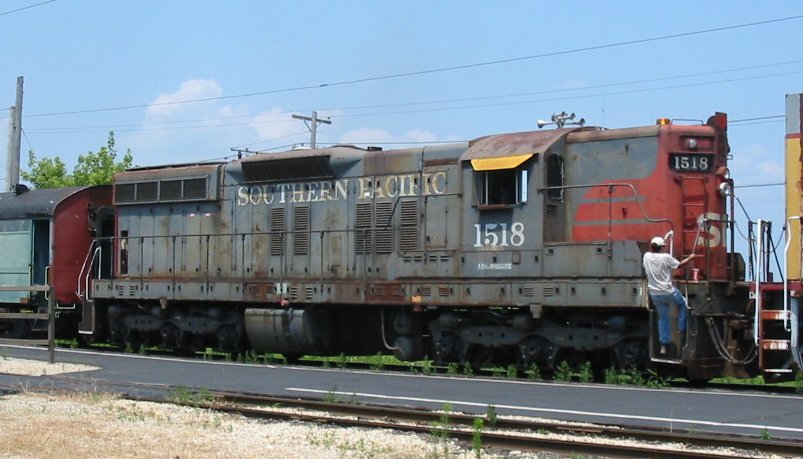
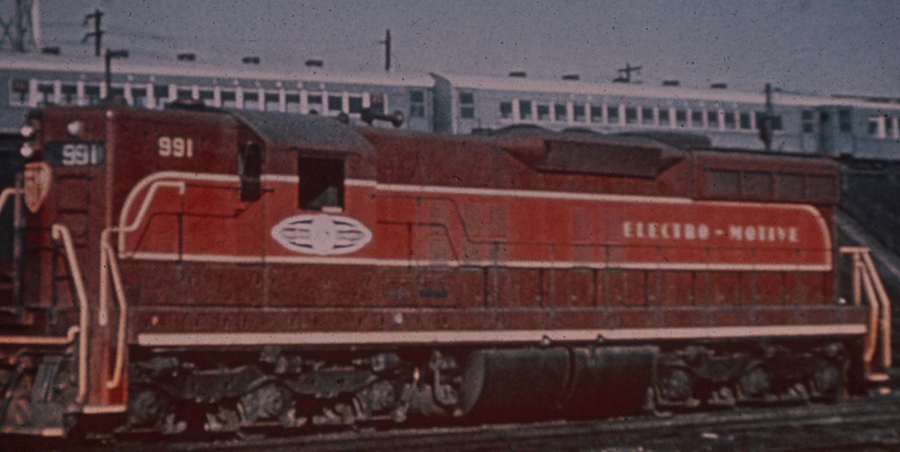
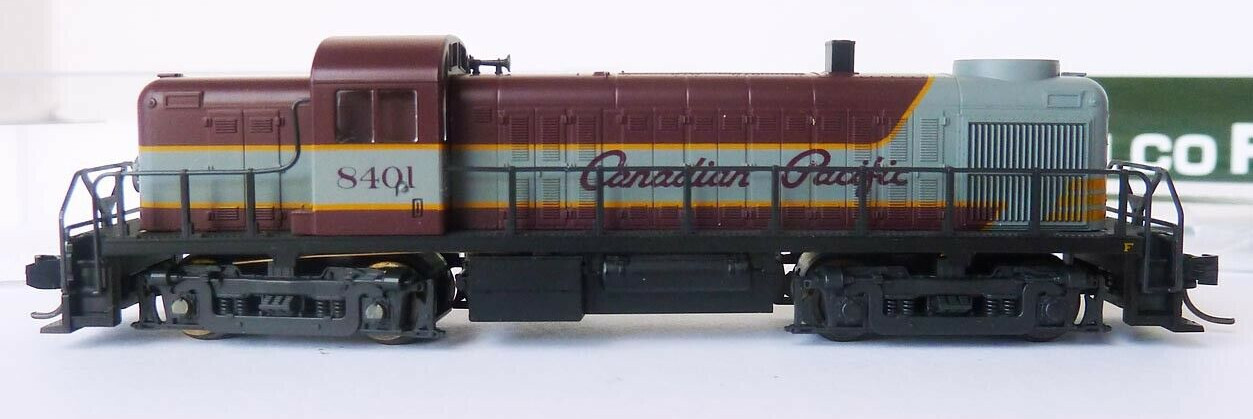
History: An SD7 is a 6-axle road switcher diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between February 1952 and November 1953. It had an EMD 567B 16-cylinder engine producing 1,500 horsepower (1.12 MW) for its six traction motors. 188 were built for United States railroads. Starting in August 1953 a total of 26 SD7s were produced which used either the 567BC engine or the 567C engine. These units are noted on the roster below.
This was the first model in EMD's SD (Special Duty) series of locomotives, a lengthened B-B GP7 with a C-C truck arrangement. The two extra axles and traction motors are useful in heavy, low speed freight service. SD series locomotives are still being produced today, with the SD70 being the most popular example in current production, and with many SD40-2s and rebuilds to SD40-2 specifications, or SD60s still in operation.
Yesterday's Special Duty eventually became today's Standard Duty, and yesterday's General Purpose has become today's Special Purpose ("time" freight and other time-sensitive lading). True GPs were discontinued after the completion of the last GP60 in 1994. Recently intermodal and other fast freights may be hauled by 6 axles locomotives with 4 powered axles, such as the SD70Ace-P4.
Many earlier model GPs, most particularly GP40s, GP39s and GP38s, also their SD equivalents, SD40s, SD39s and SD38s have been rebuilt to Dash 2 standards for another 30 to 40 years of service.
From Wikipedia
This was the first model in EMD's SD (Special Duty) series of locomotives, a lengthened B-B GP7 with a C-C truck arrangement. The two extra axles and traction motors are useful in heavy, low speed freight service. SD series locomotives are still being produced today, with the SD70 being the most popular example in current production, and with many SD40-2s and rebuilds to SD40-2 specifications, or SD60s still in operation.
Yesterday's Special Duty eventually became today's Standard Duty, and yesterday's General Purpose has become today's Special Purpose ("time" freight and other time-sensitive lading). True GPs were discontinued after the completion of the last GP60 in 1994. Recently intermodal and other fast freights may be hauled by 6 axles locomotives with 4 powered axles, such as the SD70Ace-P4.
Many earlier model GPs, most particularly GP40s, GP39s and GP38s, also their SD equivalents, SD40s, SD39s and SD38s have been rebuilt to Dash 2 standards for another 30 to 40 years of service.
From Wikipedia
Railroad/Company: Electro-Motive Diesel (EMD) is an American manufacturer of diesel-electric locomotives, locomotive products and diesel engines for the rail industry. The company is owned by Caterpillar through its subsidiary Progress Rail Services Corporation.
Electro-Motive Diesel traces its roots to the Electro-Motive Engineering Corporation, a designer and marketer of gasoline-electric self-propelled rail cars founded in 1922 and later renamed Electro-Motive Company (EMC). In 1930, General Motors purchased Electro-Motive Company and the Winton Engine Co., combining the two to form its Electro-Motive Division (EMD) in 1941.
In 2005, GM sold EMD to Greenbriar Equity Group and Berkshire Partners, which formed Electro-Motive Diesel to facilitate the purchase. In 2010, Progress Rail Services completed the purchase of Electro-Motive Diesel from Greenbriar, Berkshire, and others.
EMD's headquarters, engineering facilities and parts manufacturing operations are based in McCook, Illinois, while its final locomotive assembly line is located in Muncie, Indiana. EMD also operates a traction motor maintenance, rebuild and overhaul facility in San Luis Potosí, Mexico.
As of 2008, EMD employed approximately 3,260 people, and in 2010 it held approximately 30 percent of the market for diesel-electric locomotives in North America.
From Wikipedia
Electro-Motive Diesel traces its roots to the Electro-Motive Engineering Corporation, a designer and marketer of gasoline-electric self-propelled rail cars founded in 1922 and later renamed Electro-Motive Company (EMC). In 1930, General Motors purchased Electro-Motive Company and the Winton Engine Co., combining the two to form its Electro-Motive Division (EMD) in 1941.
In 2005, GM sold EMD to Greenbriar Equity Group and Berkshire Partners, which formed Electro-Motive Diesel to facilitate the purchase. In 2010, Progress Rail Services completed the purchase of Electro-Motive Diesel from Greenbriar, Berkshire, and others.
EMD's headquarters, engineering facilities and parts manufacturing operations are based in McCook, Illinois, while its final locomotive assembly line is located in Muncie, Indiana. EMD also operates a traction motor maintenance, rebuild and overhaul facility in San Luis Potosí, Mexico.
As of 2008, EMD employed approximately 3,260 people, and in 2010 it held approximately 30 percent of the market for diesel-electric locomotives in North America.
From Wikipedia
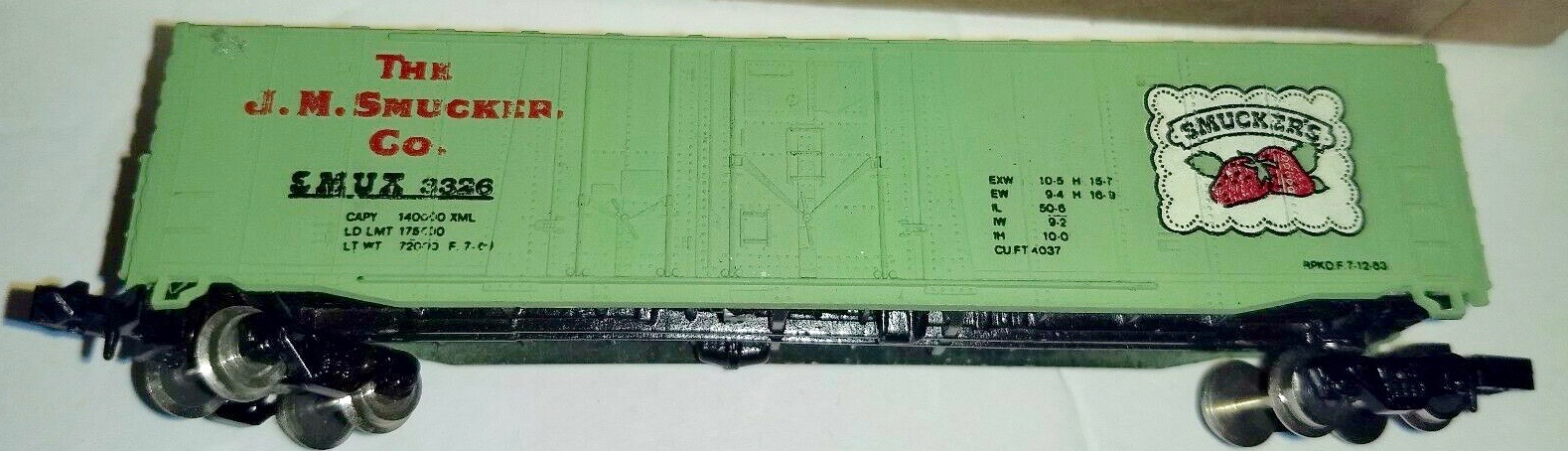
Item Links: We found: 1 different collections associated with Rail - Locomotive - EMD SD7
- Collection N Scale Model Trains: 122 different items.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-04-15 09:41:27
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.