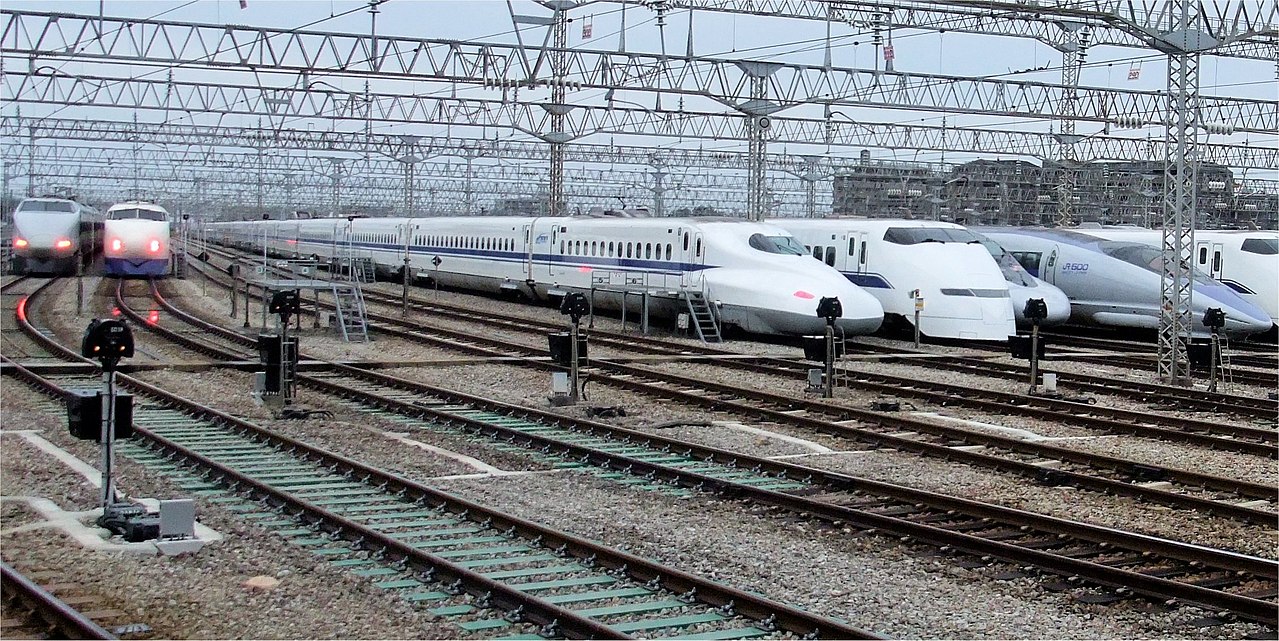
Specific Item Information: This is an individual end car with working head / tail lights and is intended to be part of a 100 Series Shinkansen train of up to 16 cars. It has a Tomix coupler that is compatible with other cars in this series.
Prototype History: The Shinkansen (Japanese: 新幹線, pronounced [ɕĩŋkã̠ɰ̃sẽ̞ɴ]), colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. Initially built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, in order to aid economic growth and development, beyond long-distance travel it is now also used as a commuter rail network. It is operated by five Japan Railways Group companies.
Starting with the Tōkaidō Shinkansen (615.4 km, 382.4 mi) in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of 2,764.6 km (1,717.8 mi) of lines with maximum speeds of 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph), 283.5 km (176.2 mi) of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of 130 km/h (80 mph), and 10.3 km (6.4 mi) of spur lines with Shinkansen services.[4] The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an extension to Sapporo under construction and scheduled to commence in March 2031. The maximum operating speed is 320 km/h (200 mph) (on a 387.5 km section of the Tōhoku Shinkansen). Test runs have reached 443 km/h (275 mph) for conventional rail in 1996, and up to a world record 603 km/h (375 mph) for maglev trains in April 2015..
From Wikipedia
Starting with the Tōkaidō Shinkansen (615.4 km, 382.4 mi) in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of 2,764.6 km (1,717.8 mi) of lines with maximum speeds of 240–320 km/h (150–200 mph), 283.5 km (176.2 mi) of Mini-Shinkansen lines with a maximum speed of 130 km/h (80 mph), and 10.3 km (6.4 mi) of spur lines with Shinkansen services.[4] The network presently links most major cities on the islands of Honshu and Kyushu, and Hakodate on northern island of Hokkaido, with an extension to Sapporo under construction and scheduled to commence in March 2031. The maximum operating speed is 320 km/h (200 mph) (on a 387.5 km section of the Tōhoku Shinkansen). Test runs have reached 443 km/h (275 mph) for conventional rail in 1996, and up to a world record 603 km/h (375 mph) for maglev trains in April 2015..
From Wikipedia
Road Name History: The Central Japan Railway Company (東海旅客鉄道株式会社 Tōkai Ryokaku Tetsudō Kabushiki-gaisha) is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai (JR東海). Its headquarters are located in the JR Central Towers in Nakamura-ku, Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture.
The company's operational hub is Nagoya Station. The busiest railway line it operates is the Tōkaidō Main Line between Atami Station and Maibara Station. JR Central also operates the Tōkaidō Shinkansen between Tokyo Station and Shin-Ōsaka Station. Additionally it is responsible for the Chūō Shinkansen?a proposed maglev service between Tokyo Station (or Shinagawa Station) and Ōsaka Station (or Shin-Ōsaka Station), of which a short demonstration section has been built. Currently, the company is conducting demonstrations of its shinkansen to railway officials from different countries in the effort to market bullet train technology overseas.
JR Central is Japan's most profitable and highest throughput high-speed-rail operator, carrying 138 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009, considerably more than the world's largest airline. Japan recorded a total of 289 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009.
From Wikipedia
The company's operational hub is Nagoya Station. The busiest railway line it operates is the Tōkaidō Main Line between Atami Station and Maibara Station. JR Central also operates the Tōkaidō Shinkansen between Tokyo Station and Shin-Ōsaka Station. Additionally it is responsible for the Chūō Shinkansen?a proposed maglev service between Tokyo Station (or Shinagawa Station) and Ōsaka Station (or Shin-Ōsaka Station), of which a short demonstration section has been built. Currently, the company is conducting demonstrations of its shinkansen to railway officials from different countries in the effort to market bullet train technology overseas.
JR Central is Japan's most profitable and highest throughput high-speed-rail operator, carrying 138 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009, considerably more than the world's largest airline. Japan recorded a total of 289 million high-speed-rail passengers in 2009.
From Wikipedia
Brand/Importer Information:  Tomix is a brand of Takara Tomy, a large Japanese conglomerate of companies that makes toys and games for the international marketplace. The Tomix brand (along with the Tomytec brand) are both managed by the Tomytec subsidiary/division of Takara Tomy. Prior to 1976 Tomy produced model trains using the "Tomy" brand name of the products. In 1976, they launched the new brand "Tomix" to segregate their model trains from their childrens toy lines.
Tomix is a brand of Takara Tomy, a large Japanese conglomerate of companies that makes toys and games for the international marketplace. The Tomix brand (along with the Tomytec brand) are both managed by the Tomytec subsidiary/division of Takara Tomy. Prior to 1976 Tomy produced model trains using the "Tomy" brand name of the products. In 1976, they launched the new brand "Tomix" to segregate their model trains from their childrens toy lines.
Generally it can be difficult to understand why Tomytec releases some items using the Tomix brand and others using the Tomytec brand. There are some generalizations we have observed. Thomas the Tank Engine falls under Tomix, as do the JNR steam engines as well as bullet trains (Shinkansen) and track cleaning cars. Maybe another curator can step in and elaborate on this section.

Generally it can be difficult to understand why Tomytec releases some items using the Tomix brand and others using the Tomytec brand. There are some generalizations we have observed. Thomas the Tank Engine falls under Tomix, as do the JNR steam engines as well as bullet trains (Shinkansen) and track cleaning cars. Maybe another curator can step in and elaborate on this section.
Manufacturer Information:  Largely a Japanese manufacturer of children's toys and baby products, Takara Tomy has established a number of different subsidiary companies, with sales offices and factories located in various locations around the world. The firm is the product of a 2006 merger-of-equals between Tomy and Takara.
Largely a Japanese manufacturer of children's toys and baby products, Takara Tomy has established a number of different subsidiary companies, with sales offices and factories located in various locations around the world. The firm is the product of a 2006 merger-of-equals between Tomy and Takara.
Takara Tomy produces N Scale model trains under their Tomytec division (we use the term loosely because it is actually a more complex relationship) using two different brand names "Tomytec" and "Tomix". Technically speaking these are not brands in the Western sense but rather they more closely resemble subsidiaries -of-subsidiaries, and where they fit in the corporate org chart may be the matter for a Master's thesis, but for our purposes we can think of them as simply two different brands with one manufacturer. In the past (prior to 1976) some model train products were branded simply "Tomy". To further confuse things, since 2000, outside of Japan, the company goes by the simple name, "Tomy" for their international subsidiaries.
If you consider both brand names as a single company, then the Tomytec/Tomix product line is the largest of its kind in Japan; with Kato following in second place (as of 2017). While Takara Tomy products are popular around the world, the firm's focus on children's toys has limited the international acceptance and distribution of its Tomytec model railroad products. Furthermore, unlike Kato, their focus tends to be heavily skewed towards Japanes prototypes.

Takara Tomy produces N Scale model trains under their Tomytec division (we use the term loosely because it is actually a more complex relationship) using two different brand names "Tomytec" and "Tomix". Technically speaking these are not brands in the Western sense but rather they more closely resemble subsidiaries -of-subsidiaries, and where they fit in the corporate org chart may be the matter for a Master's thesis, but for our purposes we can think of them as simply two different brands with one manufacturer. In the past (prior to 1976) some model train products were branded simply "Tomy". To further confuse things, since 2000, outside of Japan, the company goes by the simple name, "Tomy" for their international subsidiaries.
If you consider both brand names as a single company, then the Tomytec/Tomix product line is the largest of its kind in Japan; with Kato following in second place (as of 2017). While Takara Tomy products are popular around the world, the firm's focus on children's toys has limited the international acceptance and distribution of its Tomytec model railroad products. Furthermore, unlike Kato, their focus tends to be heavily skewed towards Japanes prototypes.
Item created by: nscalestation on 2017-10-28 16:55:42
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.