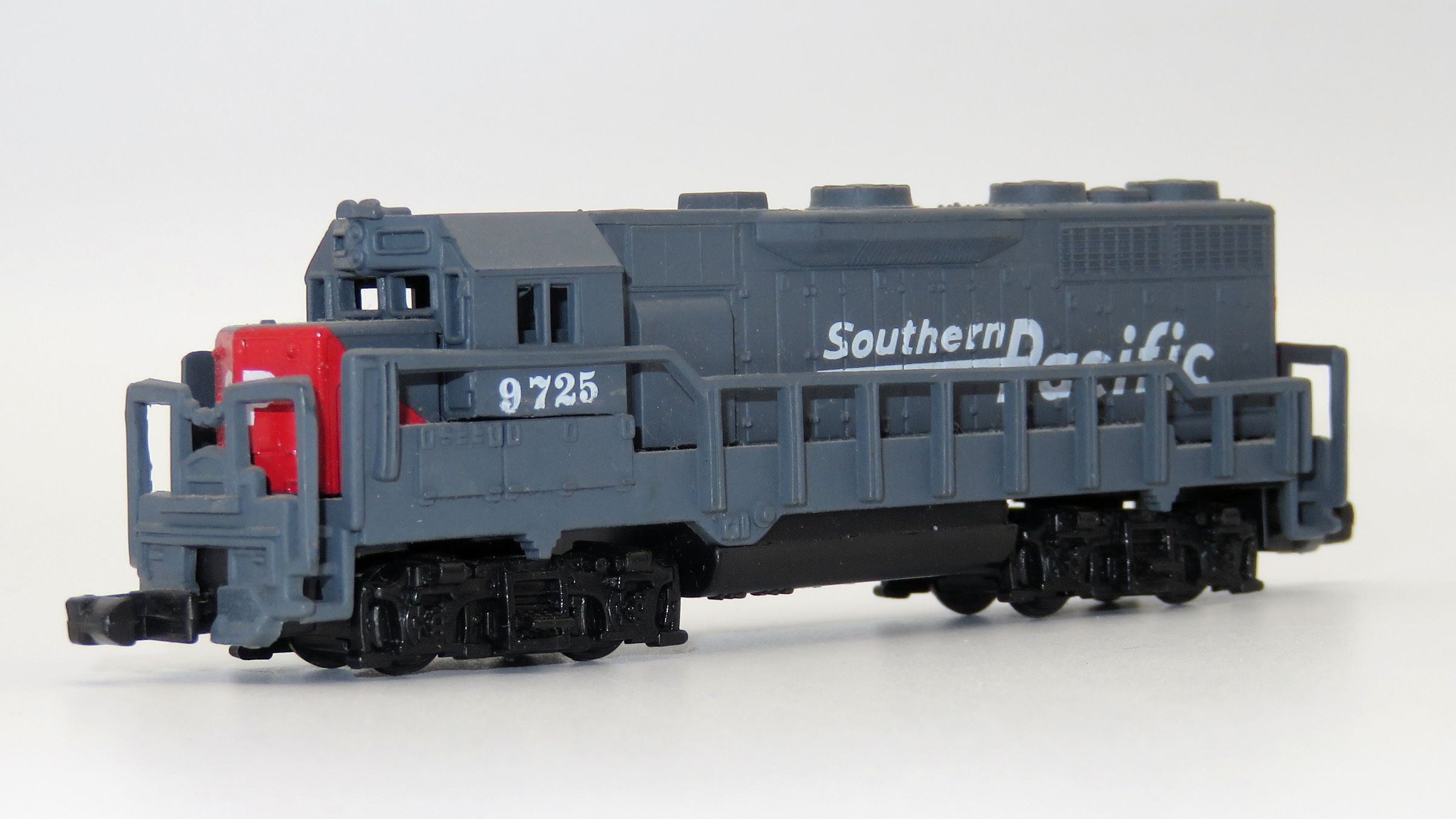
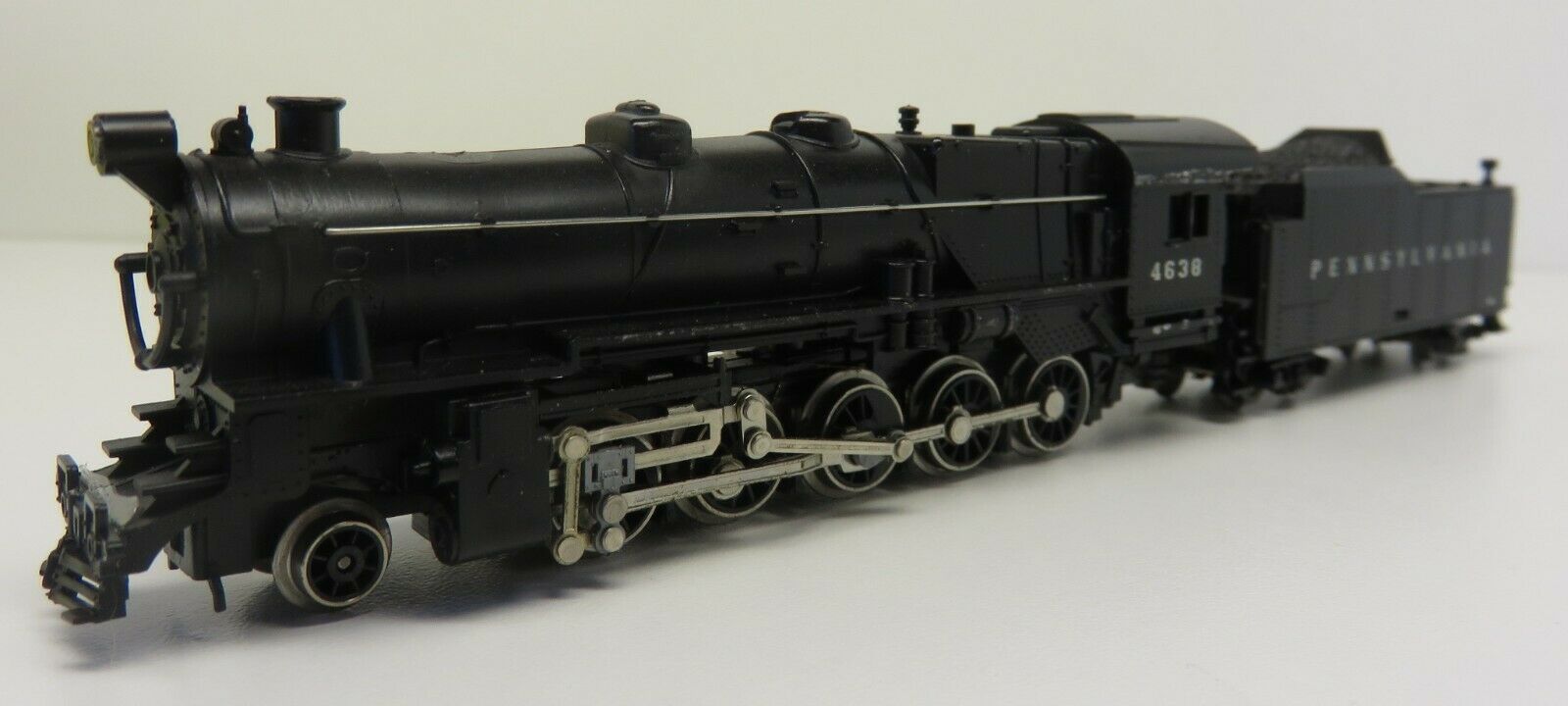
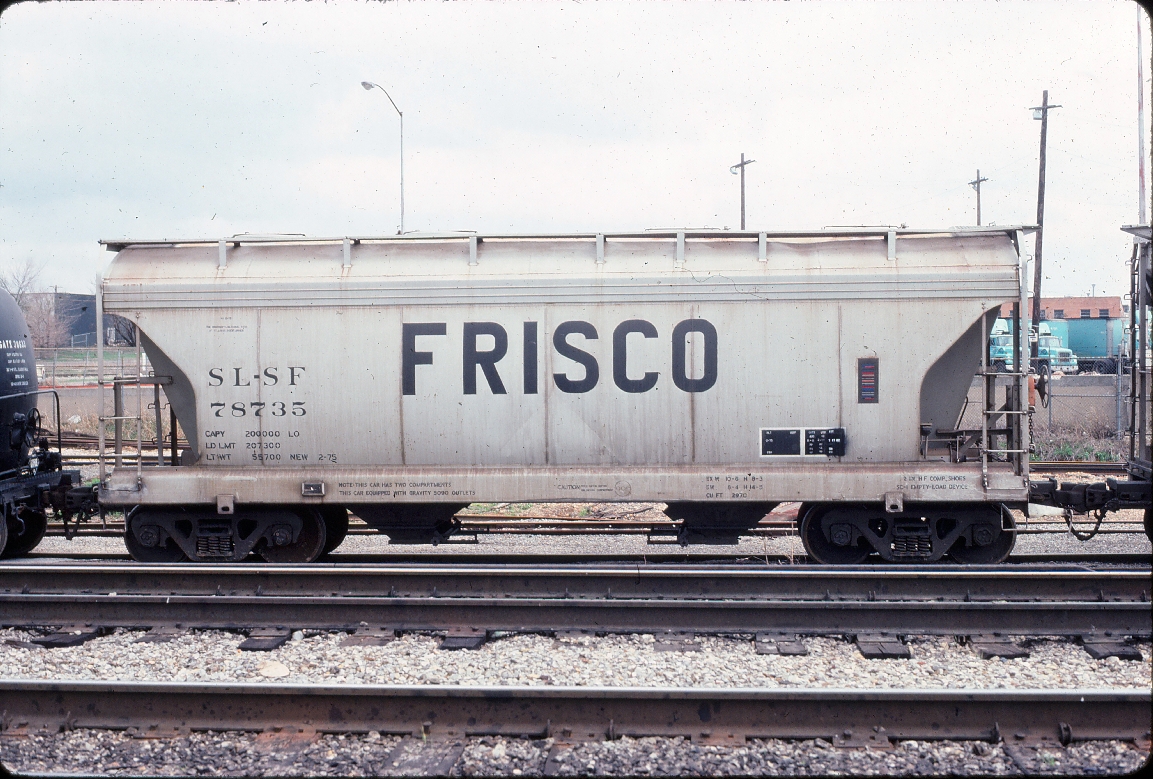Model Information: This body style first appears in Atlas' 1992 catalog with a pre-production photo and labeled "Coming in late '91". Seven road names were announced as well as a 3900 Undecorated model. The original release was made in Atlas' New Jersey facility and marked "Atlas USA" on the frame. Later production was moved to China and marketed under Atlas' Trainman® line.
Prototype History: The 2-bay covered hopper first entered service in the 1950s. The cars handle loads such as cement, sand and similar denser bulk commodities. In the 1960s, American Car and Foundry introduced the Centerflow design. The Centerflow relies on the car's rounded body to provide structural strength without the added weight of bracing, as well as making gravity unloading easier. This 2-bay car came in a 2,970-cubic foot capacity.
The first ACF covered hoppers were rib-side cars, like many others of the time. In the 1960's ACF eliminated the supporting ribs and started building what they called the Center Flow(R) hopper with a smooth, rounded side. The cars were built at several ACF plants, but the Huntington, West Virginia plant built only Center Flow cars since their inception and was the primary builder.
The first ACF covered hoppers were rib-side cars, like many others of the time. In the 1960's ACF eliminated the supporting ribs and started building what they called the Center Flow(R) hopper with a smooth, rounded side. The cars were built at several ACF plants, but the Huntington, West Virginia plant built only Center Flow cars since their inception and was the primary builder.
Road Name History: This line was established in 1852 under another name but was renamed Western Maryland Rail Road before the first rail was laid. By 1862 they had built from Baltimore to Union Bridge, Maryland at which point it became the responsibility of the Union Army. Construction resumed after the war. WM built west to Hagerstown then Cumberland where the line spilt in two. One route headed northwest to an important interchange with Pittsburgh & Lake Erie at Connellsville, Pennsylvania. The other line ran southwest into the rich coal fields around Elkins and Durban, West Virginia. On the east end, they also had routes to York and Gettysburg and an important connection with the Reading at Shippensburg, all in Pennsylvania. At 878 miles, WM was between Maine Central and Spokane Portland & Seattle in relative length.
The city of Baltimore had a large stake in the WM but sold it in 1902 to Jay Gould. The Gould empire unraveled just six years later and the WM was reorganized with Railway replacing Rail Road in the name and John D. Rockefeller holding a 43% stake. He sold those shares to Baltimore & Ohio in 1927. Accused of violating antitrust laws, B&O placed those shares in a non-voting trust.
After 1900, WM relied heavily on 2-8-0’s, ordering 177 between 1900 and 1923 (by which time other railroads were already ordering 2-8-2’s.) Some of these Consolidations were real bruisers with the same tractive effort as WM’s 2-6-6-2’s. Also in road service were 30 2-10-0 Decapods (10 Russian Decapods and 20 much larger versions,) a dozen 4-8-4’s to handle the high speed trains, and a dozen 4-6-6-4 Challengers. The Challengers turned out to be a disappointment to WM. They were rough riders and were hard on the track. As a result, they were soon demoted to pusher service alongside WM’s 25 2-8-8-2’s. A fleet of 19 low drivered Pacifics handled most of the passenger assignments. One element found on most of the WM steam fleet was low snowplow pilots in lieu of the traditional boiler tube pilots. WM was one of a few Class One railroads to employ Shay locomotives to serve steeply graded branchlines. WM had one 2-truck, two 3-truck and two 4-truck Shays. Shay #6 built in 1945 was the last Shay built by Lima Locomotive Works.
WM began to dieselize in 1947 on the east end where they would not raise the ire of their coal mining customers on the west end. The diesel fleet was surprisingly varied for a line their size with cab units from both Alco and EMD, road switchers from Alco, EMD and Baldwin and yard switchers from GE, Baldwin and Alco. The road switchers from Alco and Baldwin plus the EMD GP7;s were delivered with the long hood as the front while the EMD GP9’s were delivered with the short hood as the front. The Second Generation of diesels was all EMD.
In addition to the voluminous coal traffic, WM was a part of two bridge routes for merchandise moving between the northeast and the upper Midwest. These were the Alphabet Route (with Nickel Plate Road, Wheeling & Lake Erie, Pittsburgh & West Virginia, Reading and others) and the Central States Dispatch (with Baltimore & Ohio, Reading, Jersey Central, Lehigh & Hudson River and New Haven.) Iron ore also moved from Baltimore area ports to steel mills on the connecting P&LE.
Passenger service was a bit of an afterthought on the WM. Not only did they not have a shiny streamliner, but their heavyweight coach trains lasted only until 1957 before being discontinued. Steam generator equipped hammerhead RS-3’s replaced the Pacifics in passenger service for a few years before being reassigned to freight duty.
In 1967, B&O (by this time controlled by Chesapeake & Ohio) finally obtained permission to take overt control of the WM. Not much changed for the next five years. In 1973 they adopted the Chessie System image and 125 miles of WM mainline was abandoned in favor of trackage rights on a parallel B&O line. In 1983, the Western Maryland was absorbed into the Baltimore & Ohio. Western Maryland was known for frequently washing their locomotives in both the steam and diesel eras. They kept up this tradition until the start of the Chessie System era.
The city of Baltimore had a large stake in the WM but sold it in 1902 to Jay Gould. The Gould empire unraveled just six years later and the WM was reorganized with Railway replacing Rail Road in the name and John D. Rockefeller holding a 43% stake. He sold those shares to Baltimore & Ohio in 1927. Accused of violating antitrust laws, B&O placed those shares in a non-voting trust.
After 1900, WM relied heavily on 2-8-0’s, ordering 177 between 1900 and 1923 (by which time other railroads were already ordering 2-8-2’s.) Some of these Consolidations were real bruisers with the same tractive effort as WM’s 2-6-6-2’s. Also in road service were 30 2-10-0 Decapods (10 Russian Decapods and 20 much larger versions,) a dozen 4-8-4’s to handle the high speed trains, and a dozen 4-6-6-4 Challengers. The Challengers turned out to be a disappointment to WM. They were rough riders and were hard on the track. As a result, they were soon demoted to pusher service alongside WM’s 25 2-8-8-2’s. A fleet of 19 low drivered Pacifics handled most of the passenger assignments. One element found on most of the WM steam fleet was low snowplow pilots in lieu of the traditional boiler tube pilots. WM was one of a few Class One railroads to employ Shay locomotives to serve steeply graded branchlines. WM had one 2-truck, two 3-truck and two 4-truck Shays. Shay #6 built in 1945 was the last Shay built by Lima Locomotive Works.
WM began to dieselize in 1947 on the east end where they would not raise the ire of their coal mining customers on the west end. The diesel fleet was surprisingly varied for a line their size with cab units from both Alco and EMD, road switchers from Alco, EMD and Baldwin and yard switchers from GE, Baldwin and Alco. The road switchers from Alco and Baldwin plus the EMD GP7;s were delivered with the long hood as the front while the EMD GP9’s were delivered with the short hood as the front. The Second Generation of diesels was all EMD.
In addition to the voluminous coal traffic, WM was a part of two bridge routes for merchandise moving between the northeast and the upper Midwest. These were the Alphabet Route (with Nickel Plate Road, Wheeling & Lake Erie, Pittsburgh & West Virginia, Reading and others) and the Central States Dispatch (with Baltimore & Ohio, Reading, Jersey Central, Lehigh & Hudson River and New Haven.) Iron ore also moved from Baltimore area ports to steel mills on the connecting P&LE.
Passenger service was a bit of an afterthought on the WM. Not only did they not have a shiny streamliner, but their heavyweight coach trains lasted only until 1957 before being discontinued. Steam generator equipped hammerhead RS-3’s replaced the Pacifics in passenger service for a few years before being reassigned to freight duty.
In 1967, B&O (by this time controlled by Chesapeake & Ohio) finally obtained permission to take overt control of the WM. Not much changed for the next five years. In 1973 they adopted the Chessie System image and 125 miles of WM mainline was abandoned in favor of trackage rights on a parallel B&O line. In 1983, the Western Maryland was absorbed into the Baltimore & Ohio. Western Maryland was known for frequently washing their locomotives in both the steam and diesel eras. They kept up this tradition until the start of the Chessie System era.
Brand/Importer Information: Loco-Motives was a division of Mallerich Hobby Corp. The company provided custom printing services for railroad modeling. Mallerich Hobby Corporation was incorporated on Friday 31st January 1992 in Taneytown Maryland. They are no longer in business. They repainted other companies models.
Item created by: gdm on 2018-02-27 08:42:38. Last edited by gdm on 2020-07-24 07:29:17
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.