration began to replace ice-based systems. Soon after, mechanical refrigeration units replaced the “armies” of personnel required to re-ice the cars. Several different deliveries of the PC&F 57’ mechanical to many different railroads in the mid to late 1960s. Many have been rebuilt and are still in service today.
These 50'-10" mechanical refrigerator cars were built by PC&F in 1969-70 and featured 4269 ft3 capacity and a 10'-6" door opening. Note that this body style is sometimes referred to as 57', however, the mechanical refrigeration eqipment takes up space on one end of the car thus leaving a nominal 50' usable inside length for loading. Bangor and Aroostook often leased it’s reefer fleet to Pacific Fruit Express in the off season for the railroad. This turned out to be a peak season for PFE in California. Green Bay and Western purchased several classes of 57’ Mechanicals from the BAR. Many were hastily patched and put into service. The GB&W cars were often seen on the North Western Pacific in California carrying butter from the Humbolt Bay to eastern markets.
These 50'-10" mechanical refrigerator cars were built by PC&F in 1969-70 and featured 4269 ft3 capacity and a 10'-6" door opening. Note that this body style is sometimes referred to as 57', however, the mechanical refrigeration eqipment takes up space on one end of the car thus leaving a nominal 50' usable inside length for loading. Bangor and Aroostook often leased it’s reefer fleet to Pacific Fruit Express in the off season for the railroad. This turned out to be a peak season for PFE in California. Green Bay and Western purchased several classes of 57’ Mechanicals from the BAR. Many were hastily patched and put into service. The GB&W cars were often seen on the North Western Pacific in California carrying butter from the Humbolt Bay to eastern markets.
Road Name History:  Pacific Fruit Express (reporting mark PFE) was an American railroad refrigerator car leasing company that at one point was the largest refrigerator car operator in the world. The company was founded on December 7, 1906 as a joint venture between the Union Pacific and Southern Pacific railroads. It began operation on October 1, 1907, with a fleet of 6,600 refrigerator cars built by the American Car and Foundry Company (ACF).
Pacific Fruit Express (reporting mark PFE) was an American railroad refrigerator car leasing company that at one point was the largest refrigerator car operator in the world. The company was founded on December 7, 1906 as a joint venture between the Union Pacific and Southern Pacific railroads. It began operation on October 1, 1907, with a fleet of 6,600 refrigerator cars built by the American Car and Foundry Company (ACF).
In 1923, the Western Pacific Railroad joined the venture by leasing its own, brand new fleet of 2775 reefers to PFE. They were painted in standard PFE colors with only WP heralds on the cars instead of the paired UP-SP markings. The WP cars were all retired by the late 1950s, among the last wooden reefers in PFE's fleet. WP ended its partnership with PFE in late 1967 and joined Fruit Growers Express instead.
PFE's assets were divided between the UP and SP when the company was split on April 1, 1978. It is now a UP subsidiary.

In 1923, the Western Pacific Railroad joined the venture by leasing its own, brand new fleet of 2775 reefers to PFE. They were painted in standard PFE colors with only WP heralds on the cars instead of the paired UP-SP markings. The WP cars were all retired by the late 1950s, among the last wooden reefers in PFE's fleet. WP ended its partnership with PFE in late 1967 and joined Fruit Growers Express instead.
PFE's assets were divided between the UP and SP when the company was split on April 1, 1978. It is now a UP subsidiary.
Brand/Importer Information:  MDC Roundhouse was founded in California in 1938 and relocated in 1993 to Carson City, Nevada due to statewide restrictions on painting. MDC Roundhouse was a producer of both RTR (Ready-to-Run) and kit versions of N Scale rolling stock as well as RTR locomotives. They entered the N scale market in 1979 with a Thrall Hi-Side Gondola and a Hi-Cube Single Door Box Car. MDC Roundhouse was purchased by Horizon Hobbies in June of 2004, when its owner since 1938 C. H. Menteer retired, and merged into their Athearn line.
MDC Roundhouse was founded in California in 1938 and relocated in 1993 to Carson City, Nevada due to statewide restrictions on painting. MDC Roundhouse was a producer of both RTR (Ready-to-Run) and kit versions of N Scale rolling stock as well as RTR locomotives. They entered the N scale market in 1979 with a Thrall Hi-Side Gondola and a Hi-Cube Single Door Box Car. MDC Roundhouse was purchased by Horizon Hobbies in June of 2004, when its owner since 1938 C. H. Menteer retired, and merged into their Athearn line.
Unlike many of their contemporaries which contracted with European firms to produce their products, MDC made their own toolings. They made several popular body styles and produced them for road names that many other vendors (even Micro-Trains) wouldn't touch. This made them popular with modelers. Also, their un-assembled "kits" permitted a lower price point so they were popular with "runners" as well as "modelers".
Of particular interest was the attention given to modern 50 foot steel boxcars. They made some attempt to accurately mold the differences into distinct models to represent each of the major prototype manufacturers products. They have distinct toolings not only for the different products from FMC, BFF and PS, but also multiple models for each of these manufacturers including "standard" vs "Youngstown" doors and "waffle" vs. "rib" sides. In total they produced 13 different versions of the 50 foot steel boxcar.

Unlike many of their contemporaries which contracted with European firms to produce their products, MDC made their own toolings. They made several popular body styles and produced them for road names that many other vendors (even Micro-Trains) wouldn't touch. This made them popular with modelers. Also, their un-assembled "kits" permitted a lower price point so they were popular with "runners" as well as "modelers".
Of particular interest was the attention given to modern 50 foot steel boxcars. They made some attempt to accurately mold the differences into distinct models to represent each of the major prototype manufacturers products. They have distinct toolings not only for the different products from FMC, BFF and PS, but also multiple models for each of these manufacturers including "standard" vs "Youngstown" doors and "waffle" vs. "rib" sides. In total they produced 13 different versions of the 50 foot steel boxcar.
Item created by: Mopjunkie on 2019-06-04 23:19:31. Last edited by baggedbird on 2023-10-07 02:23:00
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.