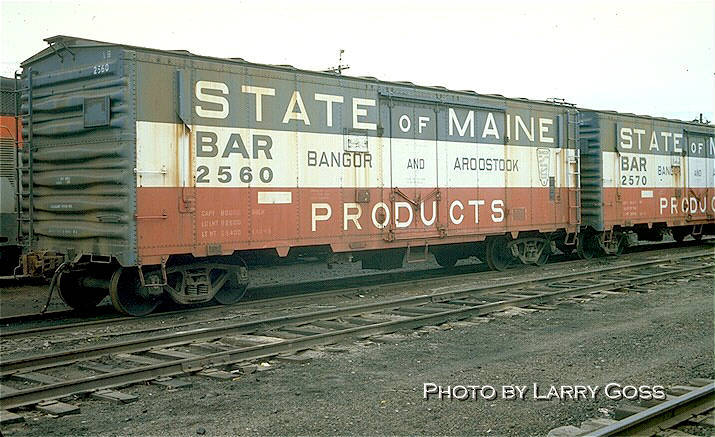Model Information: This model was introduced by ESM in 2010. The model is injection molded plastic with etched brass roofwalk and brake platform. These cars ride at the prototypically-correct height above the rails, on Micro-Trains® Bettendorf trucks fitted with low-profile wheelsets. Similar to designs in HO scale, the body-mounted coupler pockets are integrated into the underframe and body. The model is equipped with Micro-Trains® 1015 coupler knuckles. The models (at least the ones I have held) use Fox Valley metal wheels.
Prototype History: In 1950, Bangor & Aroostook commissioned Magor Car Company to build 300 insulated heated plug-door boxcars for potato service. An additional 150 cars were ordered from Pacific Car & Foundry in 1953. The cars were equipped with ventilators and charcoal heaters. New Haven piggybacked an order of 100 cars with the PC&F lot and factory-decorated its cars in the State of Maine scheme to save money on the purchase. The cars carried potatos in the winter and paper products in the summer.
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: Eastern Seaboard Models was founded in 1987. They are a manufacturer of N scale reproductions of North American eastern railroad prototypes. The have both decorated other manufacturers' models as well as designed body styles of their own. They are located at PO Box 301, Waldwick, New Jersey 07463-0301 U.S.A.
Their 2016 lineup includes ready-to-run gondolas, well cars, hoppers, tank cars and boxcars. They also produce craftsman quality kits in their "Made in America" series. ESM products may be purchased directly from their website.
Their 2016 lineup includes ready-to-run gondolas, well cars, hoppers, tank cars and boxcars. They also produce craftsman quality kits in their "Made in America" series. ESM products may be purchased directly from their website.
Item created by: CNW400 on 2019-02-05 12:18:17. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-05-21 16:16:22
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.