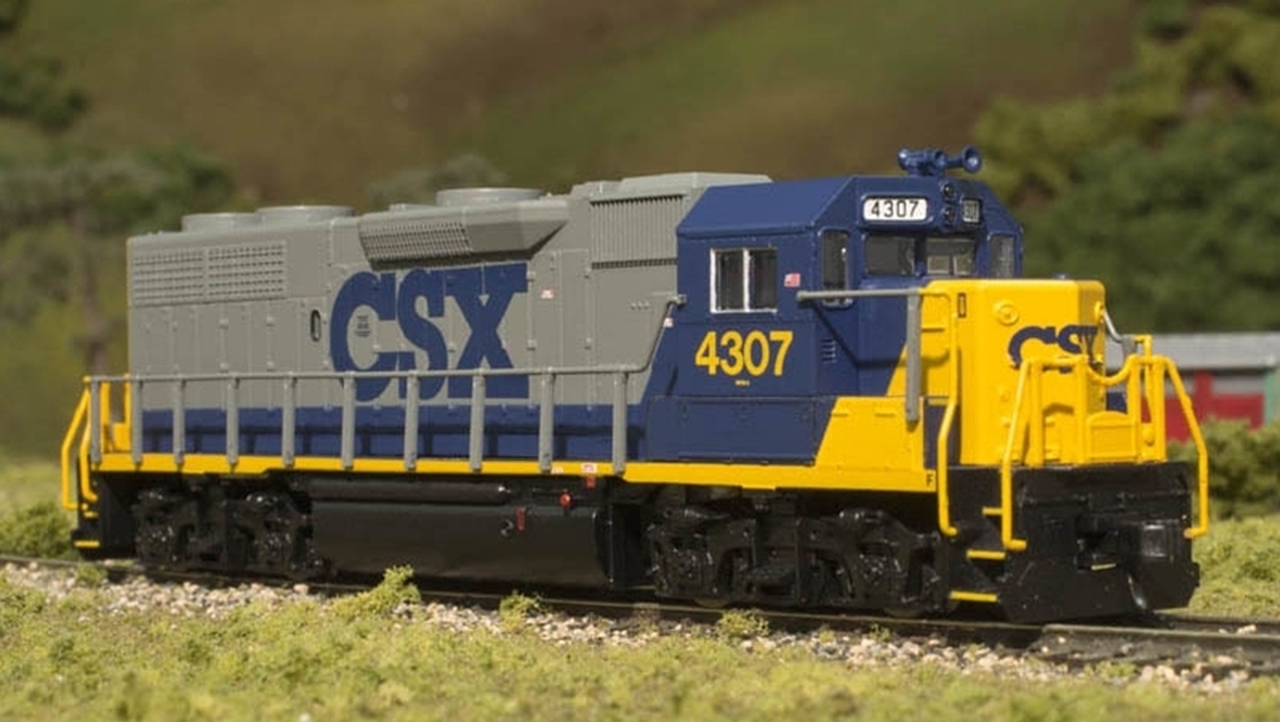
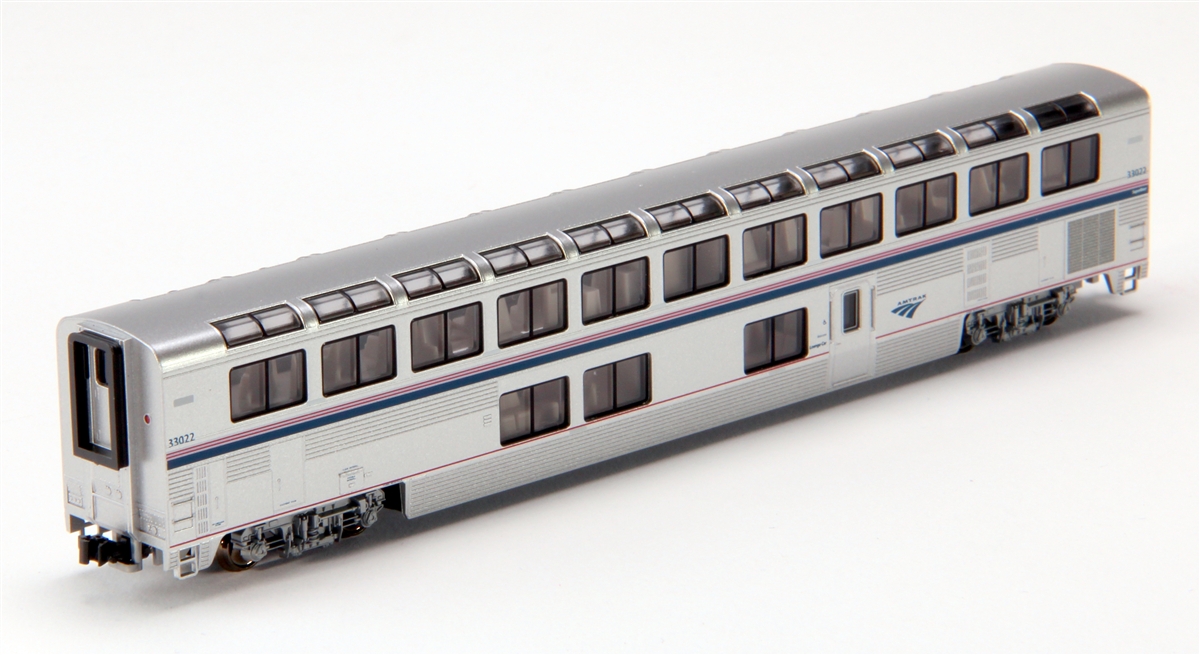
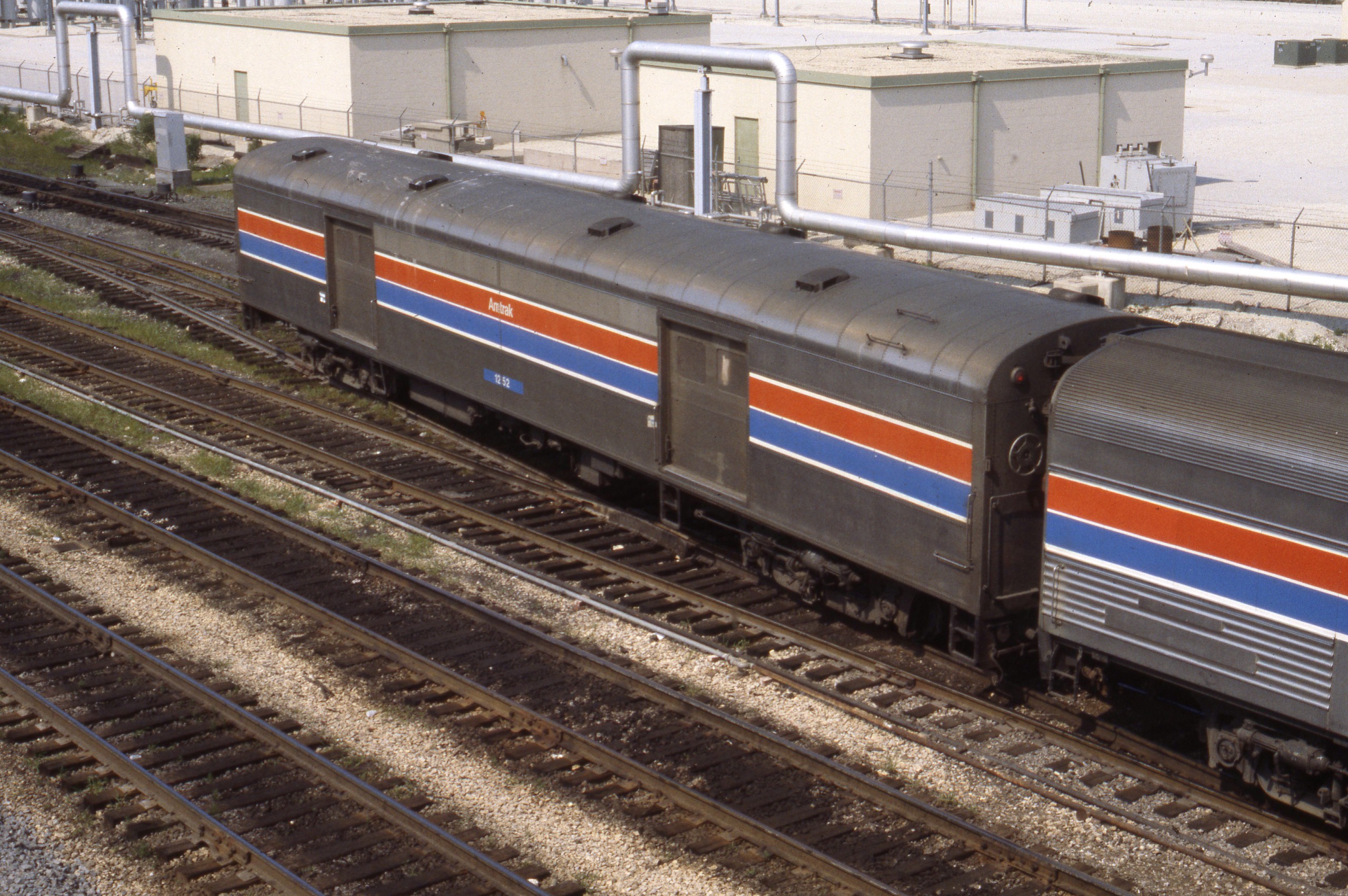
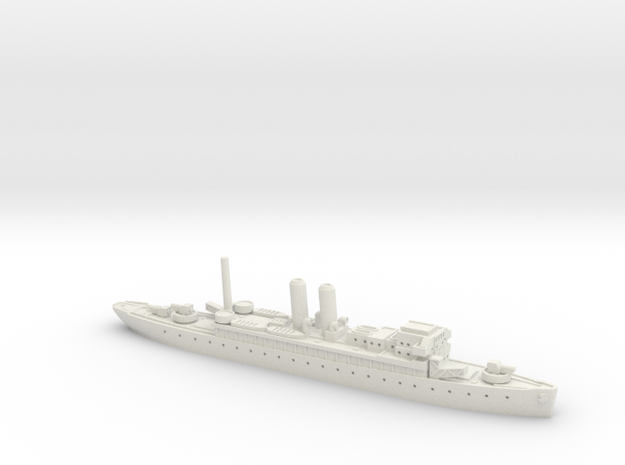
Model Information: First released by Walthers in 2009. This tooling was acquired by RailSmith in 2019.
Walthers Pullman-Standard cars feature as many as four body styles; smooth or fluted sides, with or without skirting as appropriate for each roadname:
Walthers Pullman-Standard cars feature as many as four body styles; smooth or fluted sides, with or without skirting as appropriate for each roadname:
- Prototype Specific Details: - With or without Skirts as appropriate
- Working diaphragms
- Blackened Metal Wheelsets on correct GSC 41-N style Trucks
- Come with decals permitting multiple car number and names
- Drop-In Lighting Kit will also be available, item #933-1099
Prototype History: When lightweight cars came to the Pullman fleet in the early 1940s, their smooth sides lent themselves to classy, colorful paint schemes. Baggage cars operated on everything from premier trains to mail runs from coast to coast, normally mixing with the head-end cars of connecting lines.
These versatile cars ride on GSC 41-N trucks with metal wheelsets.
Corrugated stainless-steel sides, later added to match the look (and acknowledge the competition) of Budd's stainless-steel designs, created a variety of cars that ran on premier passenger trains.
These versatile cars ride on GSC 41-N trucks with metal wheelsets.
Corrugated stainless-steel sides, later added to match the look (and acknowledge the competition) of Budd's stainless-steel designs, created a variety of cars that ran on premier passenger trains.
Road Name History:  Chicago Great Western was the result of the 1892 reorganization of the Chicago St. Paul & Kansas City. By 1903, the CGW had grown to its maximum size. The CGW had a vaguely cross-shaped system map. The east-west leg started in Chicago and linked Dubuque, Fort Dodge (both in Iowa) and finally Omaha, Nebraska. The north-south line started in St. Paul, Minnesota and linked Waterloo and Des Moines, Iowa then St. Joseph and Kansas City, Missouri. Each axis consisted of a big arc which put CGW at a distance disadvantage to most other railroads servicing the same region – and there were a lot of railroads in the area.
Chicago Great Western was the result of the 1892 reorganization of the Chicago St. Paul & Kansas City. By 1903, the CGW had grown to its maximum size. The CGW had a vaguely cross-shaped system map. The east-west leg started in Chicago and linked Dubuque, Fort Dodge (both in Iowa) and finally Omaha, Nebraska. The north-south line started in St. Paul, Minnesota and linked Waterloo and Des Moines, Iowa then St. Joseph and Kansas City, Missouri. Each axis consisted of a big arc which put CGW at a distance disadvantage to most other railroads servicing the same region – and there were a lot of railroads in the area.
Passenger service was never a major priority and many trains consisted of doodlebugs and trailers even before World War One. In the 1920s CGW did team up with Santa Fe to run through sleepers from the Twin Cities to Los Angeles.
Big mainline power in the 30s and 40s consisted of a fleet of 3 dozen 2-10-4s. In 1936, CGW launched piggyback service – one of the first in the nation. One piggyback customer was a truck line specializing in hauling steel. Since CGW charged by the trailer, the truck line would take the contents of 3 trailers which had maxed out on highway weight and reload all the steel into a single catastrophically heavy trailer that would ride the flat car. They didn’t tell CGW though. No one was the wiser until the landing gear on a trailer punched through the deck of the flat car and derailed a train at speed!
By 1950, CGW had completely dieselized with a mix of Alco, Baldwin and EMD switchers, Alco and EMD road switchers (the former running long hood forward and the latter equipped with dual controls,) and a sizable fleet of EMD F units. By this time, the Deramus family (who already controlled the Kansas City Southern) had gained control of the CGW. Over the years, they cut costs and services. CGW began holding trains until they reached maximum tonnage. Trains between 150 and 250 cars were a daily occurrance behind A-B-B-B-B-A sets of F units. What’s more, these monsters would stop and switch along the way!
Around 1951, they dropped “The Corn Belt Route” logo in favor of the Lucky Strike style logo. The first generation of diesels were delivered in ornate maroon, and red with yellow striping. This was replaced with a simplified solid maroon and then red with black roof (which was essentially the same as neighbor and fellow Deramus controlled Kansas City Southern.) The second generation of diesels consisted entirely of GP30’s and SD40’s.
Despite the iffy service and tremendous competition in the area, and thanks to the cost cutting and a dearth of money losing passenger operations that plagued their neighbors, CGW steadily made money through the 50s and 60s. But, in the age of mergers, it was clear they couldn’t make it on their own. CGW discussed merger with every possible connection but ultimately merged into Chicago & North Western in 1968. In their last full year, the CGW was a 1,411 mile line with 139 locomotives (for comparison, they were about the same size as Western Pacific.)

Passenger service was never a major priority and many trains consisted of doodlebugs and trailers even before World War One. In the 1920s CGW did team up with Santa Fe to run through sleepers from the Twin Cities to Los Angeles.
Big mainline power in the 30s and 40s consisted of a fleet of 3 dozen 2-10-4s. In 1936, CGW launched piggyback service – one of the first in the nation. One piggyback customer was a truck line specializing in hauling steel. Since CGW charged by the trailer, the truck line would take the contents of 3 trailers which had maxed out on highway weight and reload all the steel into a single catastrophically heavy trailer that would ride the flat car. They didn’t tell CGW though. No one was the wiser until the landing gear on a trailer punched through the deck of the flat car and derailed a train at speed!
By 1950, CGW had completely dieselized with a mix of Alco, Baldwin and EMD switchers, Alco and EMD road switchers (the former running long hood forward and the latter equipped with dual controls,) and a sizable fleet of EMD F units. By this time, the Deramus family (who already controlled the Kansas City Southern) had gained control of the CGW. Over the years, they cut costs and services. CGW began holding trains until they reached maximum tonnage. Trains between 150 and 250 cars were a daily occurrance behind A-B-B-B-B-A sets of F units. What’s more, these monsters would stop and switch along the way!
Around 1951, they dropped “The Corn Belt Route” logo in favor of the Lucky Strike style logo. The first generation of diesels were delivered in ornate maroon, and red with yellow striping. This was replaced with a simplified solid maroon and then red with black roof (which was essentially the same as neighbor and fellow Deramus controlled Kansas City Southern.) The second generation of diesels consisted entirely of GP30’s and SD40’s.
Despite the iffy service and tremendous competition in the area, and thanks to the cost cutting and a dearth of money losing passenger operations that plagued their neighbors, CGW steadily made money through the 50s and 60s. But, in the age of mergers, it was clear they couldn’t make it on their own. CGW discussed merger with every possible connection but ultimately merged into Chicago & North Western in 1968. In their last full year, the CGW was a 1,411 mile line with 139 locomotives (for comparison, they were about the same size as Western Pacific.)
Brand/Importer Information: Wm. K. Walthers, Inc., was founded in Milwaukee in 1932 -- but really, it started years earlier, when seven-year-old Bill Walthers got his first taste of the hobby with a small, wind-up toy train for Christmas. He continued with the hobby and eventually had an attic layout comprised primarily of his own scratch-built creations. After he wrote a series of articles on building train control and signaling systems, he got so many letters from other modelers that he began manufacturing them. The first ad (in the May issue of The Model Maker) offered a 24-page, 15c catalog that listed rail, couplers, and electrical supplies. Sales were over $500.00 for the first year, and the fledgling company was off to a strong start.
Within five years, Walthers had grown so much that larger quarters were needed. Space was found on Erie Street, where everything -- from milled wood parts to metal castings to decals -- was made in-house. 1937 also saw a new line in HO Scale, featured in its own catalog. Bill brought operating layouts to the 1939 World's Fair, which gave the hobby a big boost. Soon, though, the growing possibility of war overshadowed these successes, and supplies were becoming increasingly difficult to obtain.
During the war, model manufacturers were ordered to stop production in order to conserve critical metal supplies. Walthers produced what it could from nonessential materials. A series of ads in 1943 saw Bill literally scraping the bottom of a barrel! The postwar boom meant rapid growth for the hobby; however, small homes and new families left no room for O scale layouts, and many modelers moved to HO Scale.
The next twenty years brought great change. In 1958, Bill retired and his son Bruce took over. Just as full-size railroads were being hard-hit by new technology, so too were model railroads. Leisure time was spent in front of the TV set, not the train set. In 1960, Walthers became a full-line distributor of other manufacturers' products while continuing expansion of the Walthers lines. By the start of the 1970's, business was booming again, and Bruce's son Phil joined the company.
Expansion and diversification continue under Phil's tenure. The establishment of the Walthers Importing Division added several international lines. The manufacturing plant was modernized. Code 83 track was introduced in 1985, giving layouts more realistic proportions. In 1990, the Cornerstone Series buildings were unveiled. Combining a freight car with a related industry, the Cornerstone Series makes it possible for modelers to duplicate authentic operations, enhancing layout realism. The Train Line Deluxe Sets and locomotives debuted in 1994. These sets feature the detailing of serious models and an affordable price -- allowing newcomers to get started, and then build-on to their first set, rather than replacing it.
In 2005, Walthers purchased Life-Like from Lifoam Industries. With this purchase Walthers acquired the Proto Lines that have become the backbone of their locomotive and rolling stock segments.
Today, Walthers continues to expand, improve and develop a wide range of products. Their latest selection can be found throughout Walthers.com and their printed catalogs, along with items from over 300 other manufacturers.
In December 2017, Lowell Smith announced the ‘purchase of tooling’ of the Walthers line of N Scale passenger cars (sleeper, coach and baggage cars), and in June 2018, Atlas announced that it will purchase all N scale locomotive and rolling stock tooling owned by Walthers, including the Walthers N tooling as well as former Life-Like tooling. This divestment puts an end to Walthers involvement as a manufacturer of N scale rolling-stock, though it will continue its range of N scale structures.
Within five years, Walthers had grown so much that larger quarters were needed. Space was found on Erie Street, where everything -- from milled wood parts to metal castings to decals -- was made in-house. 1937 also saw a new line in HO Scale, featured in its own catalog. Bill brought operating layouts to the 1939 World's Fair, which gave the hobby a big boost. Soon, though, the growing possibility of war overshadowed these successes, and supplies were becoming increasingly difficult to obtain.
During the war, model manufacturers were ordered to stop production in order to conserve critical metal supplies. Walthers produced what it could from nonessential materials. A series of ads in 1943 saw Bill literally scraping the bottom of a barrel! The postwar boom meant rapid growth for the hobby; however, small homes and new families left no room for O scale layouts, and many modelers moved to HO Scale.
The next twenty years brought great change. In 1958, Bill retired and his son Bruce took over. Just as full-size railroads were being hard-hit by new technology, so too were model railroads. Leisure time was spent in front of the TV set, not the train set. In 1960, Walthers became a full-line distributor of other manufacturers' products while continuing expansion of the Walthers lines. By the start of the 1970's, business was booming again, and Bruce's son Phil joined the company.
Expansion and diversification continue under Phil's tenure. The establishment of the Walthers Importing Division added several international lines. The manufacturing plant was modernized. Code 83 track was introduced in 1985, giving layouts more realistic proportions. In 1990, the Cornerstone Series buildings were unveiled. Combining a freight car with a related industry, the Cornerstone Series makes it possible for modelers to duplicate authentic operations, enhancing layout realism. The Train Line Deluxe Sets and locomotives debuted in 1994. These sets feature the detailing of serious models and an affordable price -- allowing newcomers to get started, and then build-on to their first set, rather than replacing it.
In 2005, Walthers purchased Life-Like from Lifoam Industries. With this purchase Walthers acquired the Proto Lines that have become the backbone of their locomotive and rolling stock segments.
Today, Walthers continues to expand, improve and develop a wide range of products. Their latest selection can be found throughout Walthers.com and their printed catalogs, along with items from over 300 other manufacturers.
In December 2017, Lowell Smith announced the ‘purchase of tooling’ of the Walthers line of N Scale passenger cars (sleeper, coach and baggage cars), and in June 2018, Atlas announced that it will purchase all N scale locomotive and rolling stock tooling owned by Walthers, including the Walthers N tooling as well as former Life-Like tooling. This divestment puts an end to Walthers involvement as a manufacturer of N scale rolling-stock, though it will continue its range of N scale structures.
Item created by: Alain LM on 2019-01-19 17:58:46. Last edited by gdm on 2020-07-24 07:29:21
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.