Model Information: Life-Like first introduced this model in 2002 and did a rebuild in 2008. This is an attractive model with excellent detail. The first release lacks a traction tire and is not a particularly good puller. Furthermore although the tender has electrical pickup, the current is only used for the backup light and does not transfer to the motor in the locomotive.
The later release fortunately addresses all three issues. It has factory DCC with sound, has a traction tires and transfers current between the locomotive and the tender.
The later release fortunately addresses all three issues. It has factory DCC with sound, has a traction tires and transfers current between the locomotive and the tender.
DCC Information: The first release was DC only and the re-release in 2008 is available in DCC-Ready versions and DCC-with-sound. versions.
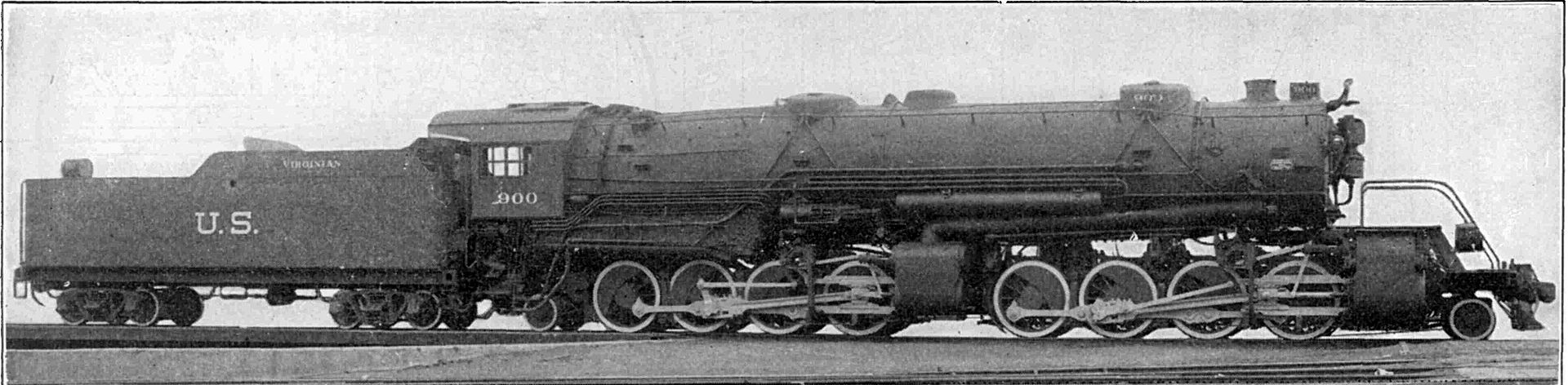
Prototype History: The USRA 2-8-8-2 was a USRA standard class of steam locomotive designed under the control of the United States Railroad Administration, the nationalized railroad system in the United States during World War I. These locomotives were of 2-8-8-2 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation, or (1'D)'D1' in UIC classification. A total of 106 locomotives were built to this plan for the USRA; postwar, it became a de facto standard design.
While the 2-8-8-2 had been built in the United States since 1909, most development work had gone into making subsequent locomotives larger and heavier. The Norfolk and Western Railway however, had taken development in a different direction. By using smaller cylinders and higher boiler pressure, the result was a locomotive capable of powerful performance, and a turn of speed higher than the 20 mph (32 km/h) maximum of the ‘traditional’ designs. The USRA 2-8-8-2 drew heavily on the Norfolk and Western Railway’s Y-2 class locomotive design, as their delegate to the 2-8-8-2 design committee had brought a full set of blueprints.
From Wikipedia
While the 2-8-8-2 had been built in the United States since 1909, most development work had gone into making subsequent locomotives larger and heavier. The Norfolk and Western Railway however, had taken development in a different direction. By using smaller cylinders and higher boiler pressure, the result was a locomotive capable of powerful performance, and a turn of speed higher than the 20 mph (32 km/h) maximum of the ‘traditional’ designs. The USRA 2-8-8-2 drew heavily on the Norfolk and Western Railway’s Y-2 class locomotive design, as their delegate to the 2-8-8-2 design committee had brought a full set of blueprints.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Norfolk and Western Railway (reporting mark NW), was a US class I railroad, formed by more than 200 railroad mergers between 1838 and 1982. It was headquartered in Roanoke, Virginia, for most of its 150-year existence. Its motto was "Precision Transportation"; it had a variety of nicknames, including "King Coal" and "British Railway of America" even though the N&W had mostly articulated steam on its roster. During the Civil War, the N&W was the biggest railroad in the south and moved most of the products with their steam locomotives to help the South the best way they could.
NW was famous for manufacturing its own steam locomotives, which were produced at the Roanoke Shops, as well as its own hopper cars. Around 1960, NW became the last major American railroad to convert from steam locomotives to diesel motive power but didn't retire its last remaining Y class locomotives until 1964 and 1965. By 1965, steam on class I railroads was gone but steam wasn't gone on class II railroads until 1974 and class III and mining railroads retired their steam locomotives from their active roster until 1983. By 1983, steam in America on class I, II, III, and mining railroads had finally closed the chapter on America's 150 years of steam from 1830 - 1983.
In December 1959, NW merged with the Virginian Railway (reporting mark VGN), a longtime rival in the Pocahontas coal region. By 1970, other mergers with the Nickel Plate Road and Wabash formed a system that operated 7,595 miles (12,223 km) of road on 14,881 miles (23,949 km) of track from North Carolina to New York and from Virginia to Iowa.
In 1980, NW teamed up with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier and created the Norfolk Southern Corporation holding company by merging its business operations with the business operations of the Southern Railway. The NW and the Southern Railway continued as separate railroads now under one holding company.
On December 31, 1990, the Southern Railway was renamed "Norfolk Southern Railway" to reflect the Norfolk Southern Corporation and on the same day, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway gained full control of the Norfolk and Western Railway with the Norfolk and Western being transferred from the holding company to the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, this began the final years of Norfolk and Western which was absorbed into the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway seven years later in 1997 (1990 to 1997 the Norfolk and Western continued operating by using paper operations).
In 1997 during the Conrail battle with CSX, Norfolk Southern Corporation's principal railroad, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway into their rail system, ending the existence of the Norfolk and Western Railway and having the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway becoming the only railroad in the entire Norfolk Southern system after that.
NW was famous for manufacturing its own steam locomotives, which were produced at the Roanoke Shops, as well as its own hopper cars. Around 1960, NW became the last major American railroad to convert from steam locomotives to diesel motive power but didn't retire its last remaining Y class locomotives until 1964 and 1965. By 1965, steam on class I railroads was gone but steam wasn't gone on class II railroads until 1974 and class III and mining railroads retired their steam locomotives from their active roster until 1983. By 1983, steam in America on class I, II, III, and mining railroads had finally closed the chapter on America's 150 years of steam from 1830 - 1983.
In December 1959, NW merged with the Virginian Railway (reporting mark VGN), a longtime rival in the Pocahontas coal region. By 1970, other mergers with the Nickel Plate Road and Wabash formed a system that operated 7,595 miles (12,223 km) of road on 14,881 miles (23,949 km) of track from North Carolina to New York and from Virginia to Iowa.
In 1980, NW teamed up with the Southern Railway, another profitable carrier and created the Norfolk Southern Corporation holding company by merging its business operations with the business operations of the Southern Railway. The NW and the Southern Railway continued as separate railroads now under one holding company.
On December 31, 1990, the Southern Railway was renamed "Norfolk Southern Railway" to reflect the Norfolk Southern Corporation and on the same day, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway gained full control of the Norfolk and Western Railway with the Norfolk and Western being transferred from the holding company to the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, this began the final years of Norfolk and Western which was absorbed into the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway seven years later in 1997 (1990 to 1997 the Norfolk and Western continued operating by using paper operations).
In 1997 during the Conrail battle with CSX, Norfolk Southern Corporation's principal railroad, the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway, absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway into their rail system, ending the existence of the Norfolk and Western Railway and having the renamed Norfolk Southern Railway becoming the only railroad in the entire Norfolk Southern system after that.
Brand/Importer Information: Wm. K. Walthers, Inc., was founded in Milwaukee in 1932 -- but really, it started years earlier, when seven-year-old Bill Walthers got his first taste of the hobby with a small, wind-up toy train for Christmas. He continued with the hobby and eventually had an attic layout comprised primarily of his own scratch-built creations. After he wrote a series of articles on building train control and signaling systems, he got so many letters from other modelers that he began manufacturing them. The first ad (in the May issue of The Model Maker) offered a 24-page, 15c catalog that listed rail, couplers, and electrical supplies. Sales were over $500.00 for the first year, and the fledgling company was off to a strong start.
Within five years, Walthers had grown so much that larger quarters were needed. Space was found on Erie Street, where everything -- from milled wood parts to metal castings to decals -- was made in-house. 1937 also saw a new line in HO Scale, featured in its own catalog. Bill brought operating layouts to the 1939 World's Fair, which gave the hobby a big boost. Soon, though, the growing possibility of war overshadowed these successes, and supplies were becoming increasingly difficult to obtain.
During the war, model manufacturers were ordered to stop production in order to conserve critical metal supplies. Walthers produced what it could from nonessential materials. A series of ads in 1943 saw Bill literally scraping the bottom of a barrel! The postwar boom meant rapid growth for the hobby; however, small homes and new families left no room for O scale layouts, and many modelers moved to HO Scale.
The next twenty years brought great change. In 1958, Bill retired and his son Bruce took over. Just as full-size railroads were being hard-hit by new technology, so too were model railroads. Leisure time was spent in front of the TV set, not the train set. In 1960, Walthers became a full-line distributor of other manufacturers' products while continuing expansion of the Walthers lines. By the start of the 1970's, business was booming again, and Bruce's son Phil joined the company.
Expansion and diversification continue under Phil's tenure. The establishment of the Walthers Importing Division added several international lines. The manufacturing plant was modernized. Code 83 track was introduced in 1985, giving layouts more realistic proportions. In 1990, the Cornerstone Series buildings were unveiled. Combining a freight car with a related industry, the Cornerstone Series makes it possible for modelers to duplicate authentic operations, enhancing layout realism. The Train Line Deluxe Sets and locomotives debuted in 1994. These sets feature the detailing of serious models and an affordable price -- allowing newcomers to get started, and then build-on to their first set, rather than replacing it.
In 2005, Walthers purchased Life-Like from Lifoam Industries. With this purchase Walthers acquired the Proto Lines that have become the backbone of their locomotive and rolling stock segments.
Today, Walthers continues to expand, improve and develop a wide range of products. Their latest selection can be found throughout Walthers.com and their printed catalogs, along with items from over 300 other manufacturers.
In December 2017, Lowell Smith announced the ‘purchase of tooling’ of the Walthers line of N Scale passenger cars (sleeper, coach and baggage cars), and in June 2018, Atlas announced that it will purchase all N scale locomotive and rolling stock tooling owned by Walthers, including the Walthers N tooling as well as former Life-Like tooling. This divestment puts an end to Walthers involvement as a manufacturer of N scale rolling-stock, though it will continue its range of N scale structures.
Within five years, Walthers had grown so much that larger quarters were needed. Space was found on Erie Street, where everything -- from milled wood parts to metal castings to decals -- was made in-house. 1937 also saw a new line in HO Scale, featured in its own catalog. Bill brought operating layouts to the 1939 World's Fair, which gave the hobby a big boost. Soon, though, the growing possibility of war overshadowed these successes, and supplies were becoming increasingly difficult to obtain.
During the war, model manufacturers were ordered to stop production in order to conserve critical metal supplies. Walthers produced what it could from nonessential materials. A series of ads in 1943 saw Bill literally scraping the bottom of a barrel! The postwar boom meant rapid growth for the hobby; however, small homes and new families left no room for O scale layouts, and many modelers moved to HO Scale.
The next twenty years brought great change. In 1958, Bill retired and his son Bruce took over. Just as full-size railroads were being hard-hit by new technology, so too were model railroads. Leisure time was spent in front of the TV set, not the train set. In 1960, Walthers became a full-line distributor of other manufacturers' products while continuing expansion of the Walthers lines. By the start of the 1970's, business was booming again, and Bruce's son Phil joined the company.
Expansion and diversification continue under Phil's tenure. The establishment of the Walthers Importing Division added several international lines. The manufacturing plant was modernized. Code 83 track was introduced in 1985, giving layouts more realistic proportions. In 1990, the Cornerstone Series buildings were unveiled. Combining a freight car with a related industry, the Cornerstone Series makes it possible for modelers to duplicate authentic operations, enhancing layout realism. The Train Line Deluxe Sets and locomotives debuted in 1994. These sets feature the detailing of serious models and an affordable price -- allowing newcomers to get started, and then build-on to their first set, rather than replacing it.
In 2005, Walthers purchased Life-Like from Lifoam Industries. With this purchase Walthers acquired the Proto Lines that have become the backbone of their locomotive and rolling stock segments.
Today, Walthers continues to expand, improve and develop a wide range of products. Their latest selection can be found throughout Walthers.com and their printed catalogs, along with items from over 300 other manufacturers.
In December 2017, Lowell Smith announced the ‘purchase of tooling’ of the Walthers line of N Scale passenger cars (sleeper, coach and baggage cars), and in June 2018, Atlas announced that it will purchase all N scale locomotive and rolling stock tooling owned by Walthers, including the Walthers N tooling as well as former Life-Like tooling. This divestment puts an end to Walthers involvement as a manufacturer of N scale rolling-stock, though it will continue its range of N scale structures.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-05-24 08:37:23
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.