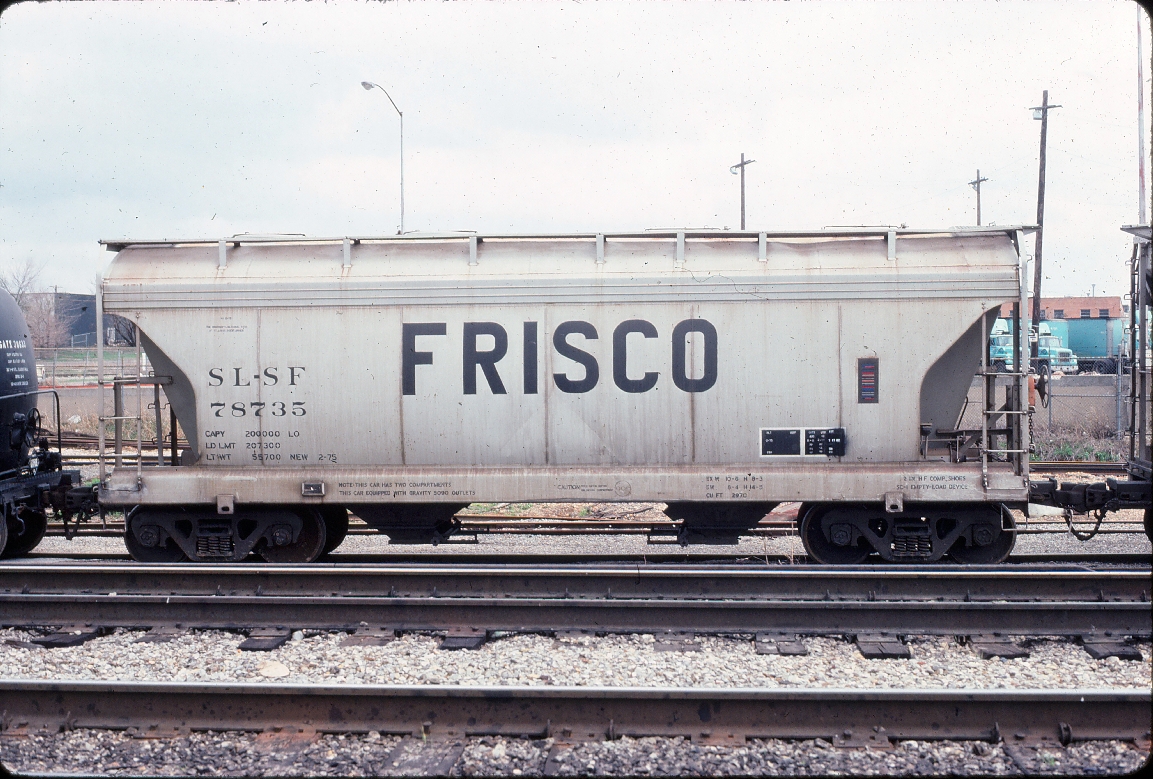Model Information: Atlas first introduced this model in 1995. It has always been manufactured in China. The early releases came equipped with Rapido couplers. Later versions come with Accumate couplers.
This is quite definitely a "2nd Generation" tooling. It does feature low-profile wheels with magnetically operated couplers (Accumate). The print quality is excellent and the mold shows great attention to detail. However, it lacks the key three features of a 3rd gen model: metal wheels, body-mount couplers and detail parts. While the tooling is very high quality, the only noticeable detail part is the brake wheel - which is nothing special. The stirrups, while not being as clunky as early Atlas and Roco designs, lack the realistic appearance of a 3rd gen model where this part is typically not part of the mold. A nice model for its time (mid 1990s) but essentially a beginner's model at the time of this review (2017).
This is quite definitely a "2nd Generation" tooling. It does feature low-profile wheels with magnetically operated couplers (Accumate). The print quality is excellent and the mold shows great attention to detail. However, it lacks the key three features of a 3rd gen model: metal wheels, body-mount couplers and detail parts. While the tooling is very high quality, the only noticeable detail part is the brake wheel - which is nothing special. The stirrups, while not being as clunky as early Atlas and Roco designs, lack the realistic appearance of a 3rd gen model where this part is typically not part of the mold. A nice model for its time (mid 1990s) but essentially a beginner's model at the time of this review (2017).
Prototype History: In addition to leasing and servicing its cars, FGE also built much of its own equipment. It should come as no surprise that the company’s main products were refrigerated cars; first ice-cooled cars and then mechanical reefers. Insulated boxcars became increasingly popular in the 1960s and 1970s.
FGE built the cars and then leased them to its parent railroads. Cars on long-term lease could be found in FGE paint schemes with the railroad’s reporting marks, or painted for the leasing road with minimal if any FGE information. Other cars roamed freely in open interchange service in FGE’s own fleet. Maintenance on these cars was also performed by FGE at their own shops.
Palletized shipments of perishables led to the introduction of this class in the early 1960s. The interior is fitted with restraints, which hold the loads securely and protect them against damage caused by slack action. To speed loading times, 10'6" plug doors are used, providing easier access for forklifts. These cars also carry electronic items, furniture, paper, machinery and other temperature-sensitive cargo.
Today, some FGE products still roam the rails. When it sold its own reefer fleet in the 1990s, cars were sold to Burlington Northern and Union Pacific. Modernized with new refrigeration units, many are still in service. While a few are still in service on local freights on Norfolk Southern and CSX, several more FGE-built cabooses of B&O, Conrail and L&N heritage can be found in parks and museums. What remains of FGE as a company is primarily paper – it is a wholly owned subsidiary of CSX.
FGE built the cars and then leased them to its parent railroads. Cars on long-term lease could be found in FGE paint schemes with the railroad’s reporting marks, or painted for the leasing road with minimal if any FGE information. Other cars roamed freely in open interchange service in FGE’s own fleet. Maintenance on these cars was also performed by FGE at their own shops.
Palletized shipments of perishables led to the introduction of this class in the early 1960s. The interior is fitted with restraints, which hold the loads securely and protect them against damage caused by slack action. To speed loading times, 10'6" plug doors are used, providing easier access for forklifts. These cars also carry electronic items, furniture, paper, machinery and other temperature-sensitive cargo.
Today, some FGE products still roam the rails. When it sold its own reefer fleet in the 1990s, cars were sold to Burlington Northern and Union Pacific. Modernized with new refrigeration units, many are still in service. While a few are still in service on local freights on Norfolk Southern and CSX, several more FGE-built cabooses of B&O, Conrail and L&N heritage can be found in parks and museums. What remains of FGE as a company is primarily paper – it is a wholly owned subsidiary of CSX.
Road Name History: The BNSF Railway (reporting mark BNSF) is one of the largest freight railroad networks in North America, second to the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) (its primary competitor for Western U.S. freight), and is one of seven North American Class I railroads. It has 48,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and over 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide high-speed links between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.[2] The BNSF and UP have a duopoly on all transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western U.S. and share trackage rights over thousands of miles of track.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
According to corporate press releases, the BNSF Railway is among the top transporters of intermodal freight in North America. It also hauls bulk cargo. For instance, the railroad hauls enough coal to generate roughly ten percent of the electricity produced in the United States.
Headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, the railroad is a wholly owned subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.
The creation of BNSF started with the formation of a holding company, the Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation on September 22, 1995. This new holding company then purchased the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway (often called the "Santa Fe") and Burlington Northern Railroad, and formally merged the railways into the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway on December 31, 1996. On January 24, 2005, the railroad's name was officially changed to "BNSF Railway," using the initials of its original name.
In 1999, Burlington Northern Santa Fe and the Canadian National Railway announced their intention to merge and form a new corporation entitled North American Railways to be headquartered in Montreal, Canada. The United States' Surface Transportation Board (STB) placed a 15-month moratorium on all rail mergers, which ended this merger.
On November 3, 2009, Warren Buffett's Berkshire Hathaway announced it would acquire the remaining 77.4 percent of BNSF it did not already own for $100 per share in cash and stock - a deal valued at $44 billion. The company is investing an estimated $34 billion in BNSF and acquiring $10 billion in debt. On February 12, 2010, shareholders of Burlington Northern Santa Fe Corporation voted in favor of the acquisition.
Brand/Importer Information: In 1924 Stephan Schaffan, Sr. founded the Atlas Tool Company in Newark, New Jersey. In 1933 his son, Stephan Schaffan, Jr., came to work for his father at the age of sixteen. Steve Jr. built model airplanes as a hobby and frequented a local hobby shop. Being an enterprising young man, he would often ask the owner if there was anything he could do to earn some extra spending money. Tired of listening to his requests, the hobby-store owner threw some model railroad track parts his way and said, "Here, see if you can improve on this".
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
In those days, railroad modelers had to assemble and build everything from scratch. Steve Jr. created a "switch kit" which sold so well, that the entire family worked on them in the basement at night, while doing business as usual in the machine shop during the day.
Subsequently, Steve Jr. engineered the stapling of rail to fiber track, along with inventing the first practical rail joiner and pre-assembled turnouts and flexible track. All of these products, and more, helped to popularize model railroading and assisted in the creation of a mass-market hobby. The budding entrepreneur quickly outgrew the limitations of a basement and small garage operation. Realizing they could actually make a living selling track and related products, Steve and his father had the first factory built in Hillside, New Jersey at 413 Florence Avenue in 1947. On September 30, 1949, the Atlas Tool Company was officially incorporated as a New Jersey company.
In 1985, Steve was honored posthumously for his inventions by the Model Railroad Industry Association and was inducted into the Model Railroad Industry Hall of Fame in Baltimore, Maryland. In addition, Steve was nominated and entered into the National Model Railroad Association Pioneers of Model Railroading in 1995.
In the early 1990s, the Atlas Tool Company changed its name to Atlas Model Railroad Company, Inc.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-03-06 09:26:31. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-12-02 11:49:19
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.