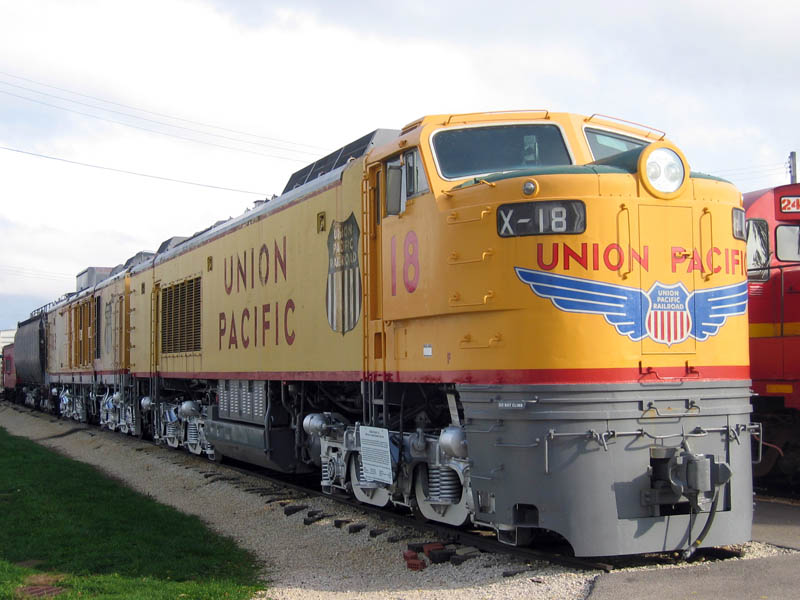
Model Information: ScaleTrains.com introduced this model in 2017. It is the first ScaleTrains.com N-Scale locomotive release. The Union Pacific 8500 horsepower "Big Blow" GTEL ships with either a 23C or a 24C tender. Each box set comes with three separate units. The first two units are the powered A and B locomotives. The final unit is the tender. The MU's have dual-flywheel, 5-pole skew-wound motors. The DCC version has a separate decoder in the tender dedicated to sound functions.
A ScaleTrains.com "Rivet Counter" product, the model has a massive number of road specific details and factory applied parts such as grab irons, coupler cut levers, and windshield wipers, photo etched metal grills and walkways, and intricate frame rail details which include traction motor cables. It is an amazingly impressive model with a hefty (but well-earned) price tag.
A ScaleTrains.com "Rivet Counter" product, the model has a massive number of road specific details and factory applied parts such as grab irons, coupler cut levers, and windshield wipers, photo etched metal grills and walkways, and intricate frame rail details which include traction motor cables. It is an amazingly impressive model with a hefty (but well-earned) price tag.
DCC Information: Factory DCC sound equipped models are fitted with ESU-LokSound Select micro decoders with "A" unit prime mover and "B" unit turbine sounds. Note that each unit, A, B and fuel tender is equipped with a separate decoder!
User manual for Sound version, including assembly drawings and parts list, can be found on ScaleTrains.com website.
User manual for Sound version, including assembly drawings and parts list, can be found on ScaleTrains.com website.
Prototype History: Union Pacific operated the largest fleet of gas turbine-electric locomotives (GTELs) of any railroad in the world. The prototype, UP 50, was the first in a series built by General Electric for Union Pacific's long-haul cargo services and marketed by the Alco-GE partnership until 1953. The prototype was introduced in 1948 and was followed by three series of production locomotives. At one point, Union Pacific said the GTELs hauled more than 10% of the railroad's freight.
Fuel economy was poor, for the turbine consumed roughly twice as much fuel as an equally powerful diesel engine. This was initially not a problem, because Union Pacific's turbines burned Bunker C heavy fuel oil that was less expensive than diesel. But this highly viscous fuel is difficult to handle, with a room-temperature consistency similar to tar or molasses. To solve this problem, a heater was built into the fuel tanks (and later into fuel tenders) to heat the fuel to 200 °F (93 °C) before feeding it into the turbine. Eventually UP switched from Bunker C to modified No. 6 heavy fuel oil, which contained fewer pollutants and solvents. Soot buildup and blade erosion caused by corrosive ash plagued all of the turbines. Changes to the air intake systems on the production turbine locomotives improved the quality of the air that reached the turbines, which in turn reduced the wear to the turbine blades and increased the turbine's running life. The GTELs were operated into late 1969 and the final two (numbers 18 and 26) were stored at the Cheyenne roundhouse in operating condition until being retired in February 1970. Both of these units were later sent to museums.
Fuel economy was poor, for the turbine consumed roughly twice as much fuel as an equally powerful diesel engine. This was initially not a problem, because Union Pacific's turbines burned Bunker C heavy fuel oil that was less expensive than diesel. But this highly viscous fuel is difficult to handle, with a room-temperature consistency similar to tar or molasses. To solve this problem, a heater was built into the fuel tanks (and later into fuel tenders) to heat the fuel to 200 °F (93 °C) before feeding it into the turbine. Eventually UP switched from Bunker C to modified No. 6 heavy fuel oil, which contained fewer pollutants and solvents. Soot buildup and blade erosion caused by corrosive ash plagued all of the turbines. Changes to the air intake systems on the production turbine locomotives improved the quality of the air that reached the turbines, which in turn reduced the wear to the turbine blades and increased the turbine's running life. The GTELs were operated into late 1969 and the final two (numbers 18 and 26) were stored at the Cheyenne roundhouse in operating condition until being retired in February 1970. Both of these units were later sent to museums.
Road Name History: The Union Pacific Railroad (reporting mark UP) is a freight hauling railroad that operates 8,500 locomotives over 32,100 route-miles in 23 states west of Chicago, Illinois and New Orleans, Louisiana. The Union Pacific Railroad network is the largest in the United States and employs 42,600 people. It is also one of the world's largest transportation companies.
Union Pacific Railroad is the principal operating company of Union Pacific Corporation (NYSE: UNP); both are headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. Over the years Union Pacific Corporation has grown by acquiring other railroads, notably the Missouri Pacific, Chicago & North Western, Western Pacific, Missouri-Kansas-Texas, and the Southern Pacific (including the Denver & Rio Grande Western).
Union Pacific Corporation's main competitor is the BNSF Railway, the nation's second largest freight railroad, which also primarily services the Continental U.S. west of the Mississippi River. Together, the two railroads have a duopoly on all transcontinental freight rail lines in the U.S.
Read more on Wikipedia and on Union Pacific official website.
Union Pacific Railroad is the principal operating company of Union Pacific Corporation (NYSE: UNP); both are headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. Over the years Union Pacific Corporation has grown by acquiring other railroads, notably the Missouri Pacific, Chicago & North Western, Western Pacific, Missouri-Kansas-Texas, and the Southern Pacific (including the Denver & Rio Grande Western).
Union Pacific Corporation's main competitor is the BNSF Railway, the nation's second largest freight railroad, which also primarily services the Continental U.S. west of the Mississippi River. Together, the two railroads have a duopoly on all transcontinental freight rail lines in the U.S.
Read more on Wikipedia and on Union Pacific official website.
Brand/Importer Information: ScaleTrains.com, Inc. is an upstart HO and N Scale model manufacturer that was founded by a team with more than 125 years of accumulated experience in the model railroad hobby and industry.
ScaleTrains is specifically focused on the tiny details in the printing and quality of the construction. The four friends who founded the company are all avid modelers themselves. Their factory is located in Tennessee. Unlike most other companies, they offer a range of different levels of complexity in their offerings so as to be able to provide products for both the budget-conscious collector as well as the detail-focused model enthusiast without compromising on quality for either.
They range covers the following, by increasing level of detailing:
ScaleTrains is specifically focused on the tiny details in the printing and quality of the construction. The four friends who founded the company are all avid modelers themselves. Their factory is located in Tennessee. Unlike most other companies, they offer a range of different levels of complexity in their offerings so as to be able to provide products for both the budget-conscious collector as well as the detail-focused model enthusiast without compromising on quality for either.
They range covers the following, by increasing level of detailing:
- Operator™ trains are built for modelers who enjoy running high-quality, realistic trains at an affordable price. Designed from builder’s drawings and photographs, Operator models have fewer factory-applied parts and simplified printing. For added versatility, super-detail parts are available separately.
- The Rivet Counter™ line strives to create the most accurately detailed models imaginable. The real-world counterpart is meticulously researched to ensure prototype fidelity. Each model features numerous factory applied parts including roadname and road number specific details whenever possible.
- Museum Quality™ models are historically accurate replicas of the most famous locomotives in North American railroading history. Exhaustive research and a commitment to perfection combine to create the ultimate scale model. Museum Quality trains establish new standards which make them just as legendary as the original.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-10-19 13:52:56. Last edited by gdm on 2020-05-24 08:03:34
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.