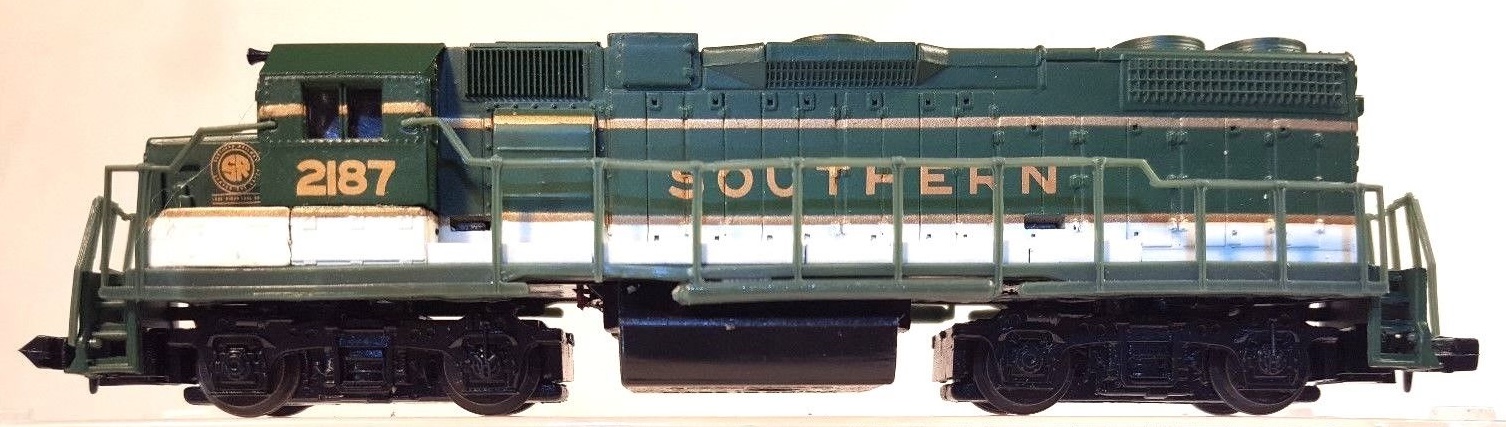
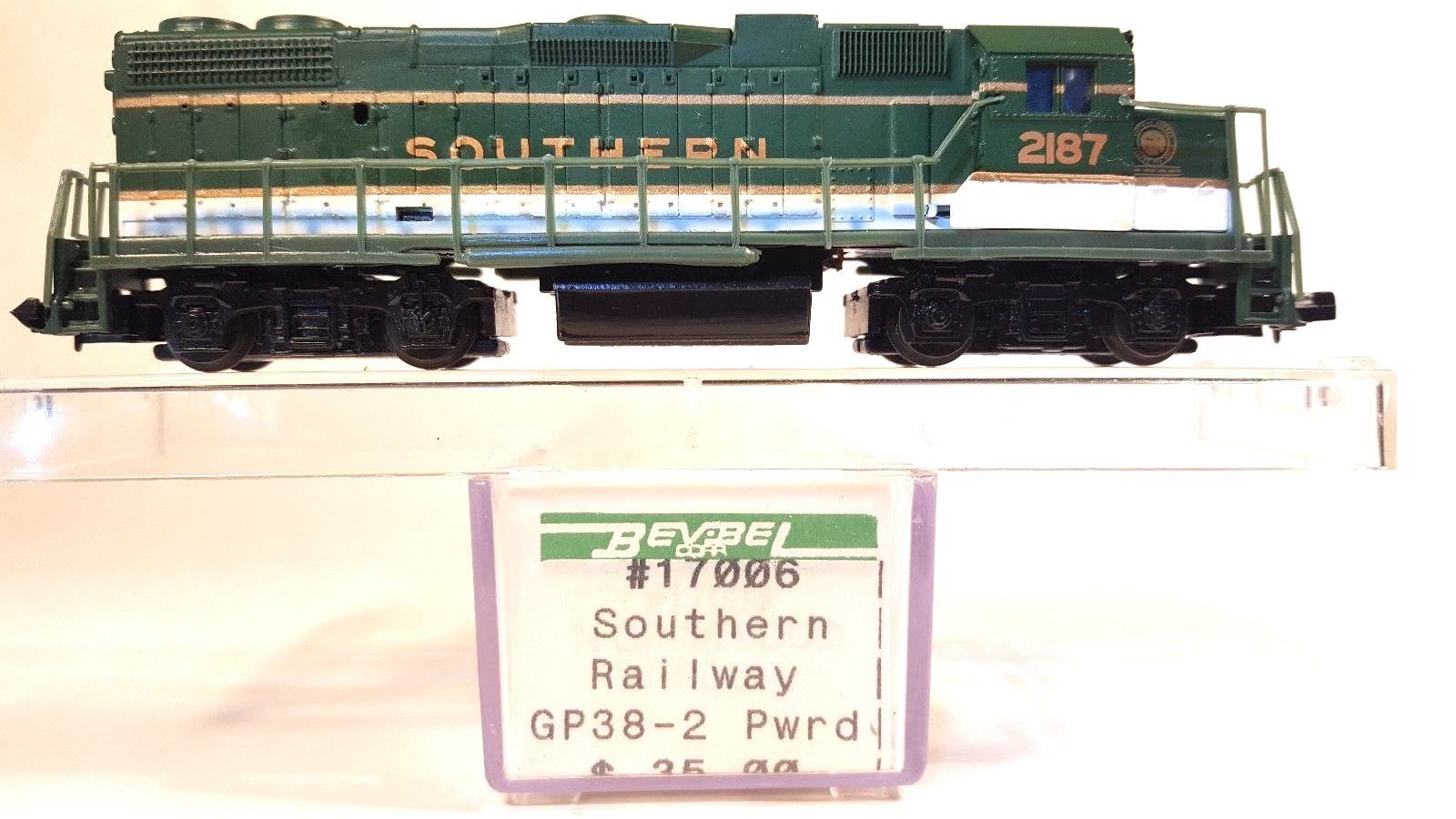
Specific Item Information: Engine underside reads 'Made in China'
Road number not matching any known prototype.
Road number not matching any known prototype.
Model Information: This model was first released by Life-Like in 1988. It was later made by Life-Like for Bev-Bel in the early 1990's. It was overhauled in 2006. After the acquisition by Walthers, it was again updated in 2015 and sold under the Walthers N brand. This has always been an economy model that runs well and doesn't cost as much as the Kato and Atlas equivalents.
The original design was a simple open-sided 5-pole motor with weights and truck-mounted rapido couplers. The 2006 version went to a split frame design with flywheels, LED lights and body mounted Accumate couplers. The motor is NOT isolated from the frame so this version is not DCC-Ready. The 2015 version does accept a drop-in decoder and is DCC-Ready. This most recent Walthers version has Micro-Trains couplers.
The original design was a simple open-sided 5-pole motor with weights and truck-mounted rapido couplers. The 2006 version went to a split frame design with flywheels, LED lights and body mounted Accumate couplers. The motor is NOT isolated from the frame so this version is not DCC-Ready. The 2015 version does accept a drop-in decoder and is DCC-Ready. This most recent Walthers version has Micro-Trains couplers.
DCC Information: The early 1988 version is not DCC anything.
The 2006 redo is marginally DCC-Friendly. A DCC decoder installation for this version can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog and in this article. Using a drop-in decoder for Atlas locos is also possible, pending some modification of the chassis and some soldering, as shown on the same article.
The 2015 version is fully DCC-Ready, and will accept the following drop-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163L0A: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Walthers/life-Like Proto GP20 and similar locos
- TCS L1D4 (Installation in Life-Like GP20, very similar to this GP38-2)
The 2006 redo is marginally DCC-Friendly. A DCC decoder installation for this version can be found on Brad Myers' N-scale DCC decoder installs blog and in this article. Using a drop-in decoder for Atlas locos is also possible, pending some modification of the chassis and some soldering, as shown on the same article.
The 2015 version is fully DCC-Ready, and will accept the following drop-in decoders:
- Digitrax DN163L0A: 1 Amp N Scale Mobile Decoder for Walthers/life-Like Proto GP20 and similar locos
- TCS L1D4 (Installation in Life-Like GP20, very similar to this GP38-2)
Prototype History: The EMD GP38-2 is a four-axle diesel-electric locomotive of the road switcher type built by General Motors, Electro-Motive Division. Part of the EMD Dash 2 line, the GP38-2 was an upgraded version of the earlier GP38. Power is provided by an EMD 645E 16-cylinder engine, which generates 2000 horsepower (1.5 MW). Most built still remain in service in the modern era due to ease of maintenance and exceptional reliability.
The GP38-2 differs externally from the earlier GP38 only in minor details. Its most distinctive identifying feature is the cooling water level sight glass on the right side of the long hood. The battery box covers of the Dash 2s are bolted down instead of hinged. It can be distinguished from the contemporary GP39-2 and GP40-2 in that its Roots blown engine had two exhaust stacks, one on each side of the dynamic brake fan, if equipped, while the turbocharged GP39-2 and GP40-2 has a single stack. The GP39-2 has two radiator fans on the rear of the long hood like the GP38-2, while the GP40-2 has three. It was also available with either a high-short-hood, common on Norfolk Southern units, or a low-short-hood, which is found on most other railroads.
From Wikipedia
The GP38-2 differs externally from the earlier GP38 only in minor details. Its most distinctive identifying feature is the cooling water level sight glass on the right side of the long hood. The battery box covers of the Dash 2s are bolted down instead of hinged. It can be distinguished from the contemporary GP39-2 and GP40-2 in that its Roots blown engine had two exhaust stacks, one on each side of the dynamic brake fan, if equipped, while the turbocharged GP39-2 and GP40-2 has a single stack. The GP39-2 has two radiator fans on the rear of the long hood like the GP38-2, while the GP40-2 has three. It was also available with either a high-short-hood, common on Norfolk Southern units, or a low-short-hood, which is found on most other railroads.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The Southern Railway (reporting mark SOU) (also known as Southern Railway Company) was a US class 1 railroad that was based in the Southern United States. It was the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.
The Southern Railway (reporting mark SOU) (also known as Southern Railway Company) was a US class 1 railroad that was based in the Southern United States. It was the product of nearly 150 predecessor lines that were combined, reorganized and recombined beginning in the 1830s, formally becoming the Southern Railway in 1894.
At the end of 1970 Southern operated 6,026 miles (9,698 km) of railroad, not including its Class I subsidiaries AGS (528 miles or 850 km) CofG (1729 miles) S&A (167 miles) CNOTP (415 miles) GS&F (454 miles) and twelve Class II subsidiaries. That year Southern itself reported 26111 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 110 million passenger-miles; AGS reported 3854 and 11, CofG 3595 and 17, S&A 140 and 0, CNO&TP 4906 and 0.3, and GS&F 1431 and 0.3
The railroad joined forces with the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) in 1982 to form the Norfolk Southern Corporation. The Norfolk Southern Corporation was created in response to the creation of the CSX Corporation (its rail system was later transformed to CSX Transportation in 1986). The Southern Railway was renamed Norfolk Southern Railway in 1990 and continued under that name ever since. Seven years later in 1997 the railroad absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway, ending the Norfolk and Western's existence as an independent railroad.

At the end of 1970 Southern operated 6,026 miles (9,698 km) of railroad, not including its Class I subsidiaries AGS (528 miles or 850 km) CofG (1729 miles) S&A (167 miles) CNOTP (415 miles) GS&F (454 miles) and twelve Class II subsidiaries. That year Southern itself reported 26111 million net ton-miles of revenue freight and 110 million passenger-miles; AGS reported 3854 and 11, CofG 3595 and 17, S&A 140 and 0, CNO&TP 4906 and 0.3, and GS&F 1431 and 0.3
The railroad joined forces with the Norfolk and Western Railway (N&W) in 1982 to form the Norfolk Southern Corporation. The Norfolk Southern Corporation was created in response to the creation of the CSX Corporation (its rail system was later transformed to CSX Transportation in 1986). The Southern Railway was renamed Norfolk Southern Railway in 1990 and continued under that name ever since. Seven years later in 1997 the railroad absorbed the Norfolk and Western Railway, ending the Norfolk and Western's existence as an independent railroad.
Brand/Importer Information:  Formerly located in Cresskill, New Jersey, the now defunct Bev-Bel Corp. was founded by the late Irvin and Beverly Belkin in 1956. A prolific "boutique" producer of after-market, limited production, special run rolling stock and locomotives (in road names and non-traditional commemorative and holiday themed paint schemes that were not typically offered by the major manufacturers), Bev-Bel' sourced its models from Atlas Tool Co., Inc., Atlas Model Railroad Co., Inc., Bachmann, and Life-Like Trains.
Formerly located in Cresskill, New Jersey, the now defunct Bev-Bel Corp. was founded by the late Irvin and Beverly Belkin in 1956. A prolific "boutique" producer of after-market, limited production, special run rolling stock and locomotives (in road names and non-traditional commemorative and holiday themed paint schemes that were not typically offered by the major manufacturers), Bev-Bel' sourced its models from Atlas Tool Co., Inc., Atlas Model Railroad Co., Inc., Bachmann, and Life-Like Trains.

Item created by: Alain LM on 2017-12-17 11:44:58. Last edited by Alain LM on 2020-10-03 11:55:49
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.