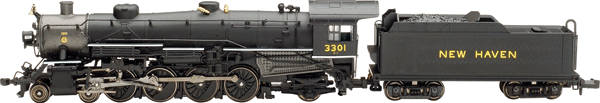Model Information: Bachmann introduced this model in 2003. They revised it in 2012. The early version runs a bit sketchy. The later version runs better. The early version has a split frame chassis with a skew-wound 5-pole motor. It does have traction tires. The later version has a 3-pole motor.
DCC Information: The 2003 version allows installation of a decoder in the tender with all wires for control of motor, power leads and lights terminating somewhere in the tender. A basic decoder with some soldering skills will likely do the trick. The 2012 redo is much easier but I am not sure if there is a factory decoder for this model.
Prototype History: Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 4-8-2 represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels and two trailing wheels. This type of steam locomotive is commonly known as the Mountain type.
The 4-8-2 was most popular on the North American continent. When the 4-6-2 Pacific fleets were becoming over-burdened as passenger trains grew in length and weight, the first North American 4-8-2 locomotives were built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) for the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) in 1911. It is possible that the "Mountain" name was originated by C&O, after the Allegheny Mountains where their first 4-8-2 locomotives were built to work. ALCO combined the traction of the eight-coupled 2-8-2 Mikado with the excellent tracking qualities of the Pacific's four-wheel leading truck. Although C&O intended their new Mountains for passenger service, the type also proved ideal for the new, faster freight services that railroads in the United States were introducing. Many 4-8-2 locomotives were therefore built for dual service.
The New York Central Railroad (NYC) called the 4-8-2 type of steam locomotive the Mohawk type. It was known as the Mountain type on other roads, but the mighty New York Central didn't see the name to be fitting on its famous Water Level Route, so it instead picked the name of one of those rivers its rails followed, the Mohawk River, to name its newest type of locomotive. Despite the more common name, the 4-8-2 was actually suited in many ways more to flatland running than slow mountain slogging, with its 4-wheel leading truck for stability at speed.
From Wikipedia
The 4-8-2 was most popular on the North American continent. When the 4-6-2 Pacific fleets were becoming over-burdened as passenger trains grew in length and weight, the first North American 4-8-2 locomotives were built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO) for the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway (C&O) in 1911. It is possible that the "Mountain" name was originated by C&O, after the Allegheny Mountains where their first 4-8-2 locomotives were built to work. ALCO combined the traction of the eight-coupled 2-8-2 Mikado with the excellent tracking qualities of the Pacific's four-wheel leading truck. Although C&O intended their new Mountains for passenger service, the type also proved ideal for the new, faster freight services that railroads in the United States were introducing. Many 4-8-2 locomotives were therefore built for dual service.
The New York Central Railroad (NYC) called the 4-8-2 type of steam locomotive the Mohawk type. It was known as the Mountain type on other roads, but the mighty New York Central didn't see the name to be fitting on its famous Water Level Route, so it instead picked the name of one of those rivers its rails followed, the Mohawk River, to name its newest type of locomotive. Despite the more common name, the 4-8-2 was actually suited in many ways more to flatland running than slow mountain slogging, with its 4-wheel leading truck for stability at speed.
From Wikipedia
Road Name History:  The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (reporting mark NH), commonly known as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated in New England from 1872 to 1968, dominating the region's rail traffic for the first half of the 20th century.
Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.

Beginning in the 1890s and accelerating in 1903, New York banker J. P. Morgan sought to monopolize New England transportation by arranging the NH's acquisition of 50 companies, including other railroads and steamship lines, and building a network of electrified trolley lines that provided interurban transportation for all of southern New England. By 1912, the New Haven operated more than 2,000 miles (3,200 km) of track, with 120,000 employees, and practically monopolized traffic in a wide swath from Boston to New York City.
This quest for monopoly angered Progressive Era reformers, alienated public opinion, resulted in high prices for acquisitions, and increased construction costs. Debt soared from $14 million in 1903 to $242 million in 1913, even as the advent of automobiles, trucks and buses reduced railroad profits. Also in 1913, the federal government filed an anti-trust lawsuit that forced the NH to divest its trolley systems.
The line became bankrupt in 1935, was reorganized and reduced in scope, went bankrupt again in 1961, and in 1969 was merged with the Penn Central system, formed a year earlier by the merger of the also bankrupt New York Central Railroad and Pennsylvania Railroad; Already a poorly conceived merger, Penn Central proceeded to go bankrupt in 1970, becoming the largest bankruptcy in the U.S. until the Enron Corporation superseded it in 2001. The remnants of the system now comprise Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line, (parts of) Amtrak's Northeast Corridor, Shore Line East, parts of the MBTA, and numerous freight operators such as CSX and the Providence and Worcester Railroad. The majority of the system is now owned publicly by the states of Connecticut, Rhode Island, and Massachusetts.
Read more on Wikipedia and New Haven Railroad Historical and Technical Association, Inc.
Brand/Importer Information: Bachmann Industries (Bachmann Brothers, Inc.) is a Bermuda registered Chinese owned company, globally headquartered in Hong Kong; specializing in model railroading.
Founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the home of its North American headquarters, Bachmann is today part of the Kader group, who model products are made at a Chinese Government joint-venture plant in Dongguan, China. Bachmann's brand is the largest seller, in terms of volume, of model trains in the world. Bachmann primarily specializes in entry level train sets, and premium offerings in many scales. The Spectrum line is the high quality, model railroad product line, offered in N, HO, Large Scale, On30, and Williams O gauge all aimed for the hobbyist market. Bachmann is the producer of the famous railroad village product line known as "Plasticville." The turnover for Bachmann model trains for the year ended 31 December 2006 was approximately $46.87 million, a slight increase of 3.36% as compared to 2005.
Founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the home of its North American headquarters, Bachmann is today part of the Kader group, who model products are made at a Chinese Government joint-venture plant in Dongguan, China. Bachmann's brand is the largest seller, in terms of volume, of model trains in the world. Bachmann primarily specializes in entry level train sets, and premium offerings in many scales. The Spectrum line is the high quality, model railroad product line, offered in N, HO, Large Scale, On30, and Williams O gauge all aimed for the hobbyist market. Bachmann is the producer of the famous railroad village product line known as "Plasticville." The turnover for Bachmann model trains for the year ended 31 December 2006 was approximately $46.87 million, a slight increase of 3.36% as compared to 2005.
Item created by: gdm on 2017-09-30 18:31:18. Last edited by CNW400 on 2020-07-09 12:46:32
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.
If you see errors or missing data in this entry, please feel free to log in and edit it. Anyone with a Gmail account can log in instantly.