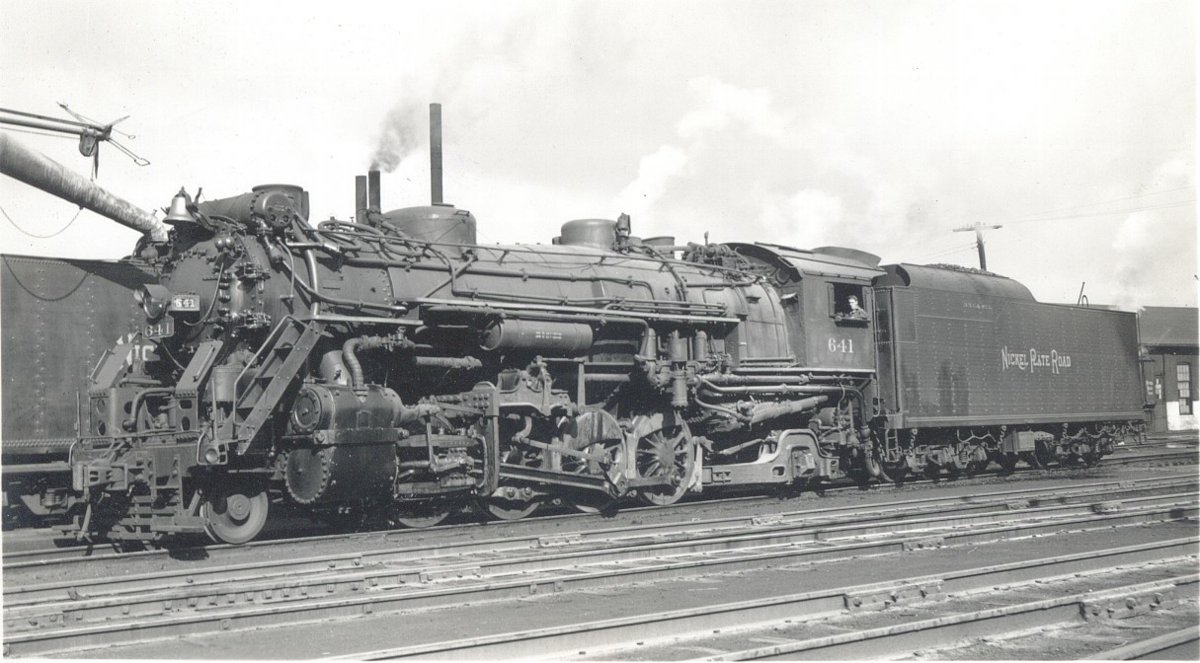
Model Information: This model was first developed by Rivarossi for Atlas and released in 1969. The model uses much the same design as Rivarossi's earlier 4-6-2 and 0-8-0 models. The first several releases were models of the USRA light Mikado. In 1982, a version was created to model the Heavy Mikado. Atlas was the sole importer of the early version through 1977. After that Con-Cor started importing them, and it at under Con-Cor's request that the 'Heavy' version was developed. Con-Cor continued to import these models (with no significant changes) through 2006 when Rivarossi went bankrupt.
Compared with the later Kato-made steamers of the 1980s, these locomotives are not very good. They use a fairly wonky electrical pickup scheme which may require some fiddling in order to produce reliable current. They don't have much in the way of shell detail either.
Compared with the later Kato-made steamers of the 1980s, these locomotives are not very good. They use a fairly wonky electrical pickup scheme which may require some fiddling in order to produce reliable current. They don't have much in the way of shell detail either.
DCC Information: Don't even think about it.
Prototype History: The Heavy Mikado was "conceived" under the auspices of the United States Railway Administration (USRA), an agency established during WWI to regulate the railroad industry during the war.
One of the first undertakings of the USRA was to develop locomotive (and rolling stock) designs that the railroads could share.
This "common design" program was highly successful in streamlining production, and many USRA engines were used long after the war was over, essentially "outliving" the agency that conceived them.
The 2-8-2 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and one trailing axle. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, or shortened to just "Mike". The USRA ultimately created 12 different steam locomotive designs, including both the Heavy Mikado and Light Mikado. Both the Light and Heavy Mikado used the same 63" drivers and running gear, but the Heavy Mike had a fatter boiler and put out more pounds on the drivers. This resulted in a more powerful locomotive.
Under the USRA's watch, 233 Heavy Mikados were built. Including copies built later, the total number of Heavy Mikes was 957 units, purchased originally by 23 different railroads, primarily in freight service. Some Mikado steam engine are still in service today, employed mostly for tourist or railfan trips.
The 2-8-2 is a railroad steam locomotive that has one leading axle followed by four powered driving axles and one trailing axle. This configuration of steam locomotive is most often referred to as a Mikado, or shortened to just "Mike". The USRA ultimately created 12 different steam locomotive designs, including both the Heavy Mikado and Light Mikado. Both the Light and Heavy Mikado used the same 63" drivers and running gear, but the Heavy Mike had a fatter boiler and put out more pounds on the drivers. This resulted in a more powerful locomotive.
Under the USRA's watch, 233 Heavy Mikados were built. Including copies built later, the total number of Heavy Mikes was 957 units, purchased originally by 23 different railroads, primarily in freight service. Some Mikado steam engine are still in service today, employed mostly for tourist or railfan trips.
Road Name History: The Great Northern was born in 1881 with the consolidation of several railroads of the northern plains under the leadership of James J. Hill. By 1893, the mainline from the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River to Seattle was complete.
The GN had two distinctly different characters. The eastern half was a largely flat, grain producing region serving cities like Fargo, the Twin Cities, Grand Forks, Duluth, Sioux Falls, Sioux City and even Winnipeg in Canada. The east end also included the iron ore rich regions of Minnesota. Half of North Dakota was blanketed by GN branchlines (21 in all) serving every imaginable grain elevator.
The western half is the mountainous portion that most people identify with Great Northern. This included crossing the northern Rockies and the even more difficult Cascade ranges. Cities on the western half included Billings, Butte, Helena, Havre, Spokane, Portland, Seattle, and Vancouver. In 1931, a connection to the Western Pacific was completed from Bieber north to Bend, Oregon. This line was disconnected from the rest of the Great Northern. They used trackage rights on the Oregon Trunk and SP&S to bridge the gap. The Cascade Tunnel, the longest on the continent at 7.8 miles, wasn’t completed until 1931. Construction included a massive sluiceway and hydro-electric power station to feed the electrified line through the tunnel and several miles of railroad on either side. This replaced the original Cascade Tunnel which was a third as long but 500 feet higher up the mountain. That replaced the original route that was another 700 feet higher, had 4% grades and 50 miles of snowsheds. All told, Great Northern had about 8,300 route miles.
The steam era was especially unkind to the Great Northern. They seemed to go out of their way to make their locomotives ugly. Belpaire fire boxes were the norm (made famous by the Pennsylvania, made hideous on the GN.) Headlights were often mounted just above center giving them a spinster look. Cab fronts were often at odd angles. The tender coal bunkers were often taller than the engines. But it wasn’t just aesthetics. GN had a knack for buying the wrong engines for the job. 150 Prarie type 2-6-2’s were so unstable at speed that they were busted down to branchline duty almost straight away and none survived after about 1930. Their first 4-8-2 Mountains built for passenger and fast freight were such a disaster, they were rebuilt into 2-10-2’s. Many railroads had built Mountains out of Mikes but no one had ever started with a Mountain and had to build something else from it. The first 2-6-6-2’s were so under-powered, the boilers were used to make Mikados instead. They did manage to build the largest, fastest, and most powerful Mikados in the country however. Their articulated fleet included 2-6-6-2, 2-6-8-0 (later rebuilt into Mikes), 2-8-8-0, 2-8-8-2 types as well as a pair of Challengers originally delivered to SP&S. Many engines were dressed up with green boilers and boxcar red cab roofs.
For the first generation of diesels, GN bought like many large railroads did: a sampling from everyone. Cab and hood units from EMD and Alco and switchers from EMD, Alco, and Baldwin populated the roster. GN’s first generation geeps and SD’s were delivered with the long hood as the front. This included their GP20’s which had high short hoods and the long hood as the front. Aside from an early black scheme for switchers, the GN fleet was delivered in Omaha Orange and green with yellow piping.
Beginning with the arrival of GP30s in 1962, the paint scheme was simplified by dropping the bottom orange band and the yellow piping. For the second generation, General Electric replaced Alco as a supplier of new road engines.
In 1962, some GN freight cars began to appear in Glacier Green which ran along side the vermilion paint adopted in 1956. In 1967, they went for a major shift. Sky Blue, white, and dark gray were joined by a new version of the Rocky the goat logo. There was talk that this would become the paint scheme for Burlington Northern. The GN name and logo was painted on a steel panel bolted the the hand railings of hood units, making it easier to remove after the merger. For whatever reason, they went with green, black and white, a version of which was simultaneously being tested on the Burlington Route. In 1970, Great Northern, Northern Pacific, Spokane Portland & Seattle, and Burlington Route merged to form Burlington Northern.
The GN had two distinctly different characters. The eastern half was a largely flat, grain producing region serving cities like Fargo, the Twin Cities, Grand Forks, Duluth, Sioux Falls, Sioux City and even Winnipeg in Canada. The east end also included the iron ore rich regions of Minnesota. Half of North Dakota was blanketed by GN branchlines (21 in all) serving every imaginable grain elevator.
The western half is the mountainous portion that most people identify with Great Northern. This included crossing the northern Rockies and the even more difficult Cascade ranges. Cities on the western half included Billings, Butte, Helena, Havre, Spokane, Portland, Seattle, and Vancouver. In 1931, a connection to the Western Pacific was completed from Bieber north to Bend, Oregon. This line was disconnected from the rest of the Great Northern. They used trackage rights on the Oregon Trunk and SP&S to bridge the gap. The Cascade Tunnel, the longest on the continent at 7.8 miles, wasn’t completed until 1931. Construction included a massive sluiceway and hydro-electric power station to feed the electrified line through the tunnel and several miles of railroad on either side. This replaced the original Cascade Tunnel which was a third as long but 500 feet higher up the mountain. That replaced the original route that was another 700 feet higher, had 4% grades and 50 miles of snowsheds. All told, Great Northern had about 8,300 route miles.
The steam era was especially unkind to the Great Northern. They seemed to go out of their way to make their locomotives ugly. Belpaire fire boxes were the norm (made famous by the Pennsylvania, made hideous on the GN.) Headlights were often mounted just above center giving them a spinster look. Cab fronts were often at odd angles. The tender coal bunkers were often taller than the engines. But it wasn’t just aesthetics. GN had a knack for buying the wrong engines for the job. 150 Prarie type 2-6-2’s were so unstable at speed that they were busted down to branchline duty almost straight away and none survived after about 1930. Their first 4-8-2 Mountains built for passenger and fast freight were such a disaster, they were rebuilt into 2-10-2’s. Many railroads had built Mountains out of Mikes but no one had ever started with a Mountain and had to build something else from it. The first 2-6-6-2’s were so under-powered, the boilers were used to make Mikados instead. They did manage to build the largest, fastest, and most powerful Mikados in the country however. Their articulated fleet included 2-6-6-2, 2-6-8-0 (later rebuilt into Mikes), 2-8-8-0, 2-8-8-2 types as well as a pair of Challengers originally delivered to SP&S. Many engines were dressed up with green boilers and boxcar red cab roofs.
For the first generation of diesels, GN bought like many large railroads did: a sampling from everyone. Cab and hood units from EMD and Alco and switchers from EMD, Alco, and Baldwin populated the roster. GN’s first generation geeps and SD’s were delivered with the long hood as the front. This included their GP20’s which had high short hoods and the long hood as the front. Aside from an early black scheme for switchers, the GN fleet was delivered in Omaha Orange and green with yellow piping.
Beginning with the arrival of GP30s in 1962, the paint scheme was simplified by dropping the bottom orange band and the yellow piping. For the second generation, General Electric replaced Alco as a supplier of new road engines.
In 1962, some GN freight cars began to appear in Glacier Green which ran along side the vermilion paint adopted in 1956. In 1967, they went for a major shift. Sky Blue, white, and dark gray were joined by a new version of the Rocky the goat logo. There was talk that this would become the paint scheme for Burlington Northern. The GN name and logo was painted on a steel panel bolted the the hand railings of hood units, making it easier to remove after the merger. For whatever reason, they went with green, black and white, a version of which was simultaneously being tested on the Burlington Route. In 1970, Great Northern, Northern Pacific, Spokane Portland & Seattle, and Burlington Route merged to form Burlington Northern.
Brand/Importer Information: Con-Cor has been in business since 1962. Many things have changed over time as originally they were a complete manufacturing operation in the USA and at one time had upwards of 45 employees. They not only designed the models,but they also built their own molds, did injection molding, painting, printing and packaging on their models.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Currently, most of their manufacturing has been moved overseas and now they import 90% of their products as totally finished goods, or in finished components. They only do some incidental manufacturing today within the USA.
Important Note: The Con-Cor product numbering can be very confusing. Please see here in the article how to properly enter Con-Cor stock numbers in the TroveStar database.
Item created by: gdm on 2019-02-12 09:16:58. Last edited by gdm on 2020-12-23 08:13:17
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.